Efficient mesh deforming method and device based on dynamic control point
A mesh deformation and dynamic control technology, applied in the field of computational mechanics, can solve problems such as inability to adapt to large deformations and low computational efficiency, and achieve the effects of good mesh quality, high computational efficiency, and improved adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
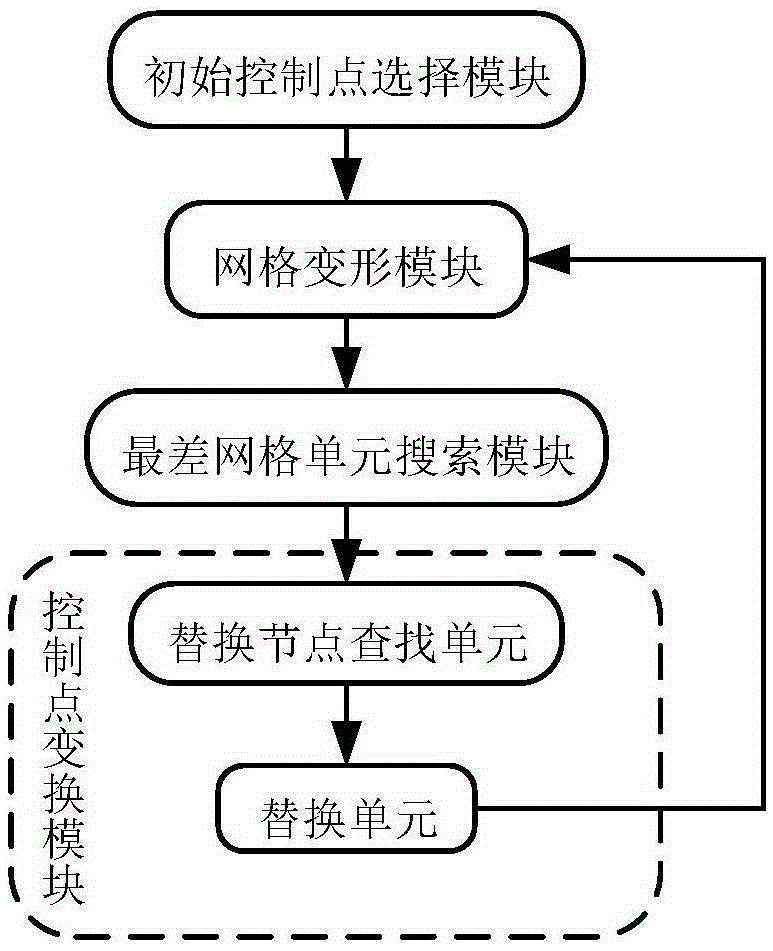
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
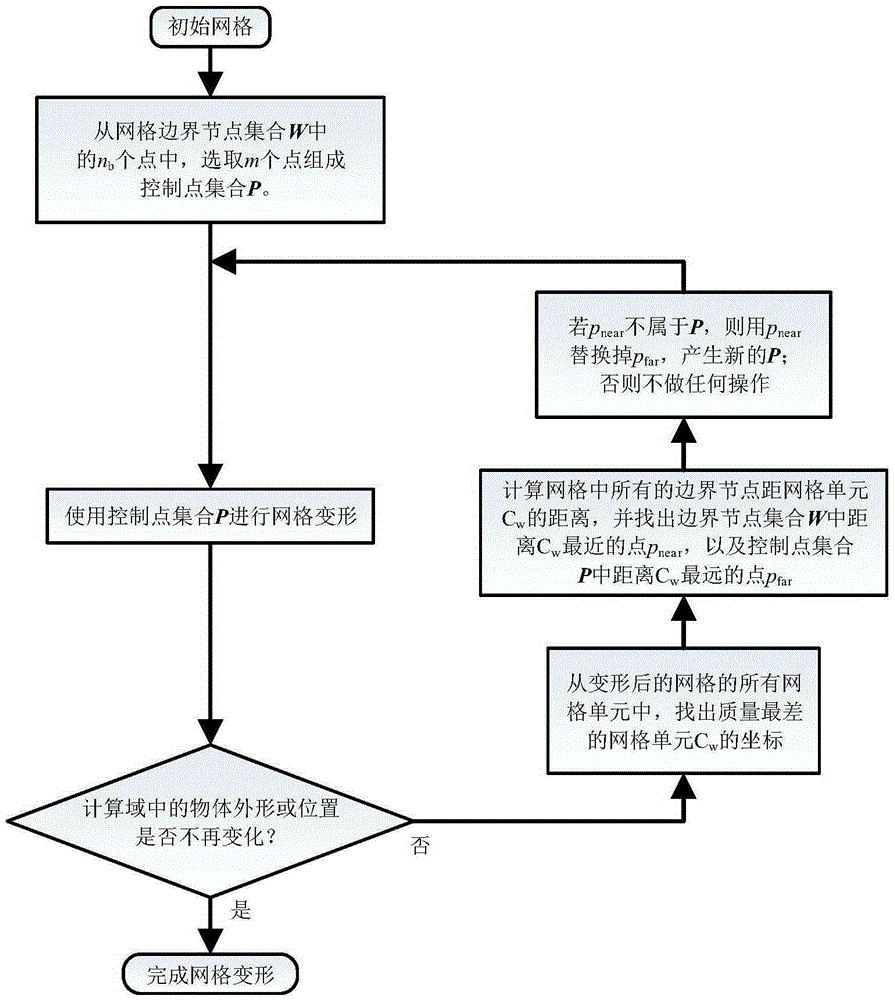
[0060] The grid deformation technology proposed by the present invention will be verified and explained below with a set of deformation problems of a simple two-dimensional unstructured grid. The effect of the present invention is compared with the original (without data reduction) RBF method (Original RBF Method) and common data reduction RBF method (Data-reduced RBF Method).
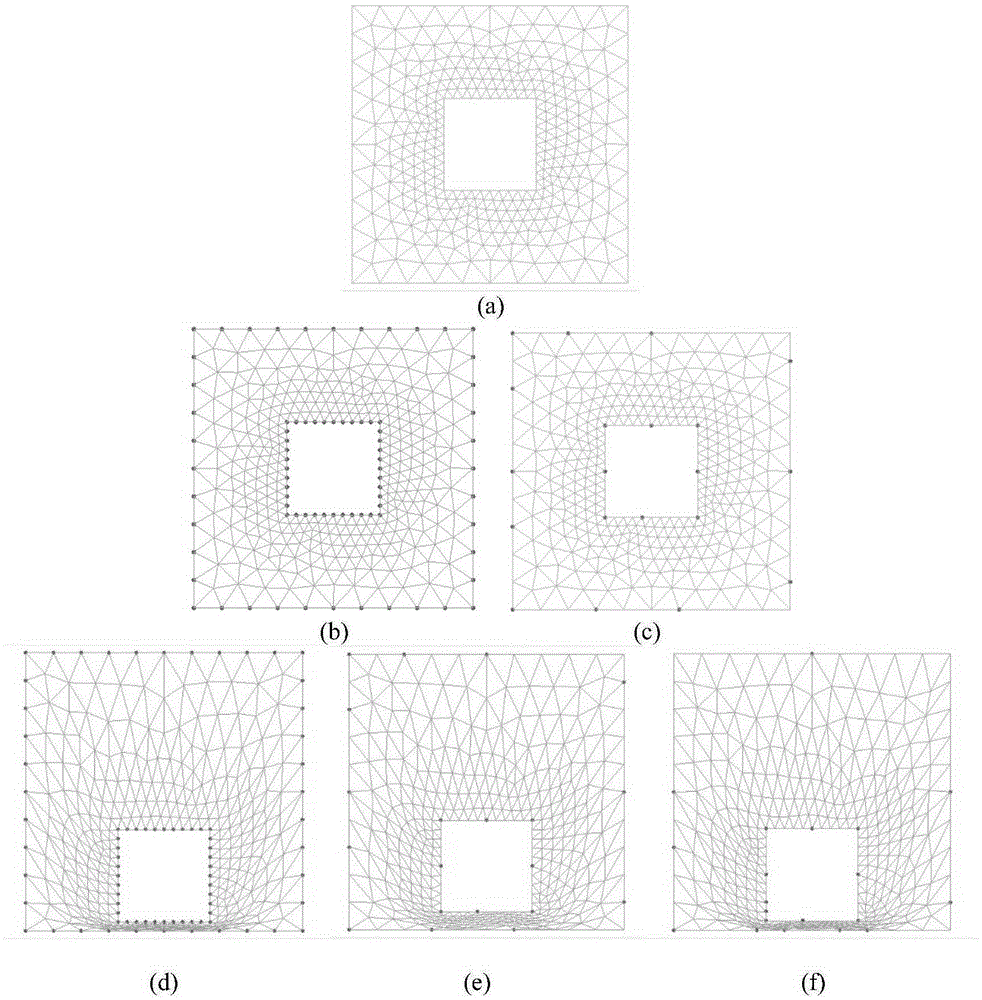
[0061] Such as image 3 As shown in (a), it is a set of simple two-dimensional unstructured grids. The inner and outer boundaries of the grid are both squares. Now we need to translate the inner boundary downwards, and each step translates a distance of 0.01, and deform the mesh in the process. Investigate the amount of deformation that the grid can withstand before negative volume appears.
[0062] The original (without data reduction) RBF method, common data reduction RBF method and DCP-RBF method are used for mesh deformation respectively. For the control points used, the original RBF method uses...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com