Method for eliminating dead zone through adopting generalized inverse matrix
A generalized inverse matrix and blind zone technology, which is applied in the field of magnetic field measurement and positioning calculation, can solve the problems of being unable to detect magnetic targets, achieve the effect of eliminating infinite positioning errors, maintaining military safety, and improving practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
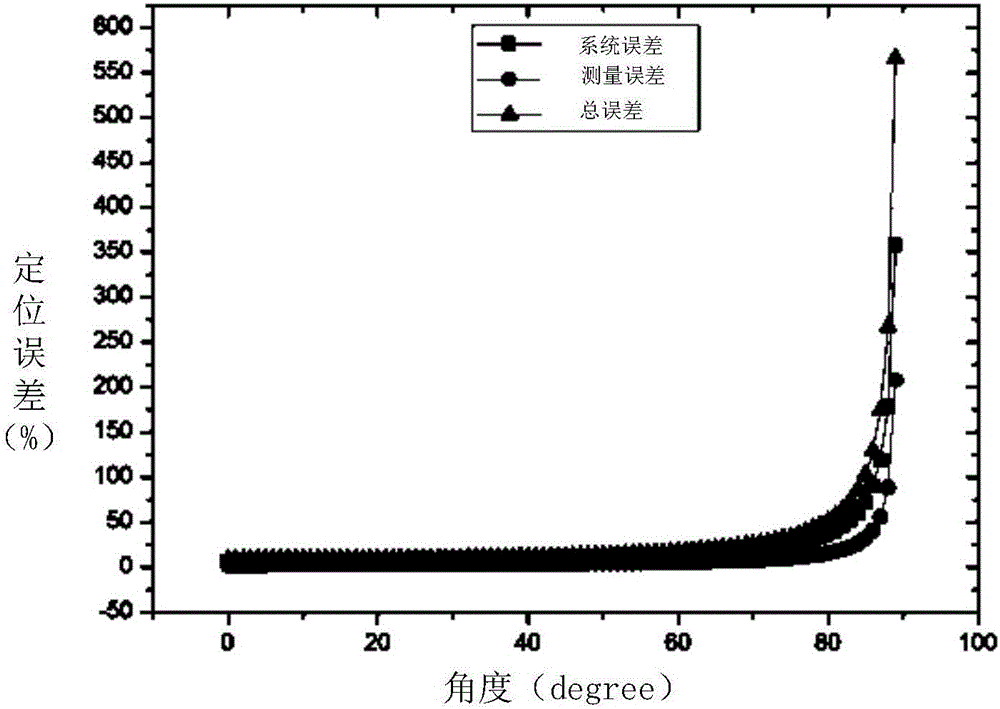
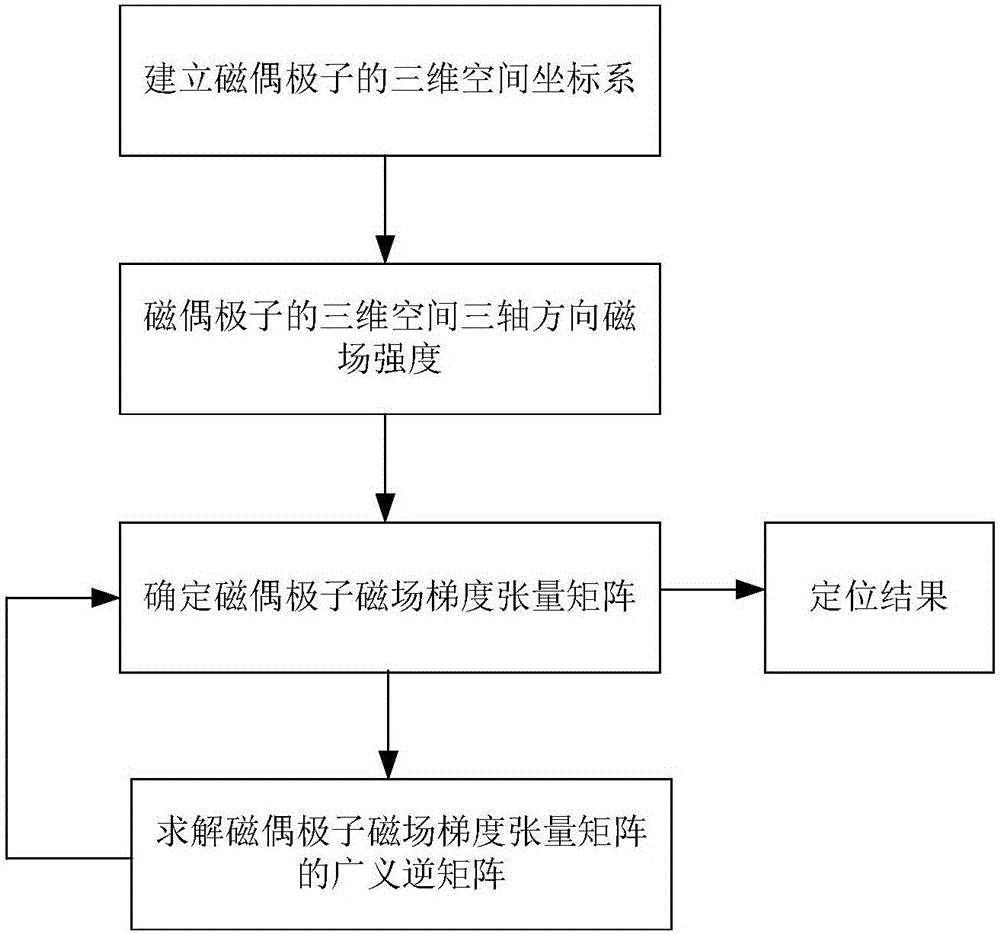
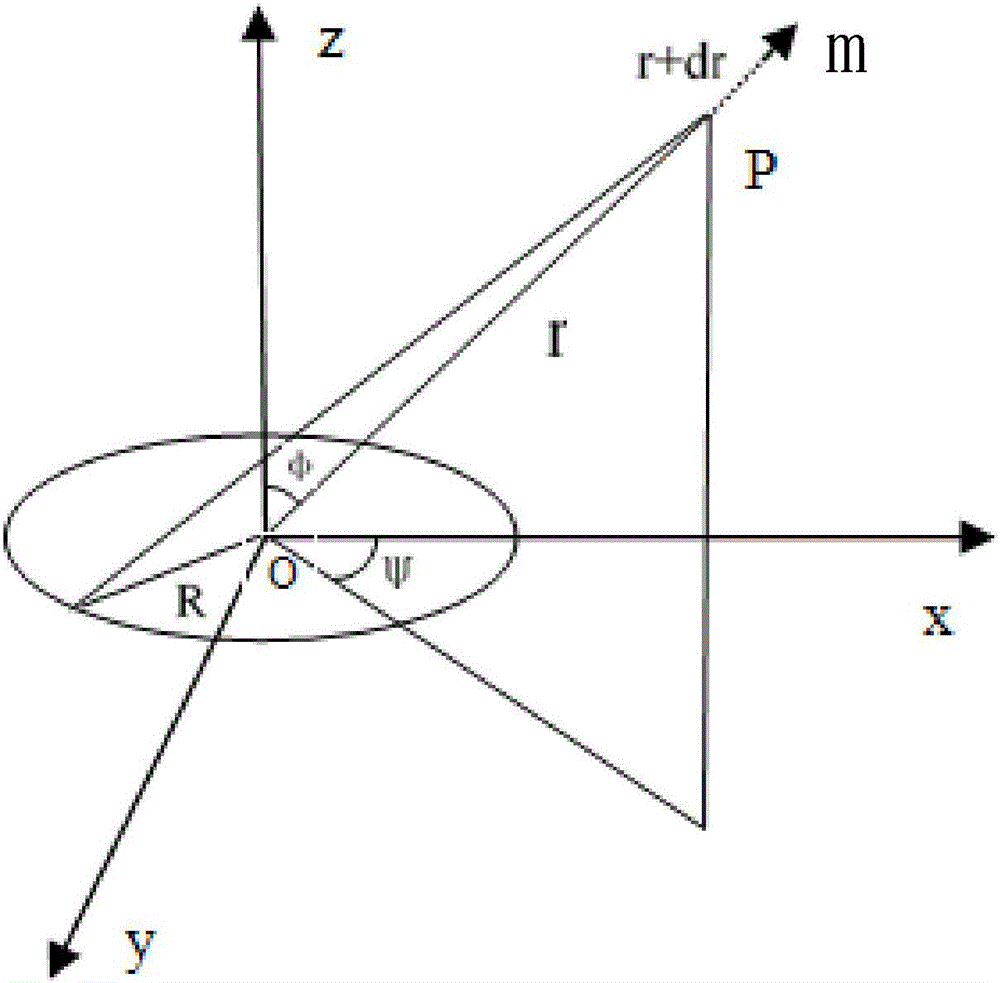
[0014] When analyzing the influence of the direction of the magnetic moment on the positioning error, the results obtained through simulation experiments are as follows: figure 1 As shown, the angle in the figure refers to the angle between the magnetic moment m and the position r of the magnetic dipole. When the angle between the magnetic moment m and r is close to 90°, the positioning error is very large, and this area is called a blind area. The blind zone is corresponding to the theory that when the generalized inverse matrix is irreversible, the positioning error is infinite, which will lead to the inability to detect the measured target, mainly because when the magnetic moment is decomposed along the coordinate system, it is divided into three coordinate axes Hxx, Hyy, one or two of Hzz are extremely small. At this time, the full tensor matrix is not a full-rank matrix, so it is irreversible. When the full tensor matrix is used for positioning operations, the error ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com