Node transmission sequence optimization competitive channel underwater acoustic network parallel communication method
A technology of sending order and underwater acoustic network, which is applied in the direction of using return channel for error prevention/detection, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc. It can solve the problem of node sending order optimization, affecting the time of nodes sending data, affecting the efficiency of transmission, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of optimizing the sending sequence and sending time, reducing time and improving utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
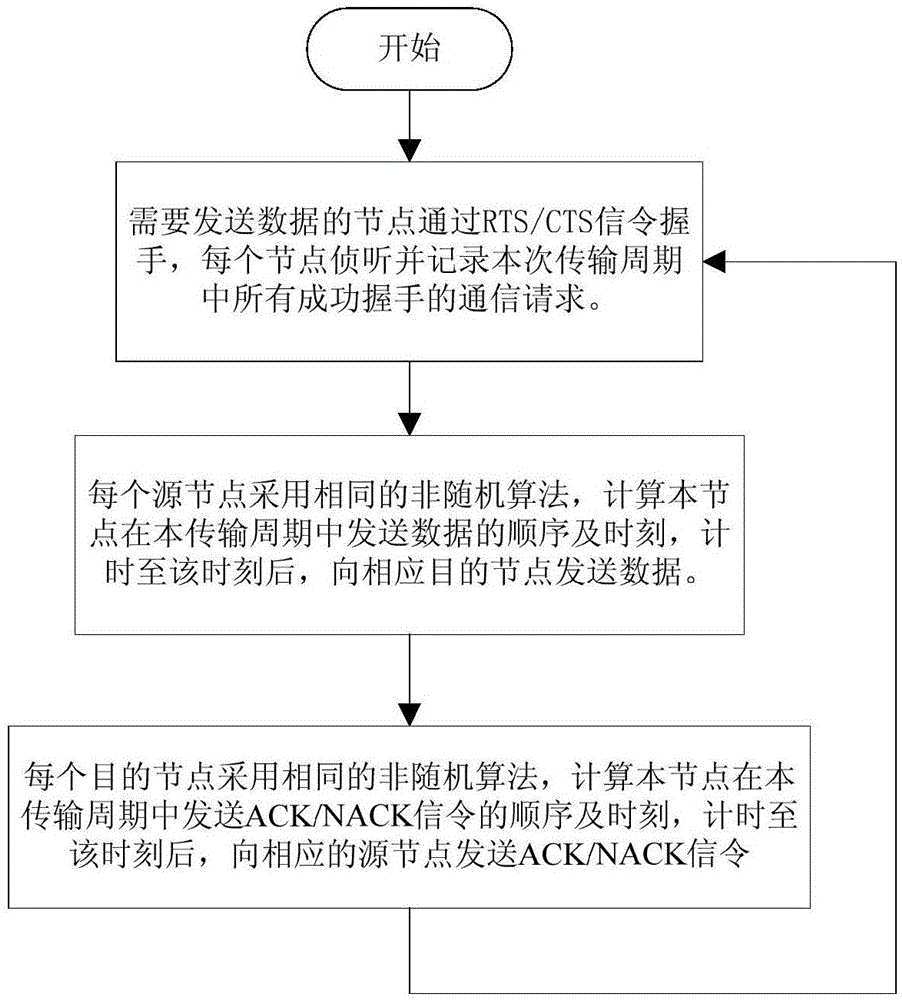
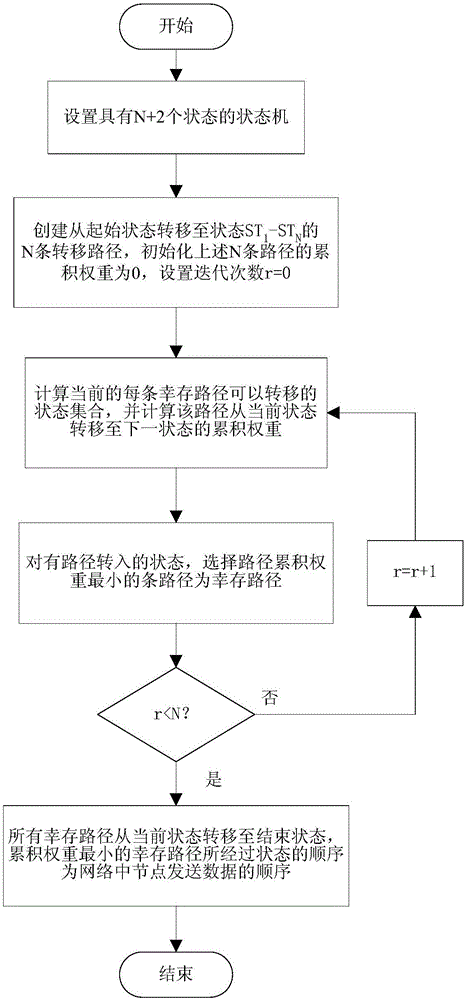
[0036] The specific implementation steps of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples, but the embodiments of the present invention are not limited thereto. Conventional expressions or what can be unambiguously derived from what has been written in this application will not be repeated here.
[0037] The embodiment of the present invention is an underwater acoustic communication network with 8 nodes. The coordinate system is established with the horizontal position and depth of the nodes as the X, Y, and Z axes. The three coordinate axes are all in meters, and the coordinates of nodes 1 to 8 are They are (50, 60, 70), (200, 60, 80), (150, 150, 150), (100, 100, 100), (500, 500, 500), (0, 0, 0), (1000, 1000, 1000), (210, 220, 400). Each node can monitor the signals of other nodes. The communication mode of each node is omnidirectional, half-duplex, and the sound speed is 1500m / s. All nodes use data packets ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com