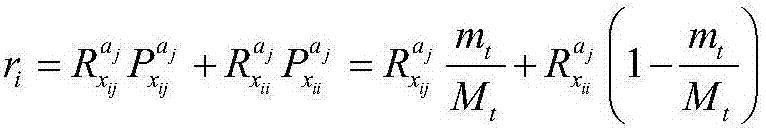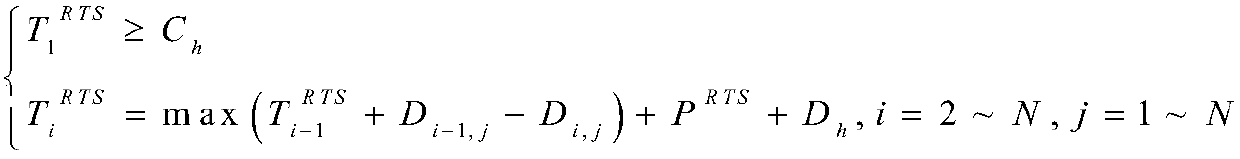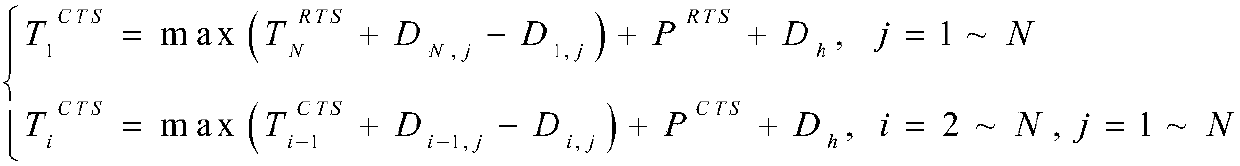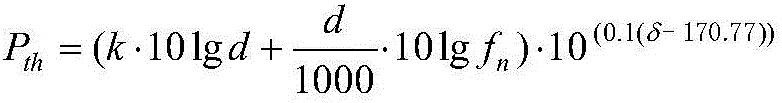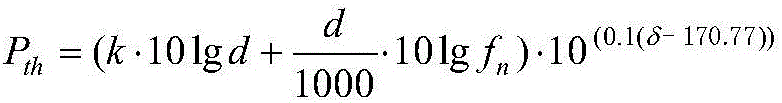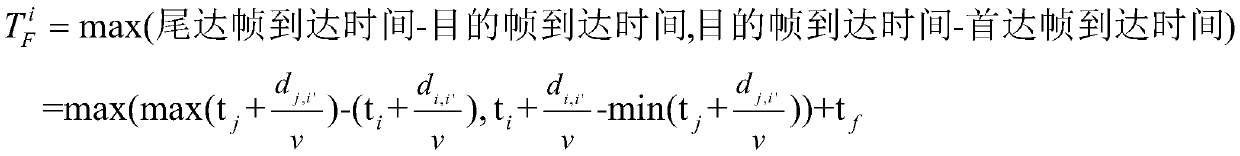Patents
Literature
129 results about "Underwater acoustic network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-node rapid communication method suitable for contention channel underwater acoustic network
InactiveCN104486005AReduce latencyImprove utilization efficiencyTransmissionWireless communicationData transmissionComputer science
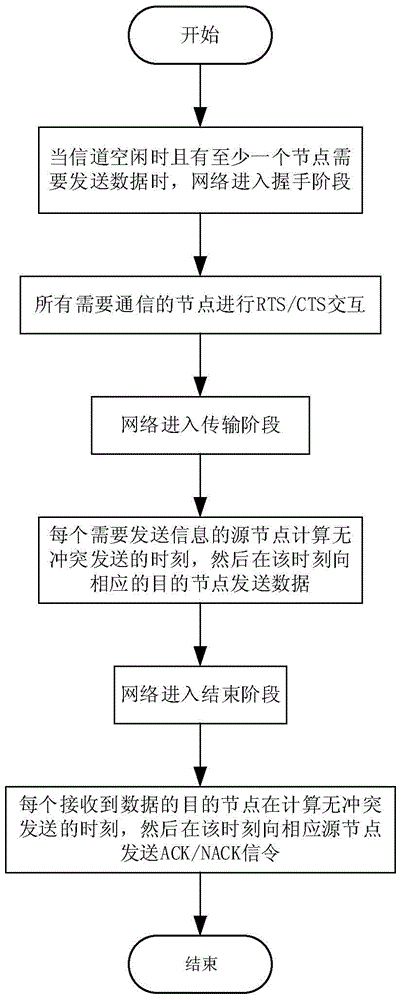
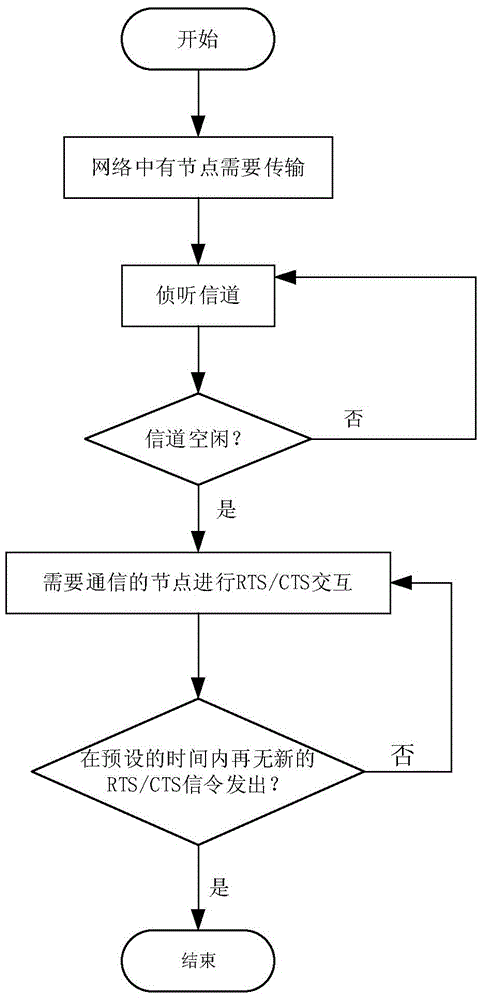
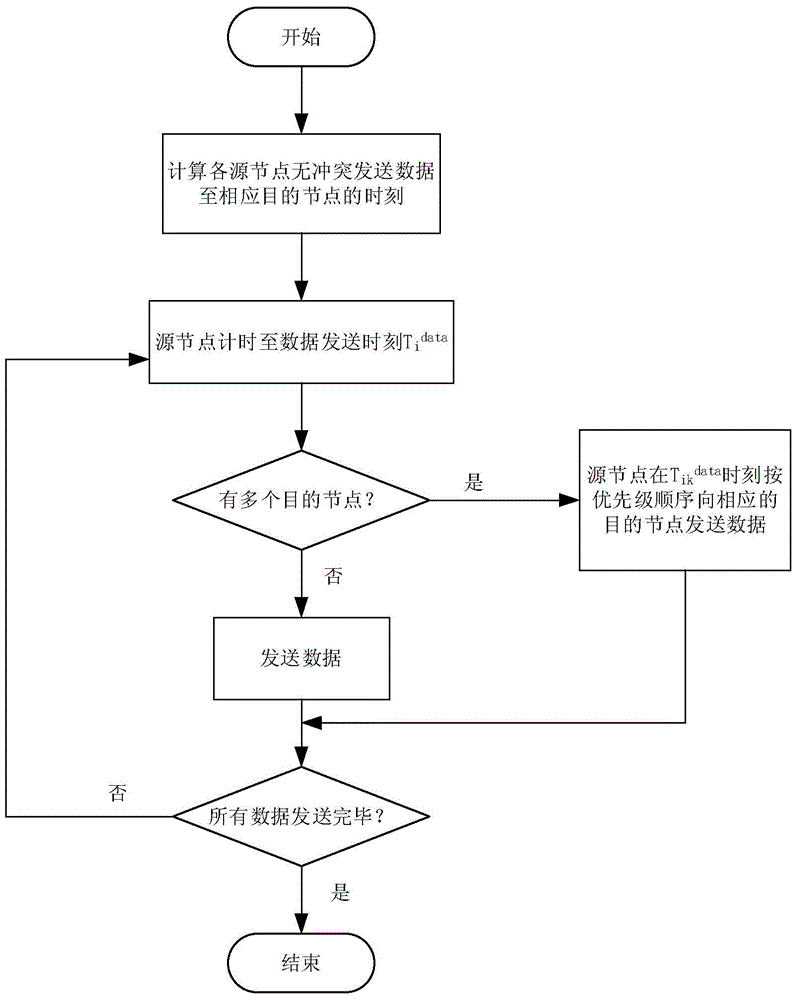
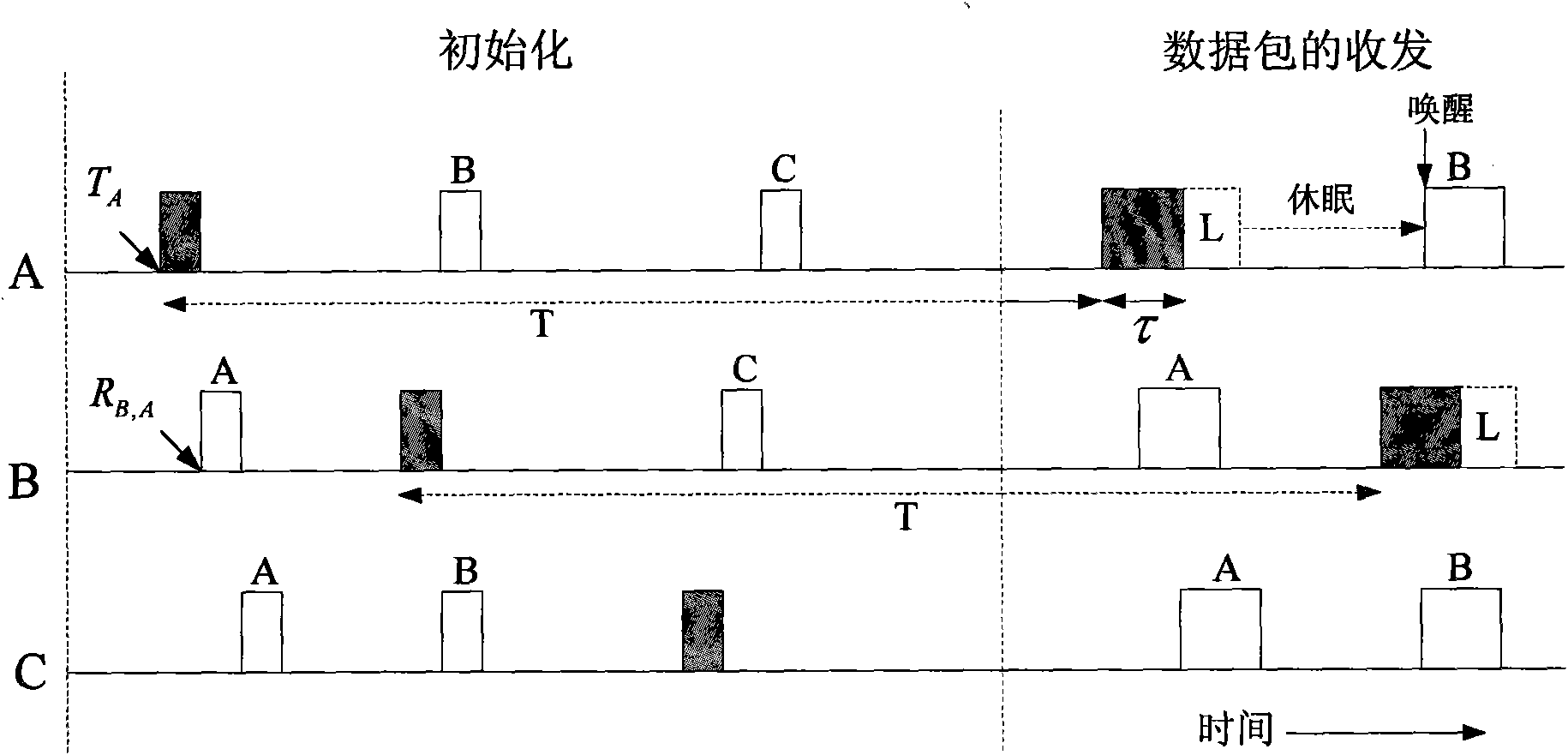
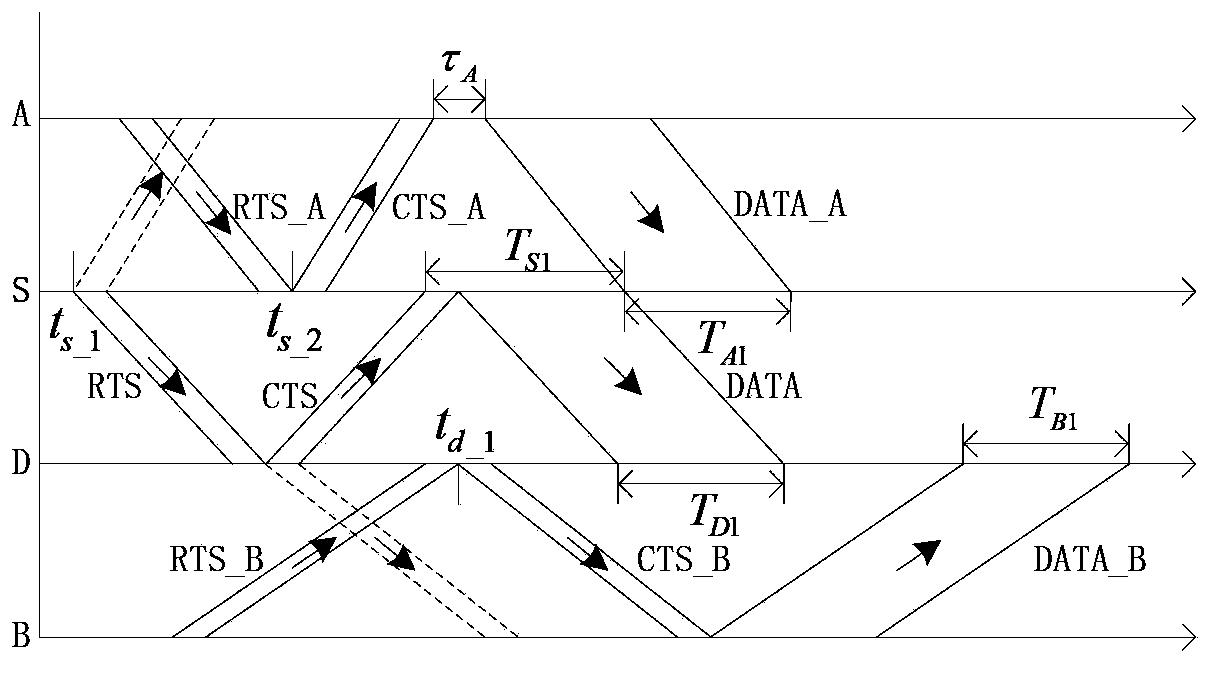
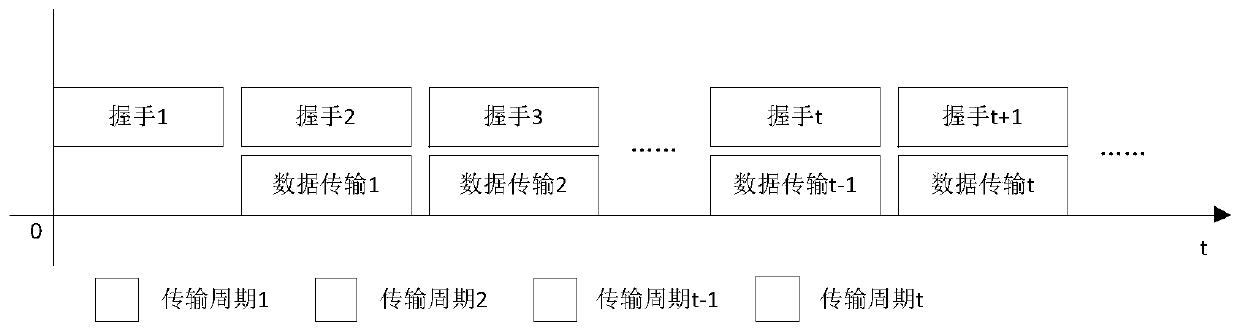
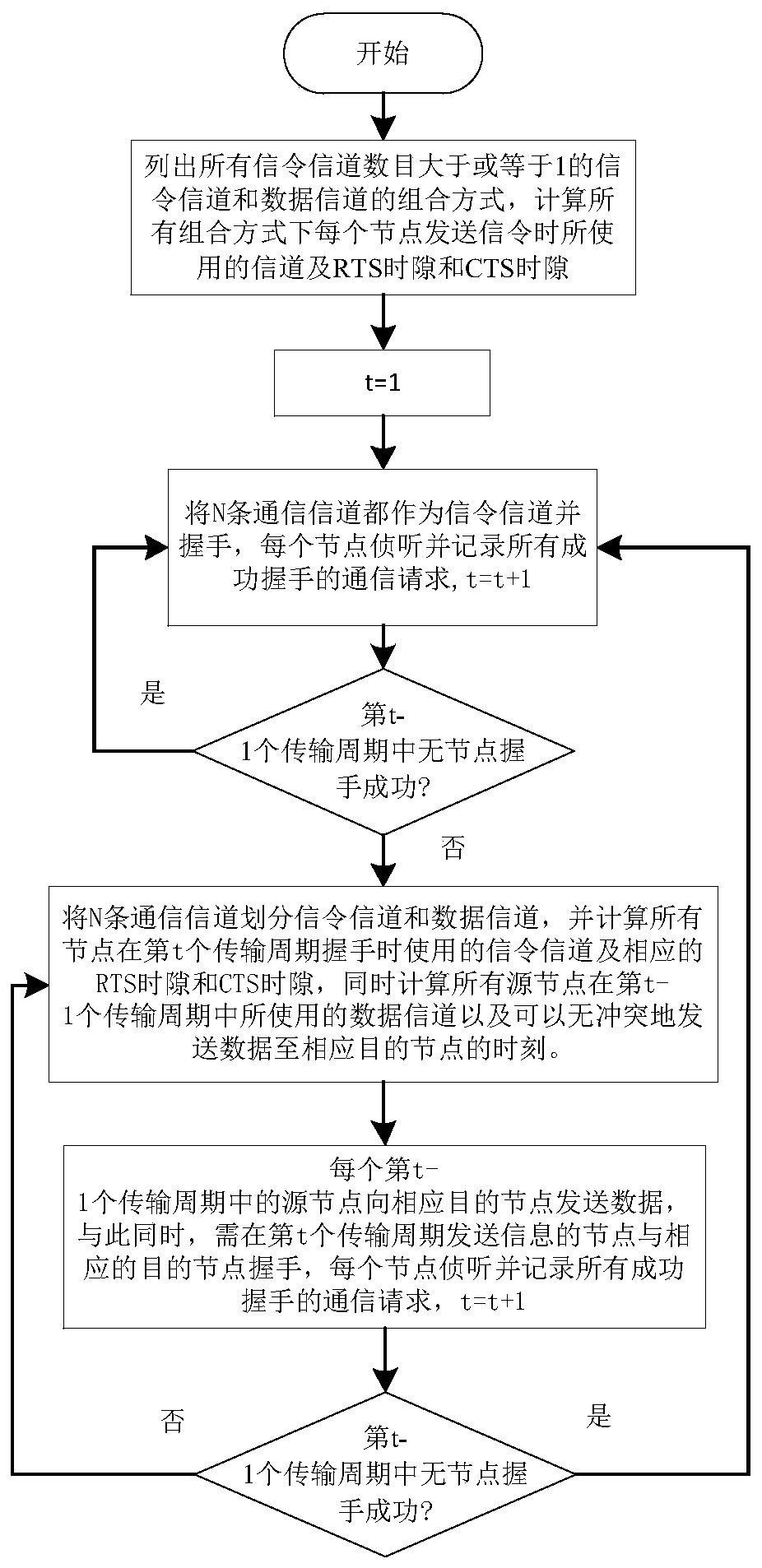
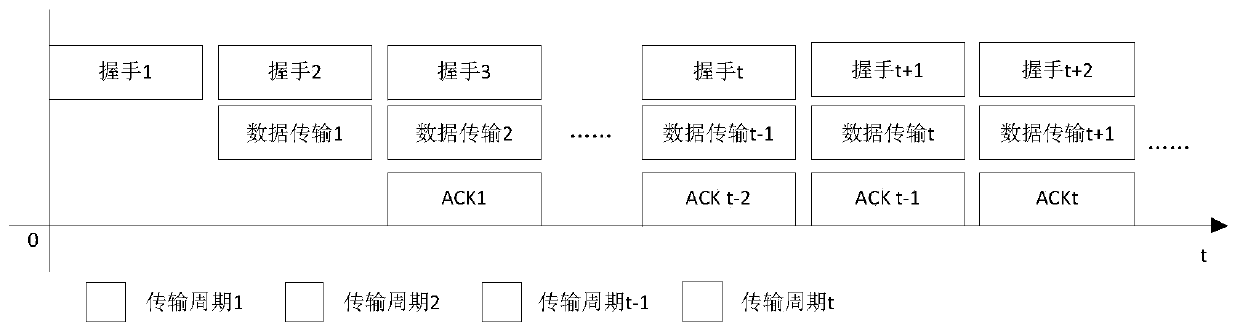
The invention discloses a multi-node rapid communication method suitable for a contention channel underwater acoustic network. Each transmission cycle in the method comprises a handshake phase, a transmission phase and an end phase; the method comprises the following concrete steps that SA1, when a channel is idle and at least one node needs to transmit data, a network enters the handshake phase; SA2, after the handshake phase is ended, the network enters the transmission phase; the moment at which the data can be transmitted to a corresponding destination node without conflict by the node is calculated by priority order through each node which needs to transmit information, and after timing is performed for the moment, the data is transmitted to the corresponding destination node; SA3, after data transmission of all the nodes is ended, the network enters the end phase. According to the multi-node rapid communication method disclosed by the invention, the data can be transmitted in batches without generating the conflict in the same transmission cycle by multiple nodes in the underwater acoustic network, so that the utilization efficiency of the channel can be effectively improved, and the average delay of the channel is reduced; the multi-node rapid communication method can be widely used for occasions with various contention protocol-based underwater acoustic communication networks, underwater acoustic sensing networks and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Data transmission system and data transmission method for underwater acoustic network
InactiveCN101567728AIncrease success rateImprove throughputFree-space transmissionData switching networksDigital signal processingTelecommunications link
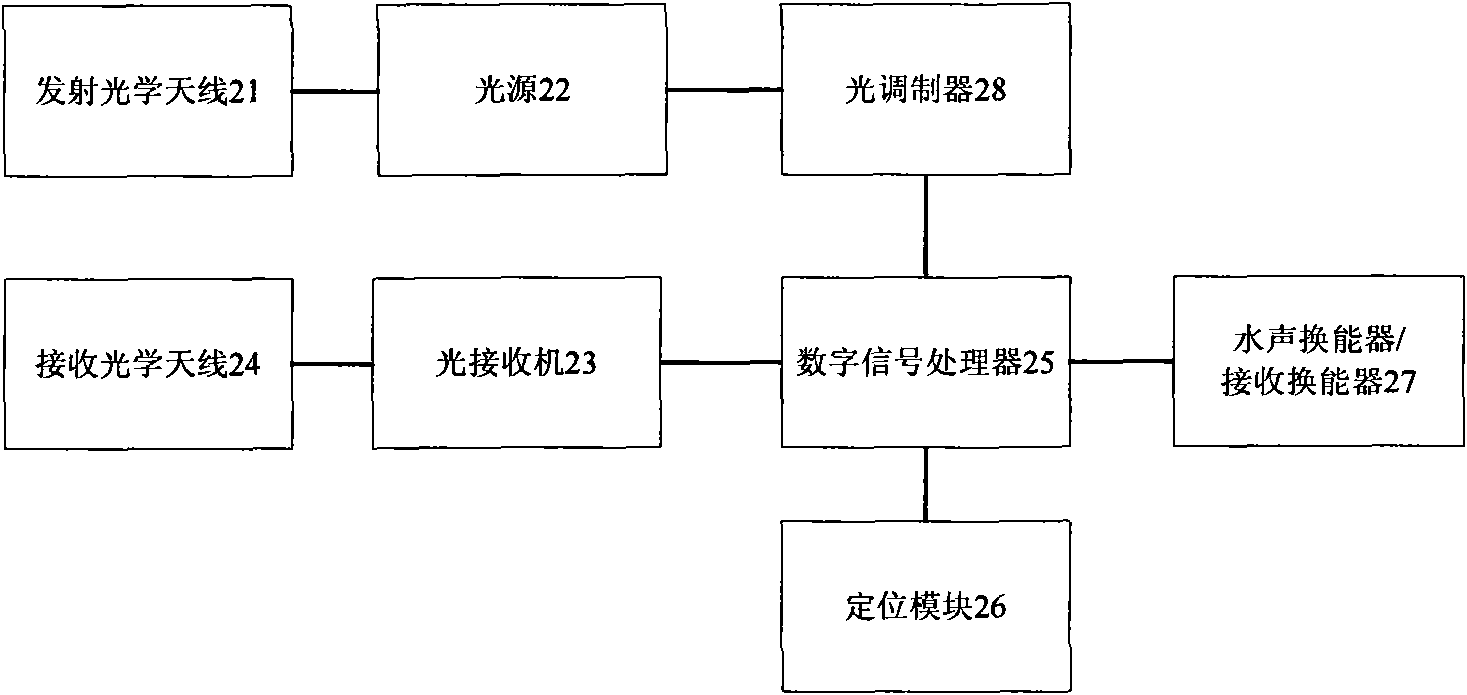
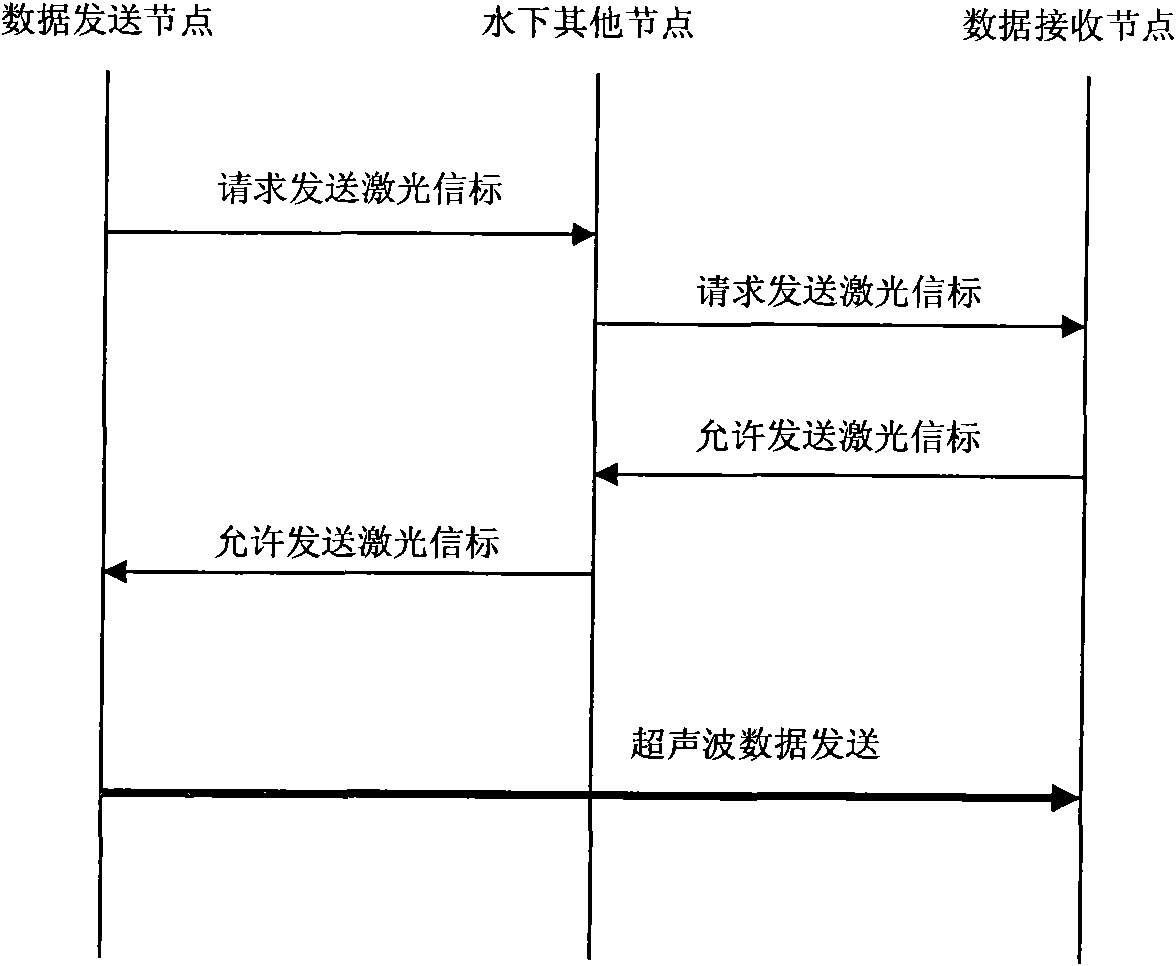
The invention relates to a data transmission system for an underwater acoustic network, which comprises a plurality of independent underwater nodes, wherein each underwater node is equivalently connected with at least the other underwater node. The data transmission system also comprises a transmitting optical antenna, a receiving optical antenna, a light source, an optical modulator, an optical receiver, an underwater acoustic transducer / receiving transducer, a digital signal processor and a positioning module, wherein the positioning module is provided with a rotating device and used for completing the alignment between the light source and the optical receiver; the transmitting optical antenna, the light source, the optical modulator and the digital signal processor are in signal connection with each other in turn; the receiving optical antenna, the optical receiver and the digital signal processor are in signal connection with each other in turn; the digital signal processor is also in signal connection with the positioning module and the underwater acoustic transducer / receiving transducer respectively; and the light source is a blue-green laser source. The invention also relates to a data transmission method for the underwater acoustic network. The invention reduces the collision probability of data in the transmission process, improves the success rate of the construction of a communication link, saves the network bandwidth, and improves the network throughout.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Integrated method integrating underwater target positioning and remote control and telemetering data underwater acoustic network transmission
ActiveCN104297727AThe number is adjusted in real timeIncreased flexibility of useTransmission systemsNetwork topologiesRemote controlBuoy
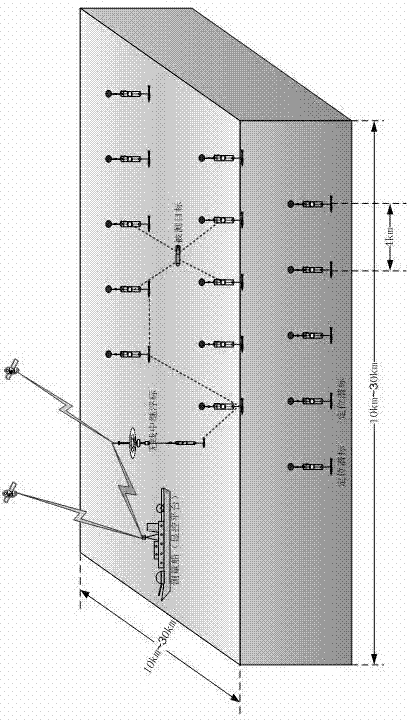
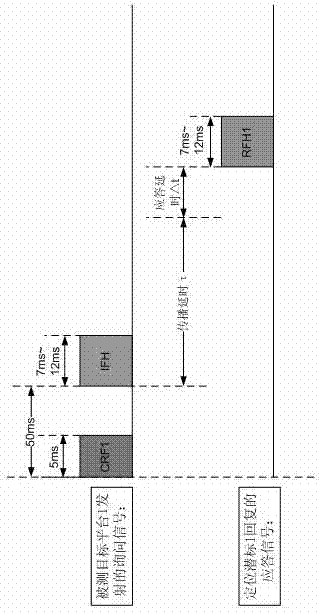
The invention relates to an integrated method integrating underwater target positioning and remote control and telemetering data underwater acoustic network transmission, which uses equipment including a plurality of positioning submersible buoys, a measured target platform, a wireless relay buoy and a shipborne display and control platform, wherein the plurality of positioning submersible buoys sink to the bottom and arranged to be a subsea measurement matrix, and then measurement is carried out on the position of the positioning submersible buoy matrix. A measured target sails in a measurement region formed by the subsea measurement matrix, the measured target platform sends acoustic inquiry signals continuously in an evenly spaced mode, a positioning submersible buoy within the operating range receives the inquiry signals, waits for fixed delay time and replies answering signals, the measured target platform receives the answering relay signals, carries out self-position calculation according to signal detection results and sends combination of a calculation result and a depth measurement result to the nearest positioning submersible buoy in an underwater acoustic communication mode, the nearest positioning submersible buoy transmits the combination of the calculation result and the depth measurement result to the shipborne display and control platform, and the underwater position of the measured target can be monitored in real time on the display and control platform.
Owner:嘉兴中科声学科技有限公司
Energy consumption balanced underwater acoustic network route establishing method
InactiveCN106992932AExtend the life cycleData switching networksWireless communicationTelecommunicationsReturn function
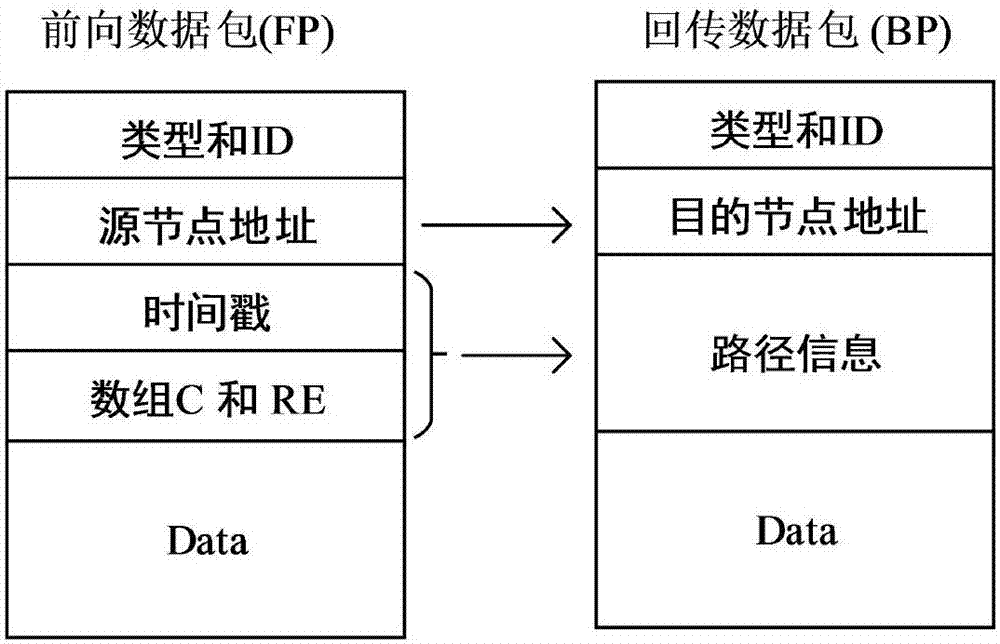
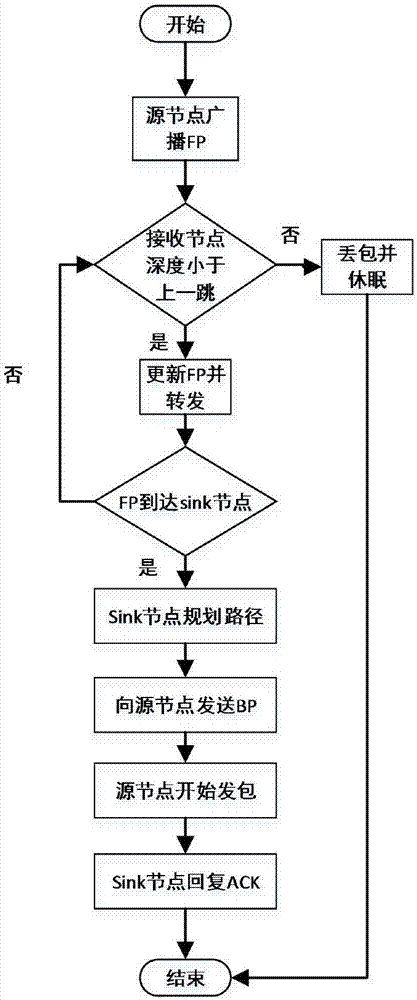
The invention relates to an energy consumption balanced underwater acoustic network route establishing method. Each node is equipped with a pressure sensor, and depth information of each node can be acquired; a current return function and a future return function are defined for communication of the nodes; in the return functions, an end-to-end delay and node residual energy are simultaneously considered; then two return functions constitute an action utility function; by solving a maximum utility value, a next hop of node is determined; a communication process is divided into a forward transmission stage and a return stage; the forward transmission stage is used for sending a communication request to a sink node by a source node and collecting information of other nodes between the sink node and the source node; and the Sink node utilizes the information to carry out path planning, then a planned path and communication request confirmation are sent to the source node by the return stage, and then data packet transmission is started.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Energy-saving medium access control method in underwater acoustic network
InactiveCN101567820AAchieve synchronizationAdapt to dynamic changesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionData switching by path configurationAlarm stateNetwork topology
The invention discloses an energy-saving medium access control method in an underwater acoustic network and aims at solving the problems of ultrahigh transmission collision rate and ultrahigh energy consumption of data packets in the underwater acoustic network. The method comprises the following steps, dividing a time shaft into cycle periods with equal lengths and establishing a network topology by initialization to realize the synchronization between nodes under the condition that transmission time delay between the nodes is not known so that various nodes at data sending and receiving stages are in alarm states only in special time to send or receive the data packets and are in rest states in most time; and meanwhile, designing a collision avoidance measure, a new node adding treatment measure and a failure node treatment measure. The method can greatly save the energy consumption of the network, prolongs the service life of the network, can lower the collision rate and can effectively bring the dynamic change of the network topology by the change of the underwater environment or the movement, the damage and the updating of the nodes.
Owner:魏昕
Multi-node parallel communication method for competitive channel underwater acoustic network containing movement node
ActiveCN106332299AIncrease profitReduce time scaleTransmissionWireless communicationVelocity vectorUnderwater acoustics
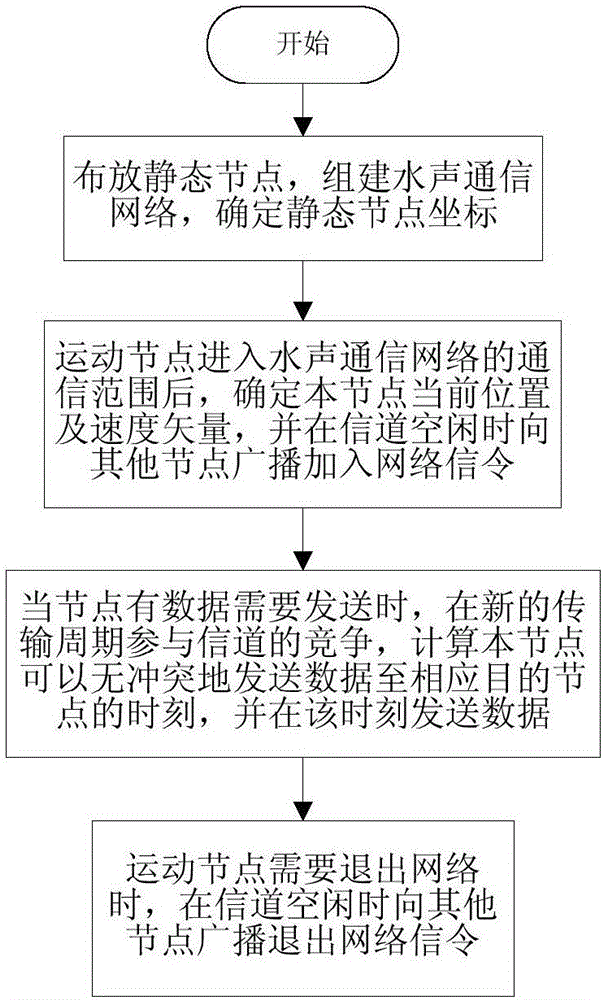
The invention discloses a multi-node parallel communication method for a competitive channel underwater acoustic network containing a movement node. The method comprises the steps of: laying static nodes; after the movement node enters the communication range of the underwater acoustic communication network, determining the current position and velocity vector of the node relative to a coordinate system, and broadcasting other nodes in the underwater acoustic communication network when a channel is idle to add network signaling; when the node needs to send data, participating in channel competition in a new transmission cycle, calculating the time when the node can send data to a corresponding destination node without conflict, and sending data at the time; and when the movement node needs to exit the network, broadcasting the other nodes when the channel is idle to exit the network signaling, and receiving, by the other nodes, the signaling. The method can effectively improve the utilization efficiency of the channel and reduce the average delay of communication, and can be widely applied to various occasions containing movement nodes, such as underwater acoustic communication networks, underwater acoustic sensor networks and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Medium access control method based on CDMA underwater acoustic network
InactiveCN101567707AImprove reusabilityLess waitingCode division multiplexTransmissionTime delaysNetwork conditions
The invention discloses a medium access control method based on a CDMA underwater acoustic network for improving the network throughput, shortening end-to-end time delay and reducing the energy consumption so as to prolong the service life of the network. The invention adopts a CDMA access mode and a distributed power control technology, and nodes participating information transmission dynamically adjust data sending power according to network conditions on the premise that the nodes do not influence the normal sending and receiving of adjacent nodes so as to overcome the near-far effect existing in a CDMA system. Meanwhile, the invention improves a handshake mechanism in a traditional medium access control method, uses a data pocket to replace an ACK as a response for successful interaction in case of satisfying special conditions and can obtain higher performance under the conditions of different network loads so as to be effectively applied to reliable data transmission in the underwater acoustic network.
Owner:赵力
MACA-U (Multiple Access Collision Avoidance for Underwater Wireless) protocol-based underwater acoustic network multiple-address accessing method
ActiveCN104349495AMake the most of free timeSuppress interferenceTransmissionWireless communicationProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessUnderwater acoustic network
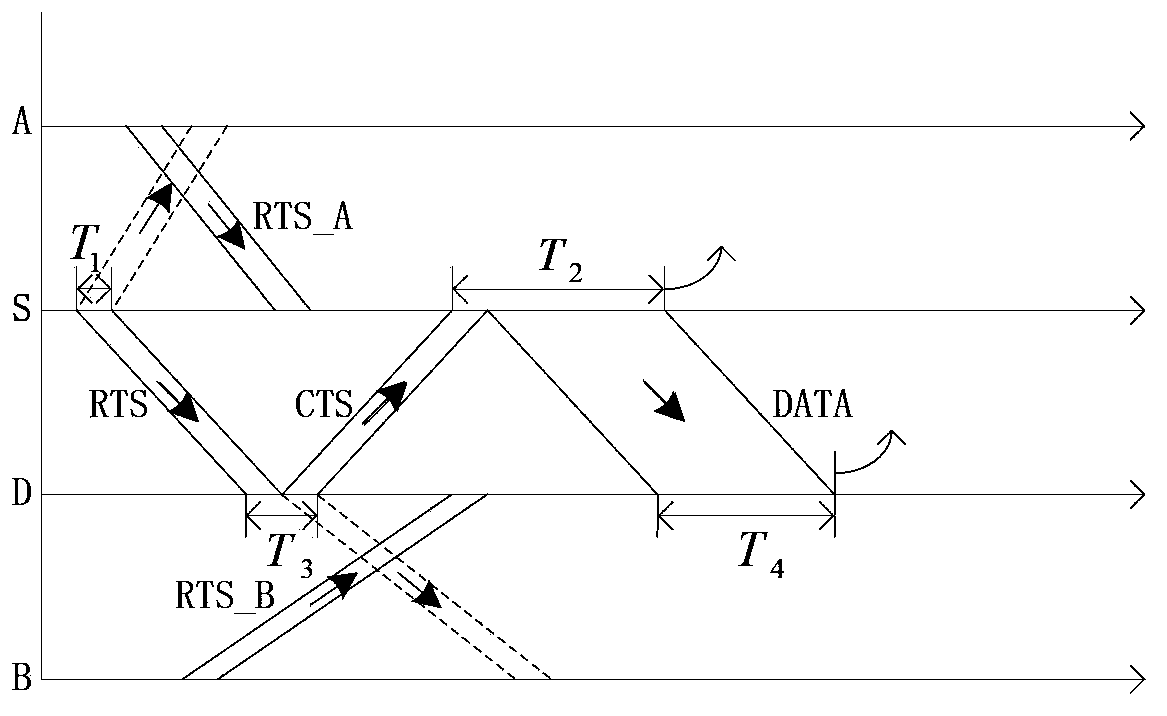
The invention relates to an MACA-U (Multiple Access Collision Avoidance for Underwater Wireless) protocol-based underwater acoustic network multiple-address accessing method. The method comprises the following steps in an RTS-CTS exchange process of a source node and a destination node, if the source node or the destination node receives an RTS transmitted by the other node, on the premise that the existing time of the source node or the destination node is enabled to not conflict, calculating the time when the source node or the destination node is suitable for the receiving of a data frame transmitted by the other node; replying a CTS to the other node, wherein the CTS comprises the time waited by the other node from the time when the CTS is received to the time when the data frame is transmitted, and the silence time after the time when the other nodes except the other node receive the CTS; after the other nodes receive the CTS, transmitting the data frame after waiting for some time according to the CTS.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
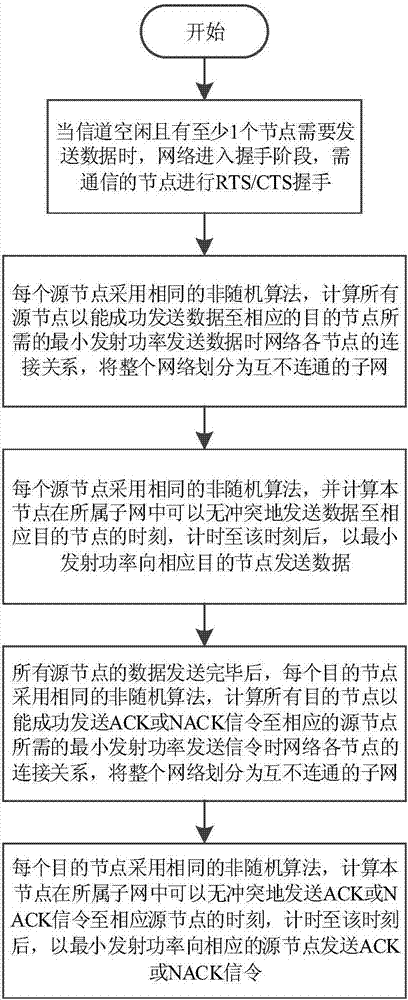
Node transmission sequence optimization competitive channel underwater acoustic network parallel communication method
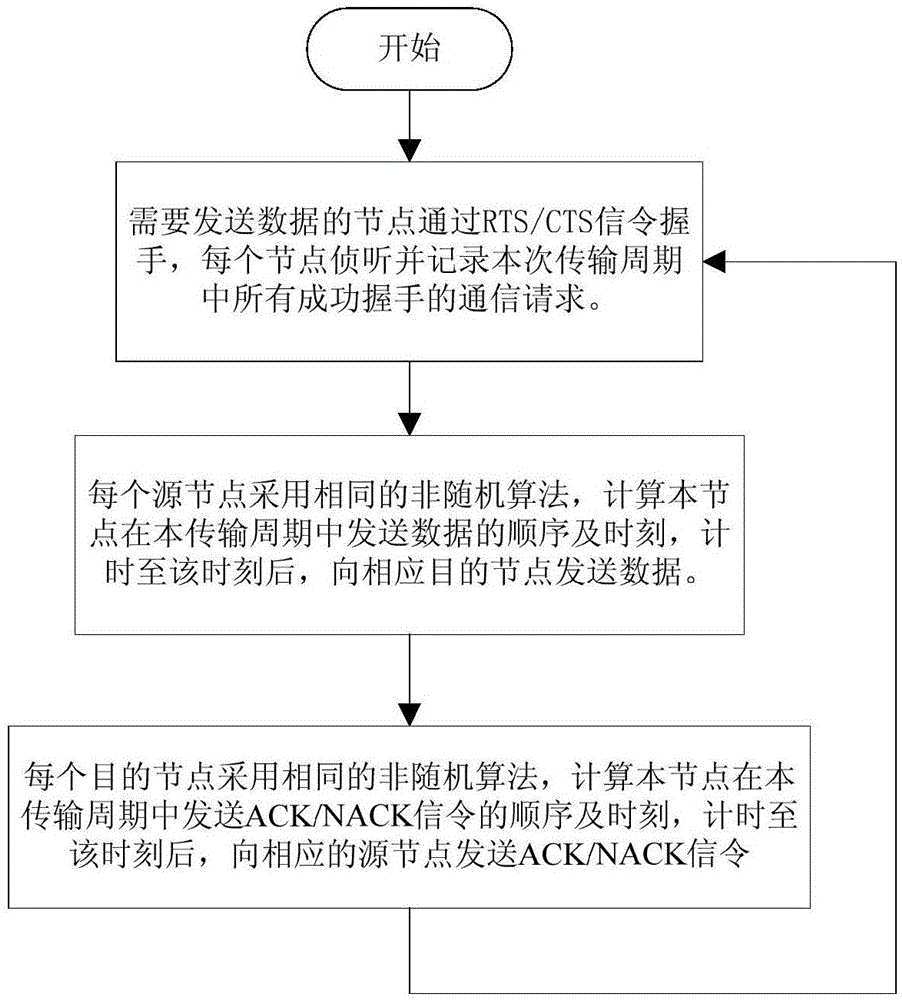
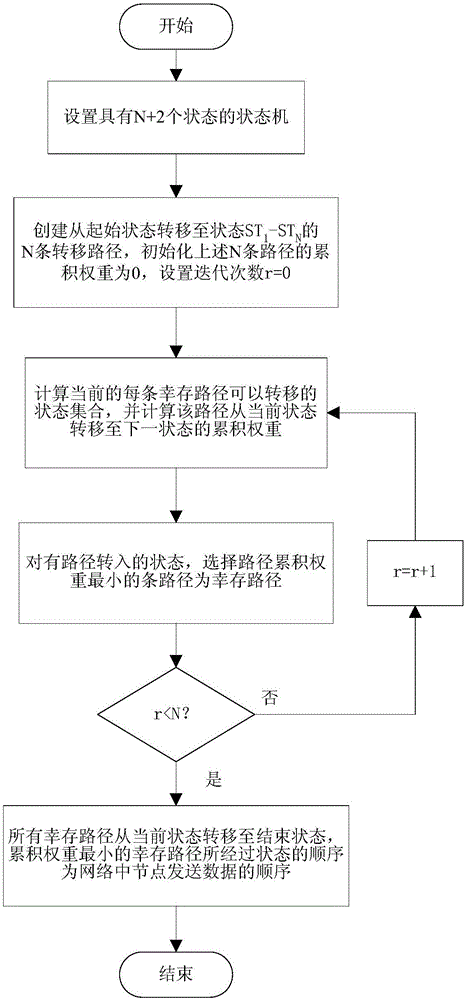
ActiveCN106656356AOptimize sending orderOptimize sending timeError prevention/detection by using return channelStochastic algorithmsConflict free
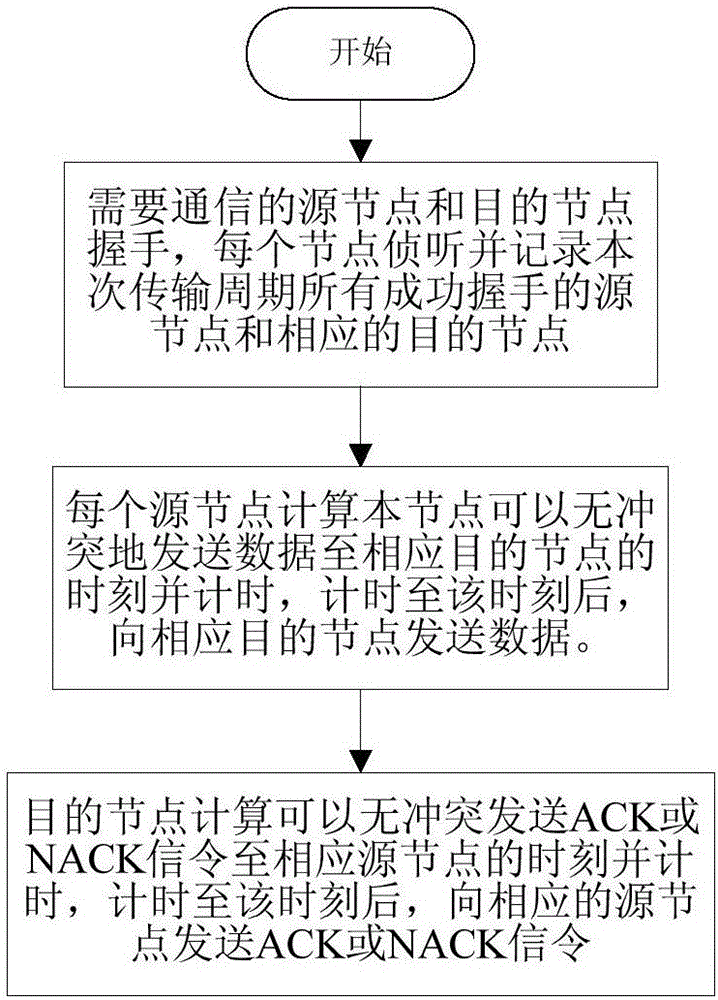
The invention discloses a node transmission sequence optimization competitive channel underwater acoustic network parallel communication method. According to the invention, each source node uses the same non-random algorithm to calculate the sequence and time of data transmission of the node in the transmission cycle; data are transmitted to a corresponding destination node after timing is up to the time; after the data of all source nodes are transmitted, each destination node uses the same non-random algorithm to calculate the sequence and time of ACK or NACK signaling transmission of the node in this transmission cycle; and after timing is up to the time, the destination node with correct received data transmits ACK signaling to the corresponding source node, and the destination node with wrong received data transmits NACK signaling to the corresponding source node. According to the method, the time required for one transmission cycle is effectively reduced and the channel utilization efficiency is improved under the premise of conflict-free parallel node data transmission. The method can be widely used in various underwater acoustic communication networks based on competition agreement, an underwater acoustic sensor network and other occasions.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Conflict-free competition-channel parallel communication method of underwater acoustic network
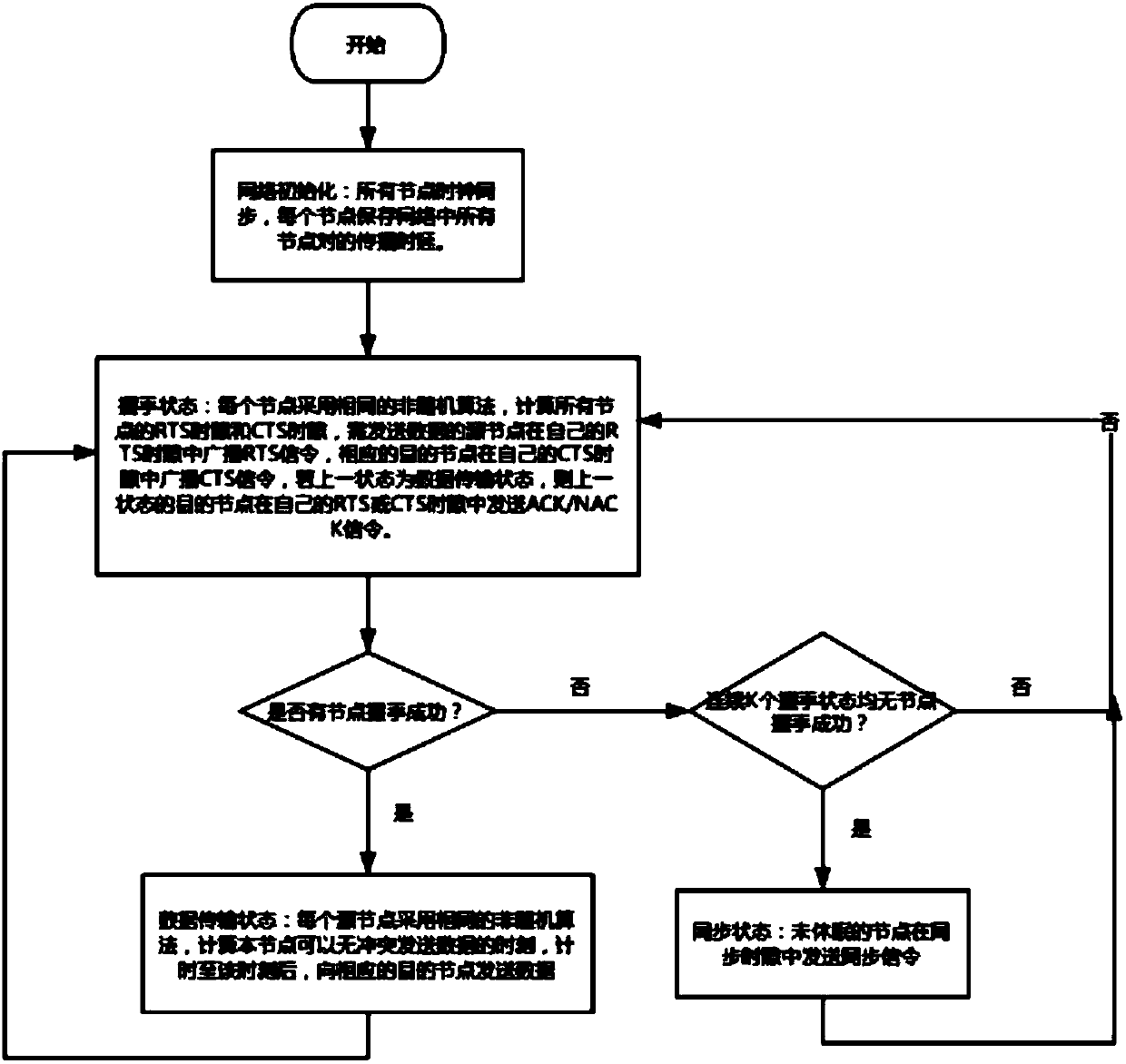
ActiveCN107919950AEliminate conflictAvoid Data Transmission ConflictsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSignal allocationPresent methodData transmission time
The invention discloses a conflict-free competition-channel parallel communication method of an underwater acoustic network, and the method is used for competition protocol based underwater acoustic communication network, underwater acoustic sensing network of full communication structure and the like. In a handshake stage, RTS / CTS signaling are transmitted in parallel via a concurrent time division multiplexing mechanism, conflict between RTS / CTS signaling can be eliminated completely, data transmission conflict caused by that a node cannot master all nodes of successful handshake in the sametransmission period and makes errors in calculating data transmission time in a present method is avoided, the handshake time can be reduced, and the transmission efficiency is improved; and in a last data transmission state, ACK / NACK signaling is sent in an RTS or CTS time slot in the next handshake state instead of time arranged independently, and the utilization efficiency of channels is higher. According to the method of the invention, two dormancy mechanisms are provided, energy consumption of the nodes can be reduced effectively, and the method has significance in the condition that energy of the underwater nodes is limited and not easy to supplement.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
UUV cluster ad hoc network method and system based on underwater acoustic communication
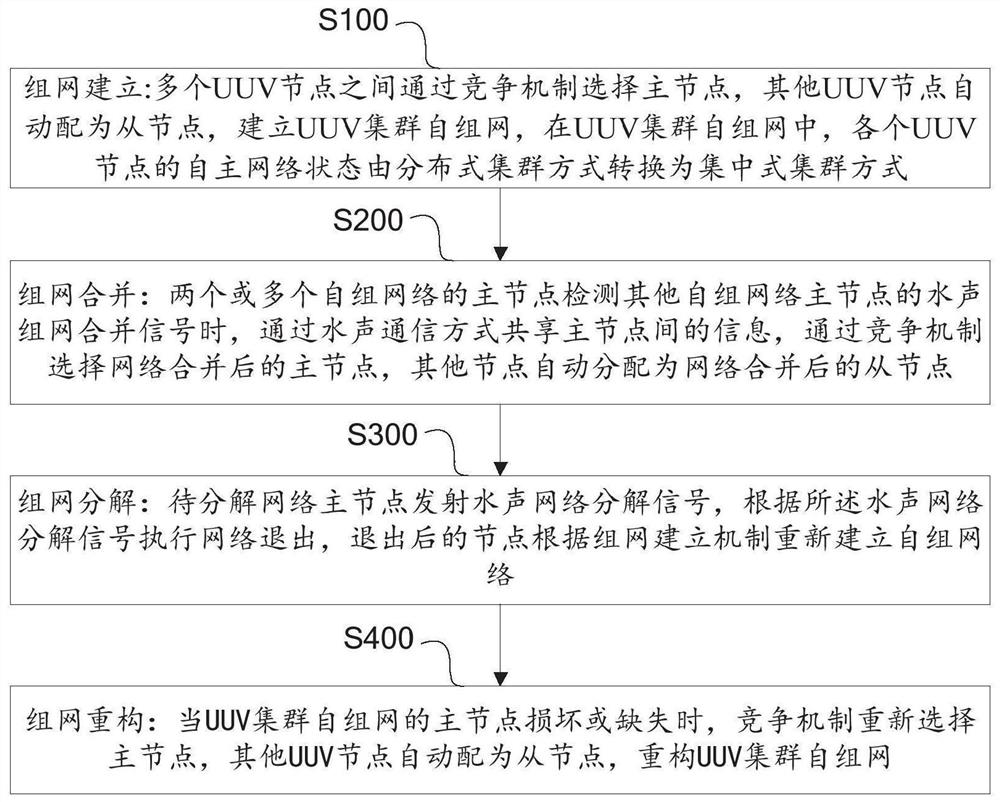
ActiveCN111669228ADecentralizedDoes not affect functional compositionSynchronisation arrangementSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSimulationNetwork decomposition
The invention discloses a UUV cluster ad hoc network method and system based on underwater acoustic communication. The method comprises the following steps: network building: a master node is selectedamong a plurality of UUV nodes through a competition mechanism, other UUV nodes are automatically configured as slave nodes, and a UUV cluster ad hoc network is built; network combination: two or more ad hoc networks are combined; network decomposition: a to-be-decomposed network master node transmits an underwater acoustic network decomposition signal, network quitting is executed according to the underwater acoustic network decomposition signal, and the quitted node reestablishes an ad hoc network according to a networking establishment mechanism; and network reconstruction: when the masternode of the UUV cluster ad hoc network is damaged or lost, the competition mechanism reselects a master node, other UUV nodes are automatically configured as slave nodes, and a UUV cluster ad hoc network is reconstructed. A centralized UUV clustering mode and a distributed UUV clustering mode are combined, the method and the system have the characteristics of autonomous state conversion, data exchange, resource sharing and the like, and a node joining / exiting mechanism and a network combining / decomposing mechanism are supported within an acoustic action distance range.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACOUSTICS LAB CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Joint optimization underwater acoustic multi-hop cooperative communication network route selection method
ActiveCN111049743AExtend the life cycleReduce consumptionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionArtificial lifeHydroacousticsUnderwater acoustic network
The invention discloses a joint optimization underwater acoustic multi-hop cooperative communication network route selection method, and relates to an underwater acoustic network. The randomness of the artificial fish swarm algorithm and the positive feedback mechanism of the ant colony algorithm are utilized to search the superiority of the globally optimal solution. An artificial fish swarm algorithm is used as a main body; and determining a part of nodes in the routing sequence nodes, fusing the other part of nodes selected by the ant colony algorithm to form a new routing sequence table, and finding a global optimal path by taking energy consumption of the nodes as a cost function based on an underwater acoustic communication energy consumption model and in combination with a cooperative communication technology, so that the system energy consumption of information transmission is minimized. The optimal path can reduce the overall energy consumption of the system, prolong the lifecycle of the underwater acoustic multi-hop communication network, and improve the underwater acoustic multi-hop cooperative communication efficiency. The defects that the precision of solving the global solution by singly using the artificial fish swarm algorithm is low and the local optimum is easily caused by singly using the ant colony algorithm are overcome.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Underwater acoustic network communication method for joint optimization of node sending time and power
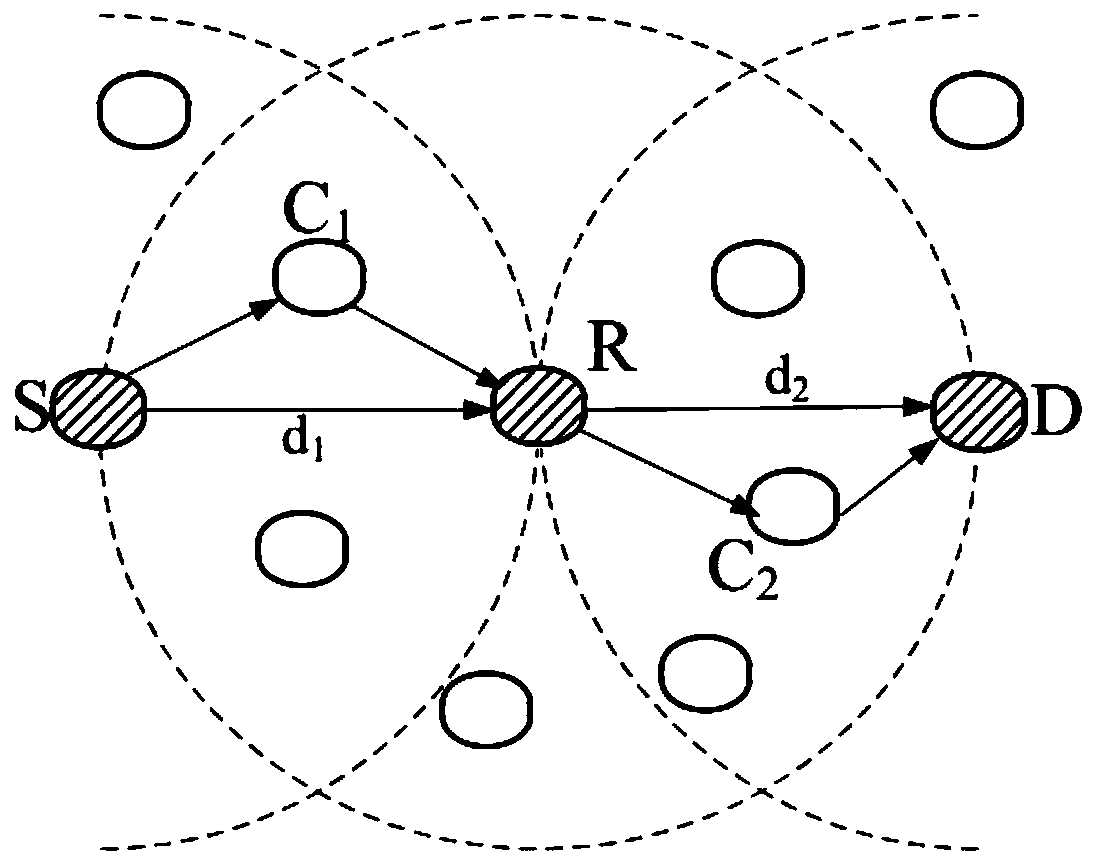
ActiveCN106899981AImprove transmission efficiencyShorten the timePower managementTransmissionEnergy consumptionTransmission cycle
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic network communication method for joint optimization of node sending time and power. The method comprises the following steps: when a channel is idle and at least one node needs to transmit the data, the network enters a handshake phase; each source node adopts the same non-random algorithm to calculate the connection relation of each node of the network when all the source nodes transmit the data at the minimum transmitting power that is required for successfully transmitting the data to the corresponding destination node, divides the whole network to sub-networks which are not communicated with each other, calculates the time that the node can transmit the data to the corresponding destination node without conflicts in the local sub-network, and transmits the data to the corresponding destination node at the minimum transmitting power after timing to the moment; and when all the source nodes complete the data transmission, the network enters an end phase. According to the underwater acoustic network communication method disclosed by the invention, the fully-communicated network is converted to multiple sub-networks which are not communicated with each other during the data transmission phase, the time required for a transmission cycle can be effectively reduced, the utilization efficiency of the channel can be increased, and the energy consumption can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Data packets of underwater sound sensor network and transmission method
InactiveCN102255713AReduce data volumeError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork packetPage header
The invention provides data packets of an underwater sound sensor network and a transmission method. Each data packet consists of a packet header part, a packet header verification part and a data part, wherein the packet header part comprises address information; the packet header verification part only comprises verification information related to the packet header part; the data part consists of one or more data blocks of equal length; and each data block consists of a transmitted data part and verification information of the transmitted data part respectively. The basic thought of the invention is to partition the conventional large transmitted data block into certain data blocks of equal length for respective verification, so that the data volume of retransmission in an environment, such as an underwater acoustic network in which a transmission error occurs easily, can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Energy balance underwater acoustic network routing protocol method based on layering
InactiveCN111866982ALimit transmissionReduce energy consumptionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionData switching networksEnergy balancingEngineering
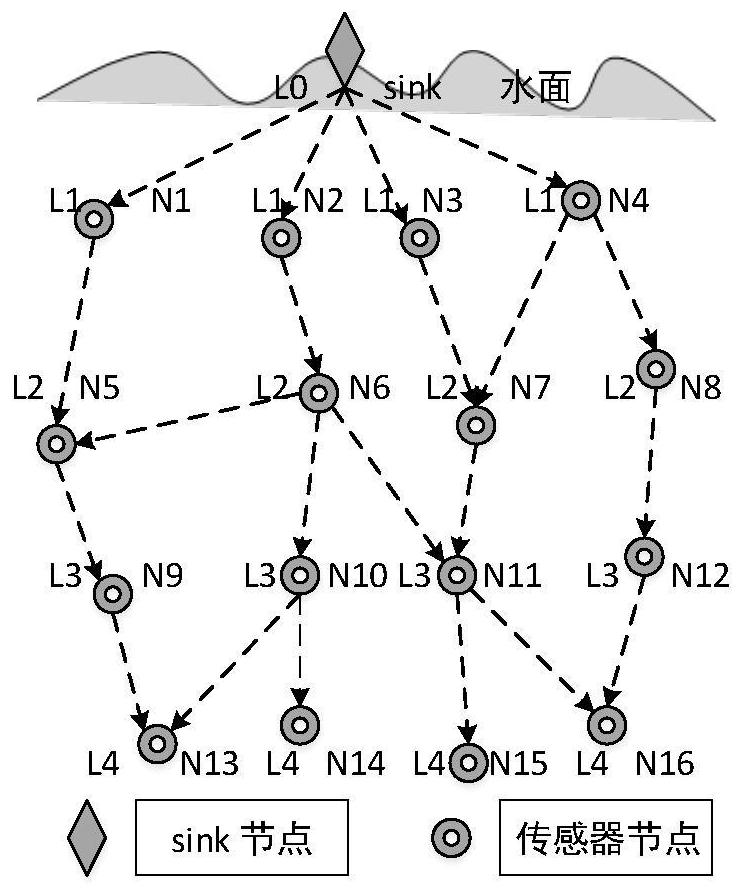
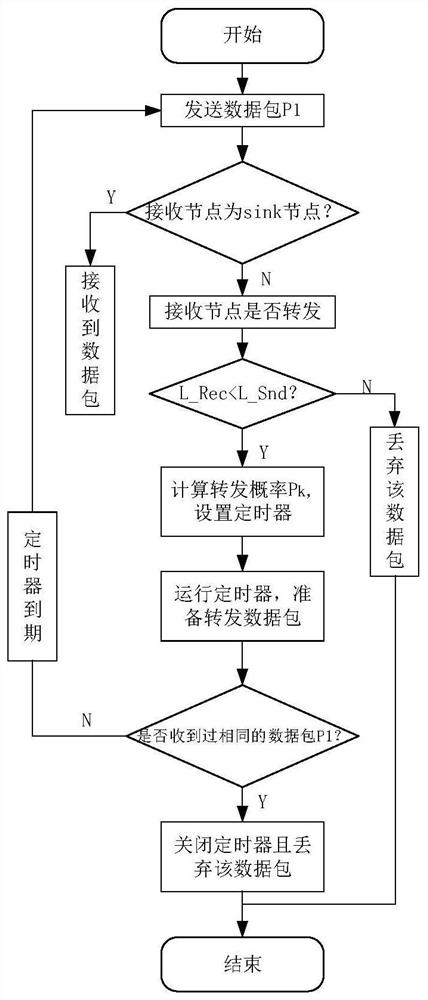
The invention relates to an energy balance underwater acoustic network routing protocol method based on layering. The method comprises a data forwarding step, wherein the data forwarding step comprises the following contents of S11, when the receiving node is not a sink node, judging the size relationship between the own hierarchy L_Rec and the sending node hierarchy L_Snd, and if L_Rec (L_Snd), executing the step S12; S12, the receiving node calculates the forwarding probability of the receiving node according to the one-hop delay and the residual energy so as to set the timeout value of thetimer, and when the timer expires, the receiving node is changed into a sending node to forward the data message; and S13, repeating the steps S11 and S12 till the receiving node is a sink node. The method is advantaged in that the receiving node judges whether to forward the data or not according to the three factors of the hierarchy, the residual energy and the one-hop delay; by taking the nodewith high residual energy and small one-hop delay as the node for data forwarding, energy balance is effectively realized, the service life of the network is prolonged, and the end-to-end delay in thenetwork is reduced.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV
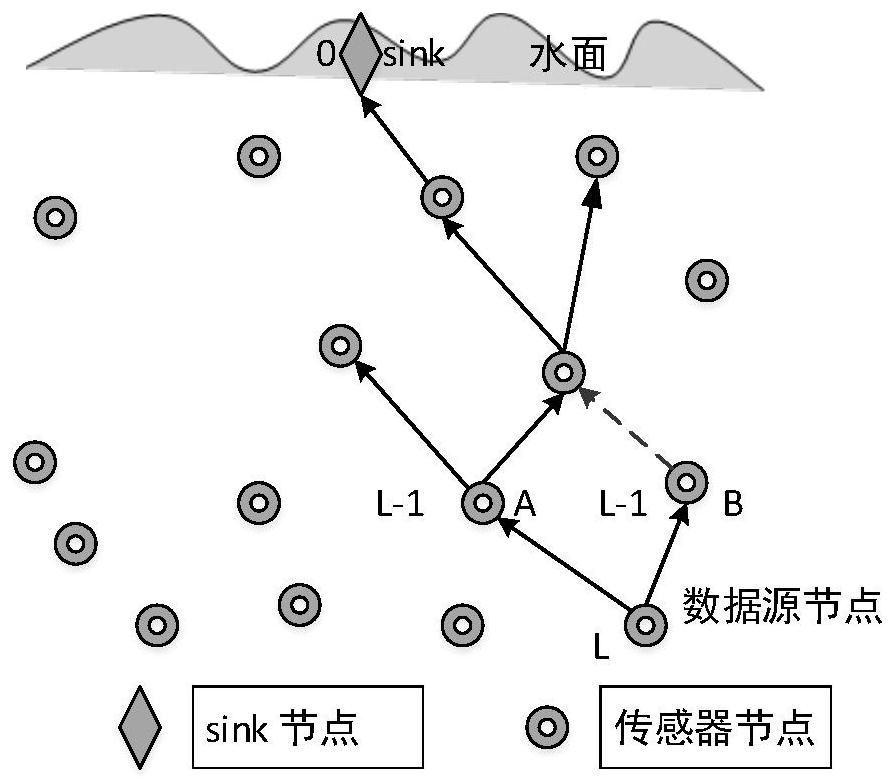
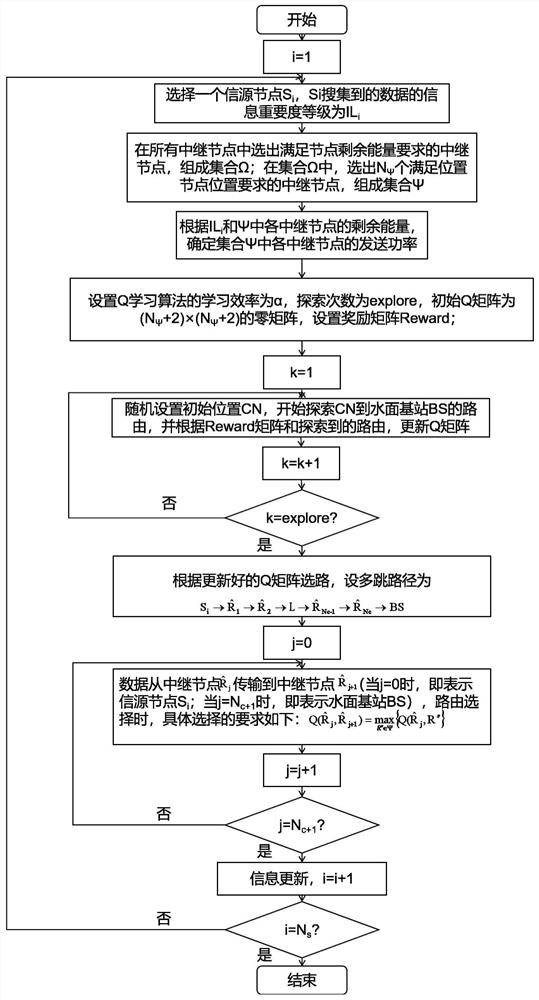
Underwater acoustic network routing method based on information importance and Q learning algorithm
ActiveCN112867089ABalance Energy ExpenditureExtend the life cycleGeometric CADNetwork topologiesAlgorithmEngineering
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic network routing method based on information importance and a Q learning algorithm, and relates to an underwater acoustic network. The method comprises the following steps: introducing information importance into a multi-hop underwater acoustic sensor network, taking an information importance level as a first priority condition, taking relay node residual energy as a second priority condition, and selecting an optimal route by using a Q learning algorithm: selecting a shorter route for information with a high information importance level, and ensuring that important information is quickly and accurately transmitted to a water surface base station; for the information with low information importance level, selecting the relay node with sufficient residual energy, so the situation that due to the fact that some relay nodes are repeatedly utilized for multiple times, node death is too fast, and energy holes occur is avoided. The number of nodes selected for the Q learning algorithm is only 1 / 7 of the total number of survival nodes of the whole network, exploration of the survival nodes of the whole network is avoided, the candidate node set range of the Q learning iterative algorithm is shortened, the number of times of exploration needed for finding the optimal route is reduced, the algorithm operation time is saved, the underwater node power consumption is saved, and the life cycle of the underwater acoustic network is prolonged.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Underwater acoustic network MAC access method
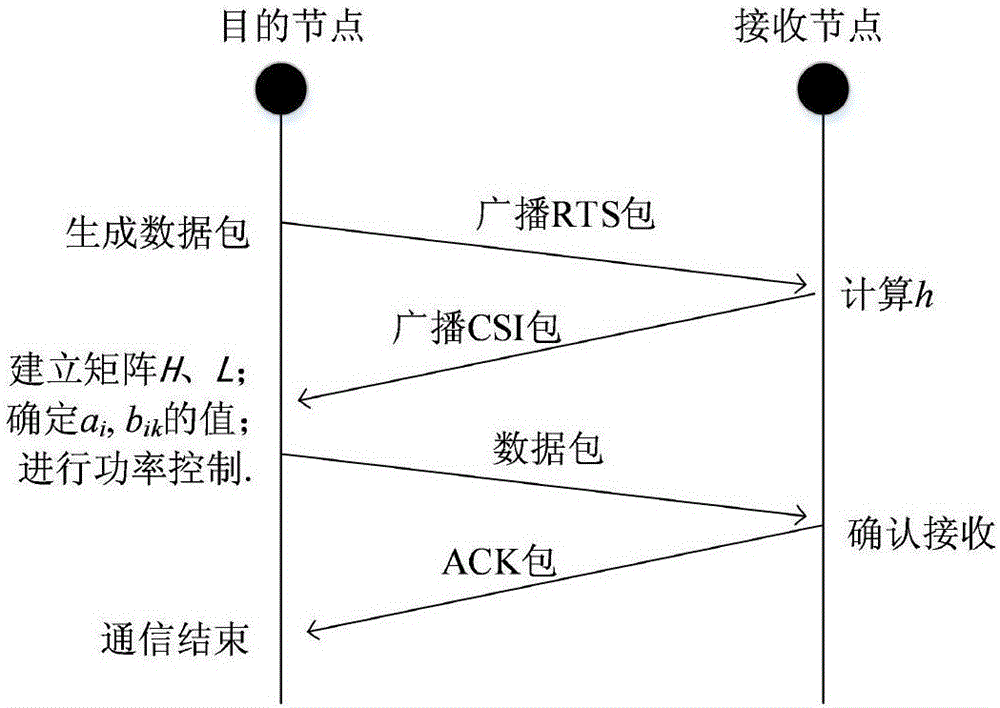
InactiveCN107171739AError prevention/detection by using return channelRelay systems monitoringElevation angleSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to an underwater acoustic network MAC access method. The method comprises the following steps: when a data packet needs to send, a source node omni-directionally sends a reservation request control packet RTS with the maximum powder, after receiving the RTS, all nodes in the source node radiation range compute respective signal-to-noise ratio relative to the source node, and compute the azimuth angle and elevation angle of the resource node relative to all nodes; after receiving the first RTS, a destination node waits the time duration W, selects the node with the maximum theta value as a communication node, and omni-directionally broadcasts the reservation confirming data packet CTS; the node receiving the CTS computes the direction and signal-to-noise ration of the destination node relative to itself, establishes a channel state matrix H and a neighbor node direction matrix L; the node in the relay selection region computes the own mean value relative to the source node and destination node signal-to-noise ratio after acquiring that one source node sends the request but the request is not agreed by the destination node through the RTS and the CTS, when the mean value is greater than one threshold, the node takes charge of the relay node.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
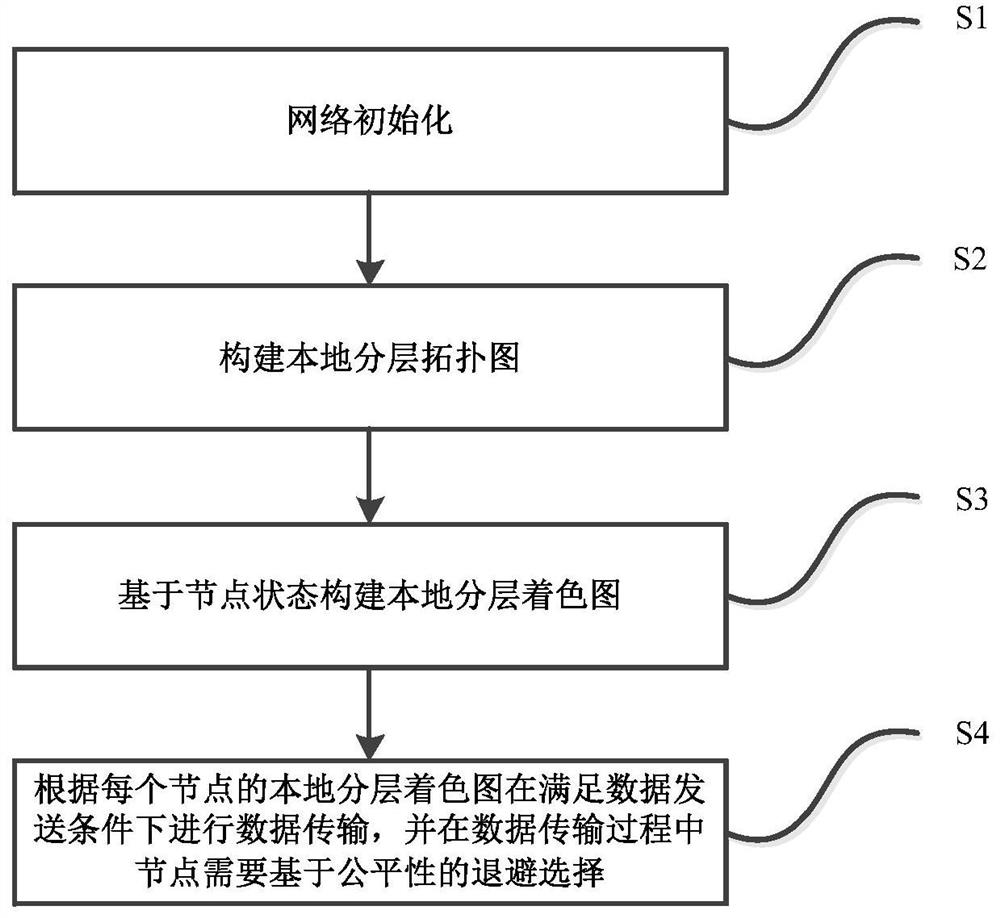
Underwater acoustic network MAC protocol generation method based on state coloring
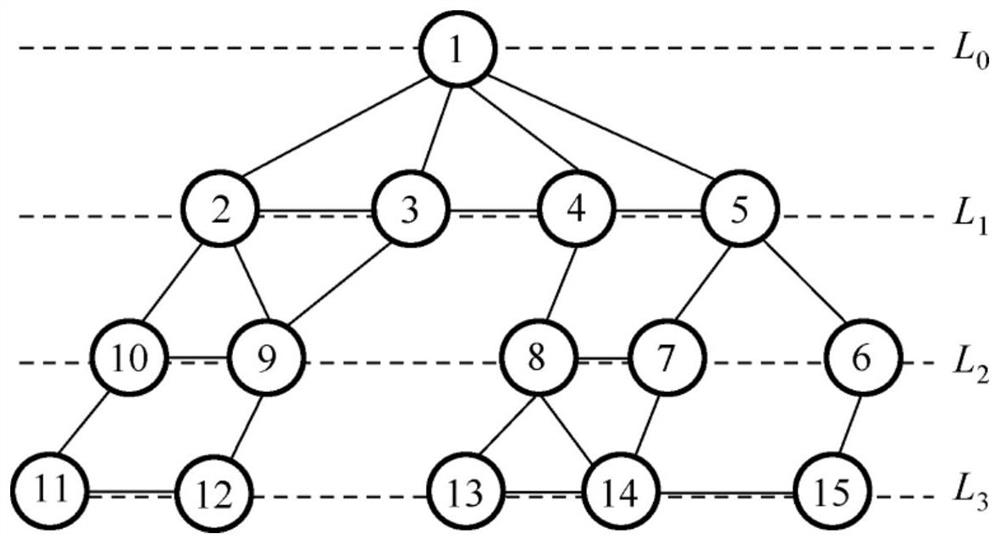
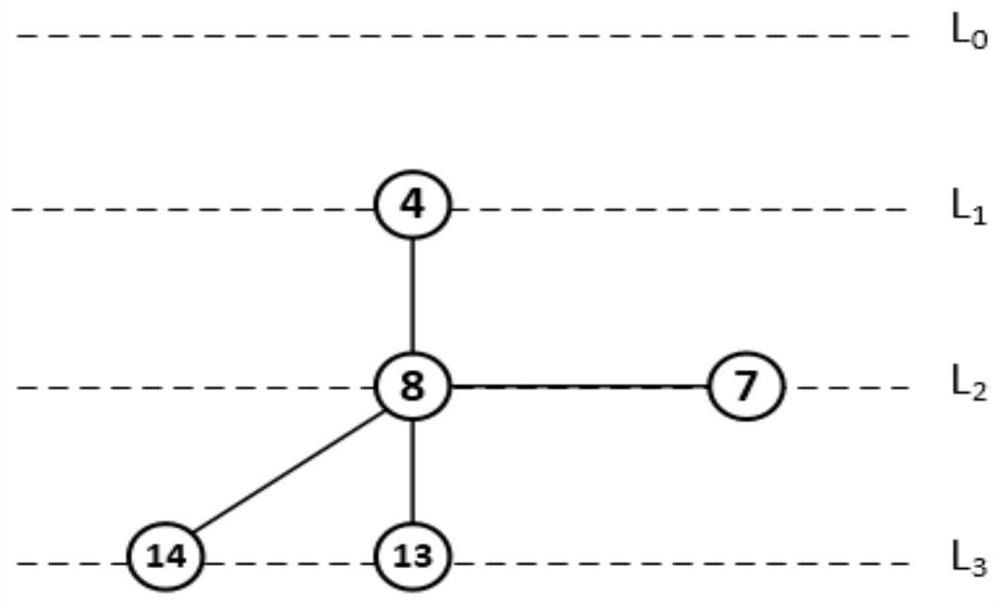
ActiveCN112398806AReduce consumptionIncrease profitSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionNetwork topologiesData packNetworking protocol
The invention relates to an underwater acoustic network MAC protocol generation method based on state coloring. The method comprises the steps: constructing a local hierarchical graph: assigning a hierarchy for each node in UANs according to the hop count from a node to a sink, obtaining a hierarchical topological graph, constructing a local one-hop neighbor table for each sensor node according tothe control information received by the node, and constructing a local hierarchical graph for each sensor node through the local one-hop neighbor table of each sensor node; constructing a local layered coloring graph: judging node states by monitoring data packets or ACK frame header information in a channel, and coloring nodes in the local layered graph in multiple colors to obtain the local layered coloring graph of each node; and performing data transmission according to the local layered coloring graph of each node under the condition of meeting the data transmission condition. Accordingto the method, the conflict is avoided through the local layered coloring graph, the conflict can be effectively avoided without an RTS / CTS handshake mechanism, the control packets are reduced, the energy consumption is reduced, and the channel utilization rate is improved.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV
Coordination mechanism method of multiple-hop underwater acoustic network data transmission
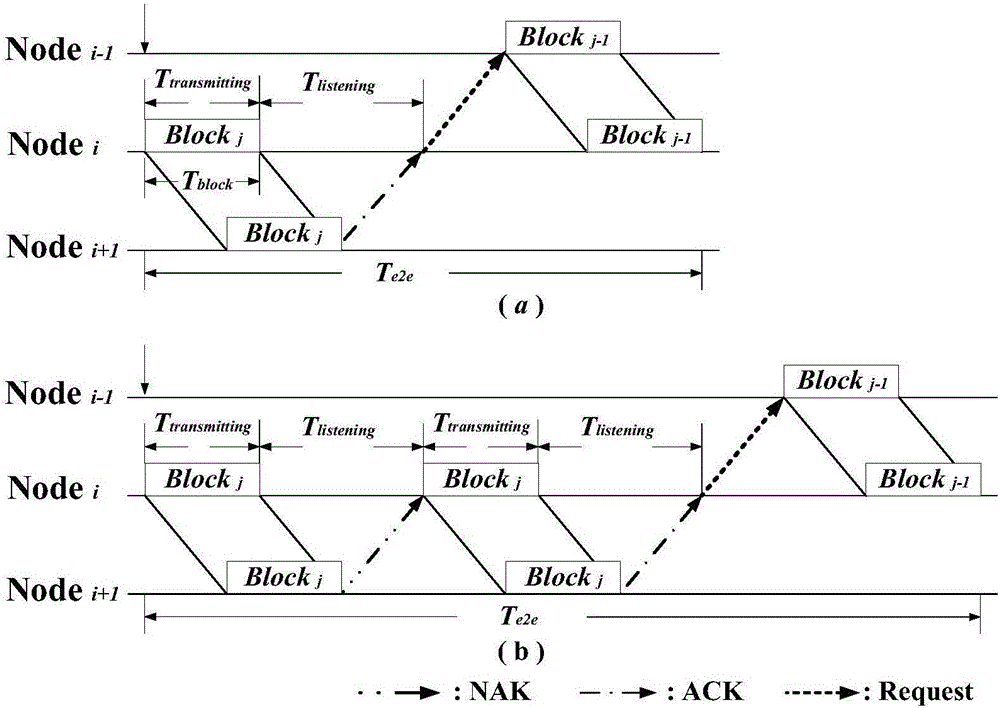
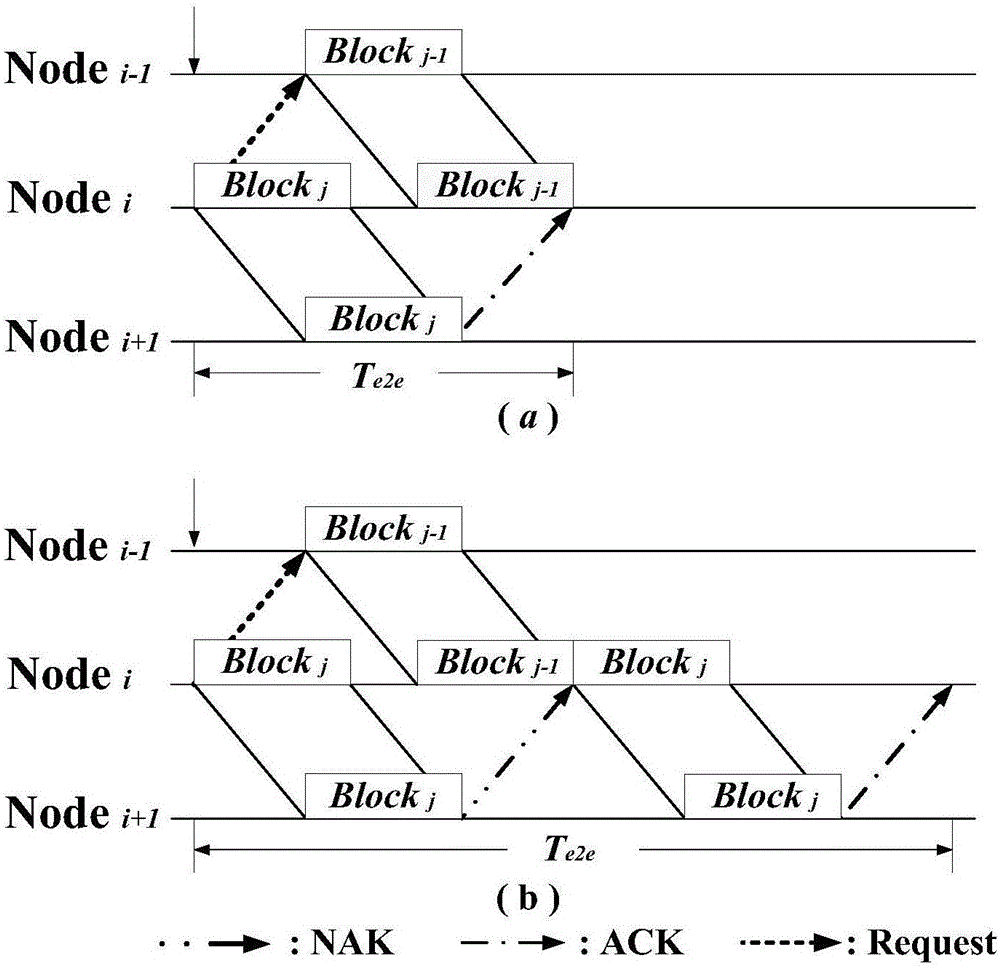
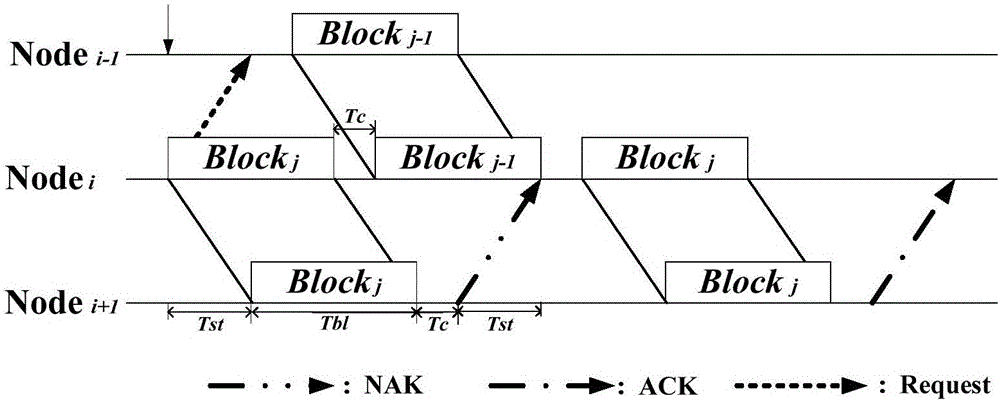
ActiveCN105813130AReduce end-to-end latencyAdaptableError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTransport systemOriginal data
The invention relates to a coordination mechanism method of multiple-hop underwater acoustic network data transmission and belongs to the underwater communication field. According to the method, a coordination mechanism of inter-node data transmission is established based on the transmission characteristic of large time delay of an underwater acoustic channel; the length of data blocks is set reasonably, the distances between nodes are controlled, and the magnitude of transmission power of each node is controlled; and after a node i sends a data block j, the next data block j-1 of a node i-1 is received at first, then the feedback signals from a node i+1 are received, if acknowledgement signals are received, the node i directly begins sending the next data block j-1 from the node i-1, otherwise, the node i re-transmits the original data block j, and thus, the listening state time of the node i can be fully utilized. With the method of the invention adopted, the average end-to-end delay of the transmission of an underwater acoustic data multiple-hop transmission system can be effectively reduced with the bit error rate performance of the underwater acoustic data multiple-hop transmission system ensured; and underwater acoustic data are sent and received by using the idle time of the listening of the underwater acoustic network nodes; and the average end-to-end delay changes slowly with a signal to noise ratio.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Layering based mobile multi-hop underwater acoustic network dynamic self-localization method
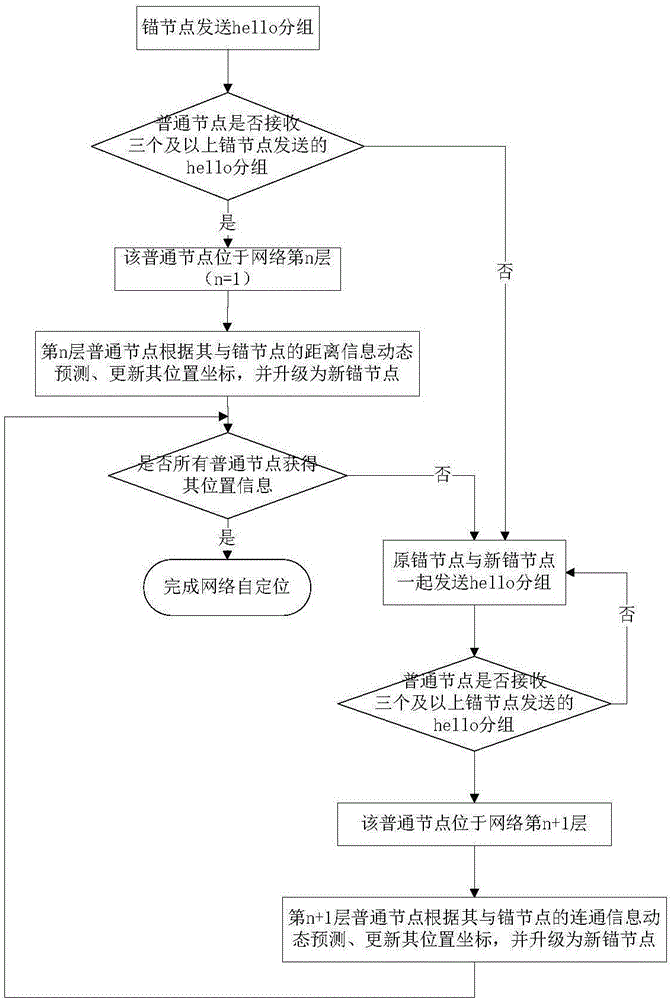
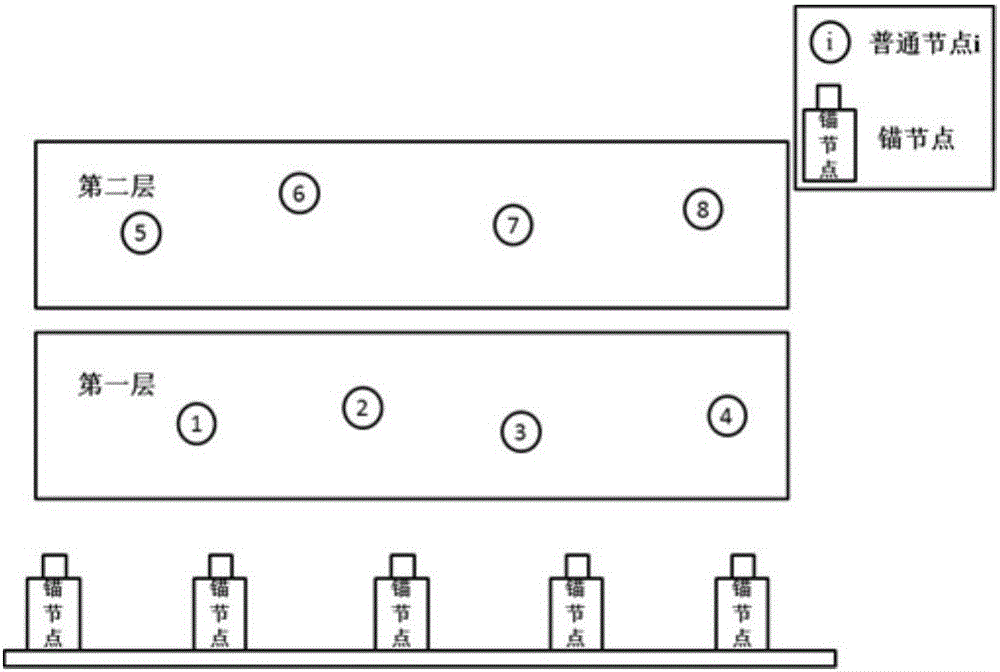
ActiveCN106488526ASolve self-positioning problemsGuaranteed self-positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesMobile WebUnderwater acoustic network
The invention provides a layering based mobile multi-hop underwater acoustic network dynamic self-localization method and relates to the technical field of underwater acoustic communication and an underwater acoustic network. The layering based mobile multi-hop underwater acoustic network dynamic self-localization method comprises the steps of dividing common nodes into a plurality of layers; adopting different self-localization algorithms by the nodes in different layers based on the characteristics of the nodes in each layer; and finishing self-localization by the common nodes through communication with an anchor node and rest adjacent nodes to obtain the location information of the common nodes. As a layered localization mechanism is adopted, the underwater acoustic network coverage and detection range is enlarged, and the self-localization problem of the multi-hop mobile network can be solved. after the network nodes are subjected to layering, different self-localization methods are adopted by the nodes in different layers and a self-localization method which is based on or not based on distance information is used at the same time, so that communication expense in a mobile network self-localization process is greatly reduced whole the localization precision is ensured, and the layering based mobile multi-hop underwater acoustic network dynamic self-localization method is more suitable for an underwater environment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
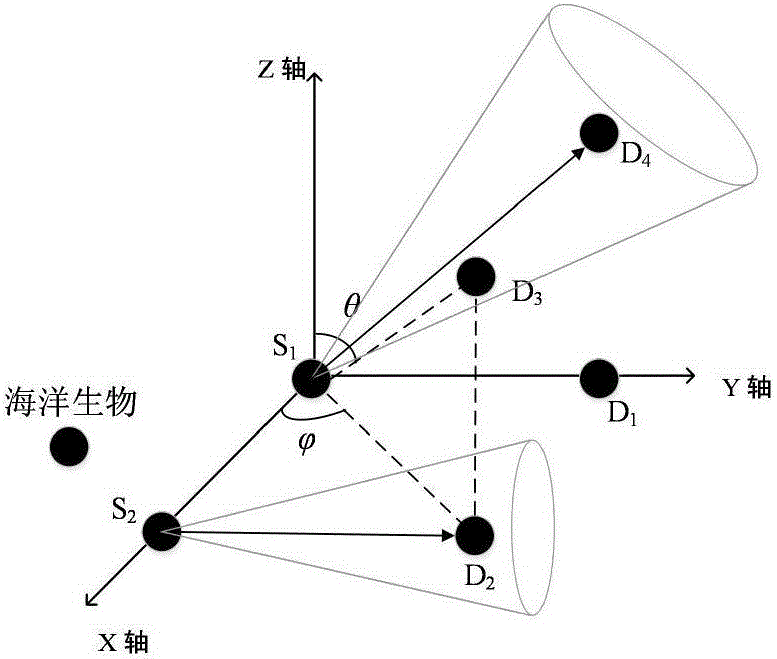
Directional underwater acoustic network power control method
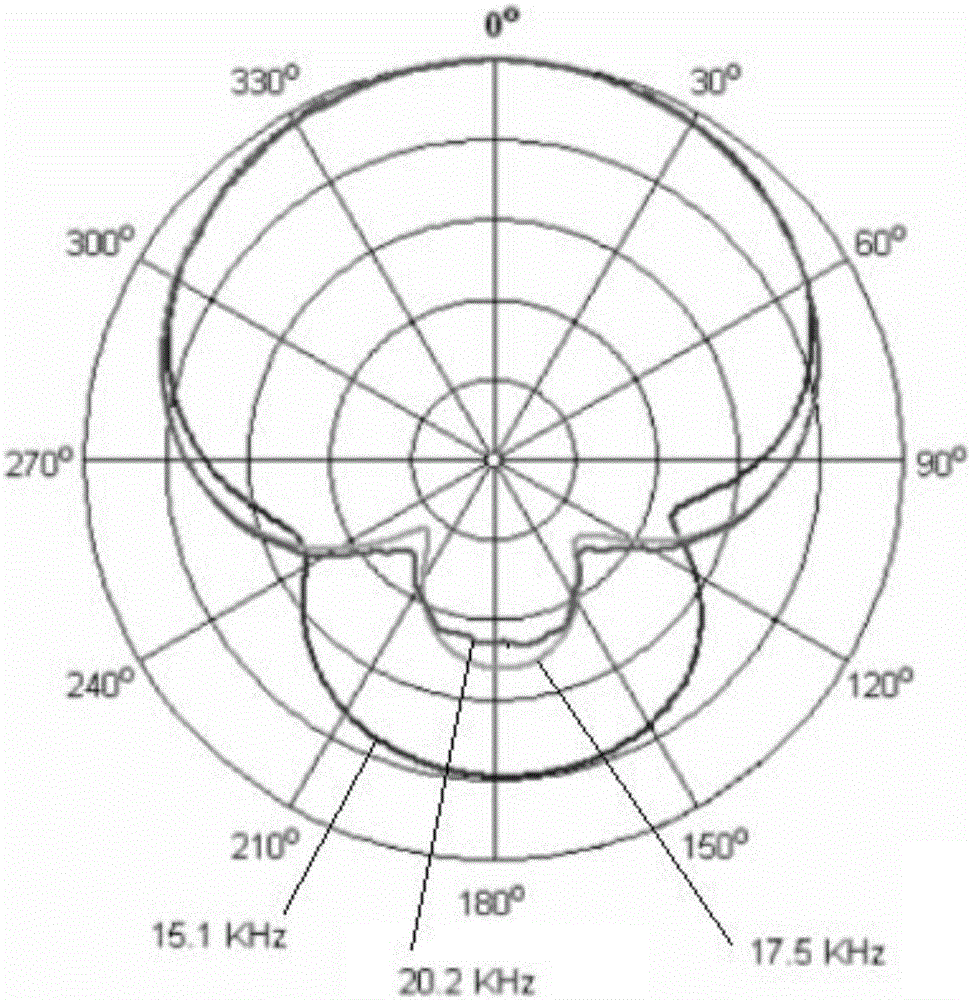
The invention relates to a directional underwater acoustic network power control method. The directional underwater acoustic network power control method comprises the following steps: a source node performs neighbor discovery, and sends an RTS control packet in all directions through the maximum power; the beam width alpha and the self transmission power are included; after receiving the RTS, all nodes in the irradiation range of the source node calculate the channel gain h, and broadcast a CSI control packet in all directions; after receiving the CSI, the source node calculates the azimuthal angles and the elevation angles of various destination nodes corresponding to the source node; a channel state matrix H and a neighbor node orientation matrix L are respectively established; the source node performs environmental perception, judges whether a marine organism exits in the irradiation range or not, and judges which node can be interfered in a communication process according to the relative angles of the destination nodes and other neighbor nodes and the beam width alpha; according to an environmental perception result, a utility function is defined for each node at first; power is distributed to the node by solving a power value for enabling the utility function to be maximum; the power value is corrected; and, a data packet is sent in a destination node alignment manner.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Underwater acoustic network node mutual distance measurement method based on gamma distribution model
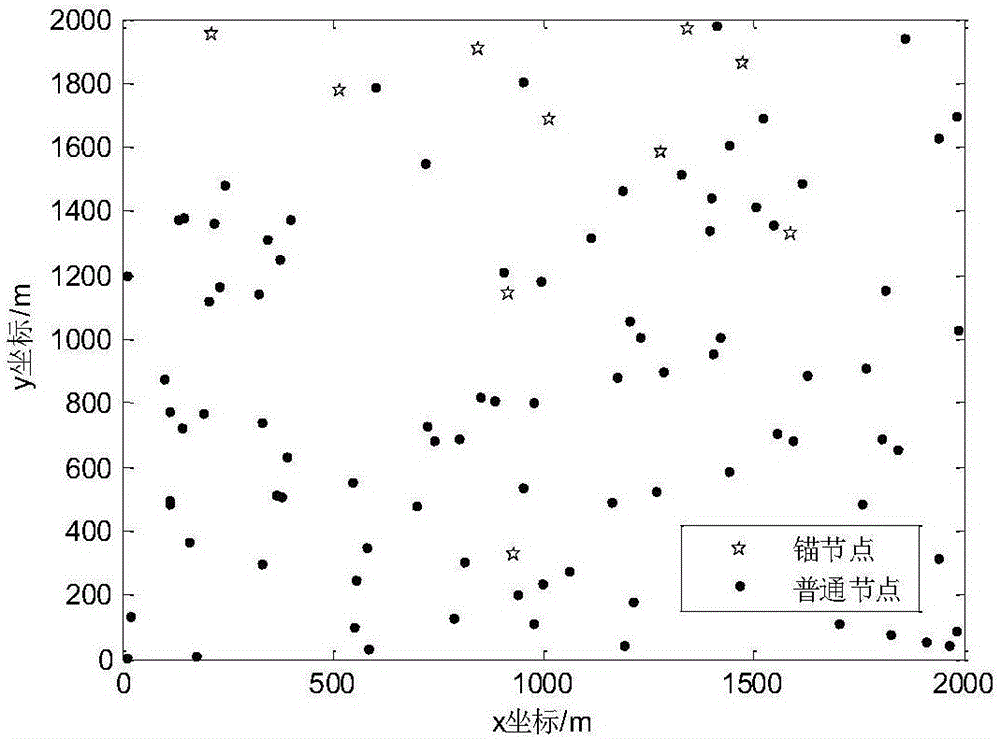
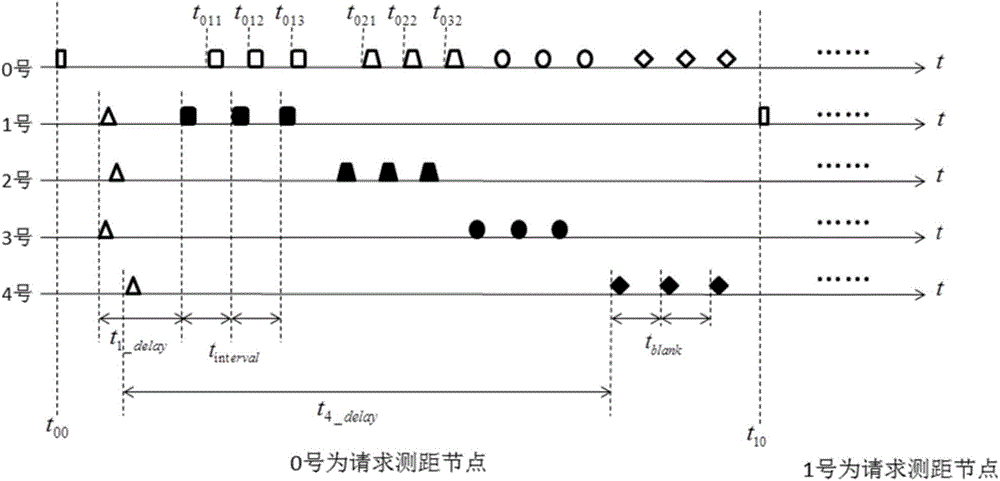
InactiveCN104391275AHigh positioning accuracyHigh precisionPosition fixationTime distributionComputer science
The invention provides an underwater acoustic network node mutual distance measurement method based on a gamma distribution model; the TDOA distance measurement process of multiple response mechanism is finished through certain time distribution strategy for the underwater communication network composed of N sub-nodes and one main control node and the range information is corrected based on gamma model. The distance measurement information is corrected and compensated for offering reliable guarantee for improving location accuracy. The underwater acoustic network node mutual distance measurement method based on the gamma distribution model takes full advantage of slower propagation speed of the sound in the water and adopts multiple response mechanism on distance measurement request signal for improving the distance measurement operation precision and efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
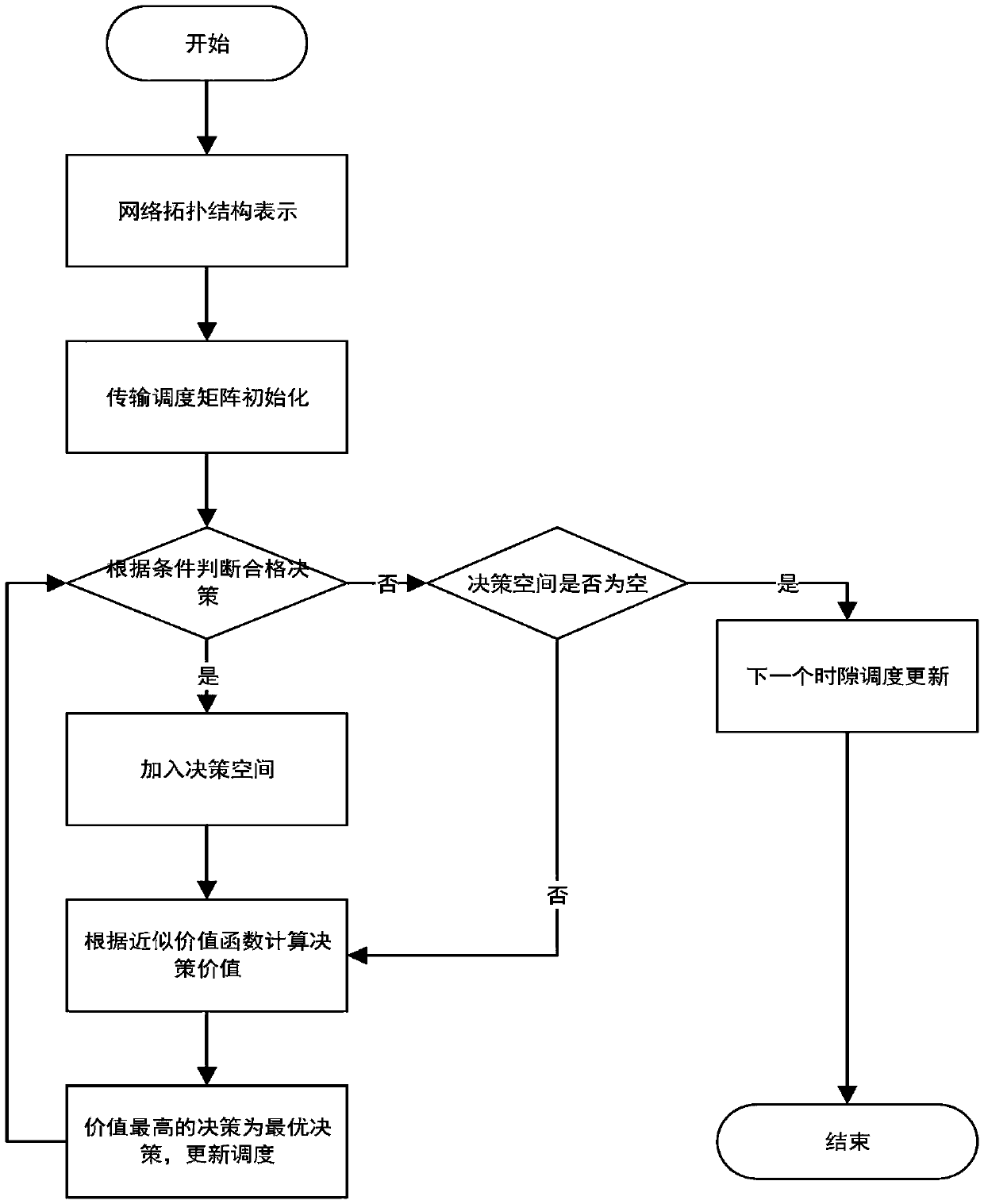
Multichannel transmission scheduling method based on time domain interference alignment in underwater acoustic network
InactiveCN111294137AImprove throughputReduce data conflictsNetwork topologiesOrthogonal multiplexEngineeringNetwork model
The invention provides a multichannel transmission scheduling method based on time domain interference alignment in an underwater acoustic network. The method comprises the following steps: S1, network topology representation is carried out, a time slot division model is adopted, the whole message transmission process is divided into a plurality of time slots with the length of [tau], the transmission delay between nodes refers to the time required by message transmission between two nodes, a transmission delay matrix is used for representing a network topology structure, and elements in the matrix represent the number of the time slots required by message transmission between the nodes; S2, transmission scheduling is initialized, the states of the nodes are stored through a three-dimensional matrix, and transmission time slots of the nodes, selected transmission channels and destination nodes are determined; and S3, optimal transmission decision search is carried out, an optimal scheduling problem is searched to be regarded as a sequential decision problem, and the problem can be solved by using dynamic planning. In the multi-channel network model, a plurality of nodes can transmit messages in one time slot at the same time, so that data conflicts are reduced, and the network throughput is increased.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Time-reversal multiple access method applicable to underwater acoustic network
ActiveCN106571876AGood transmission concealmentImprove confidentialityError prevention/detection by using return channelBaseband system detailsConfidentialityUnderwater network
The invention provides a time-reversal multiple access method applicable to an underwater acoustic network and relates to the underwater acoustic communication and underwater network technology field. According to the method, a multiple access mechanism is appointed for an active time-reversal underwater acoustic network, conflicts and bump can be completely avoided when channel correlation is broken, success transmission probability is improved, through active TR space time focusing, spatial variation characteristics of an underwater acoustic channel is utilized to weaken broadcast characteristics of the underwater acoustic channel, not only can the crucial effect of effectively isolating signal interference among adjacent links under the distributed multi-hop environment be realized, but also excellent transmission concealment and confidentiality of the multiple access method is realized through weakening the broadcast characteristics of the underwater acoustic channel, on the condition that underwater acoustic correlation is not determined, spatial reuse and network throughput can be further improved even when channel weak correlation is broken, system time delay is reduced, and energy is saved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
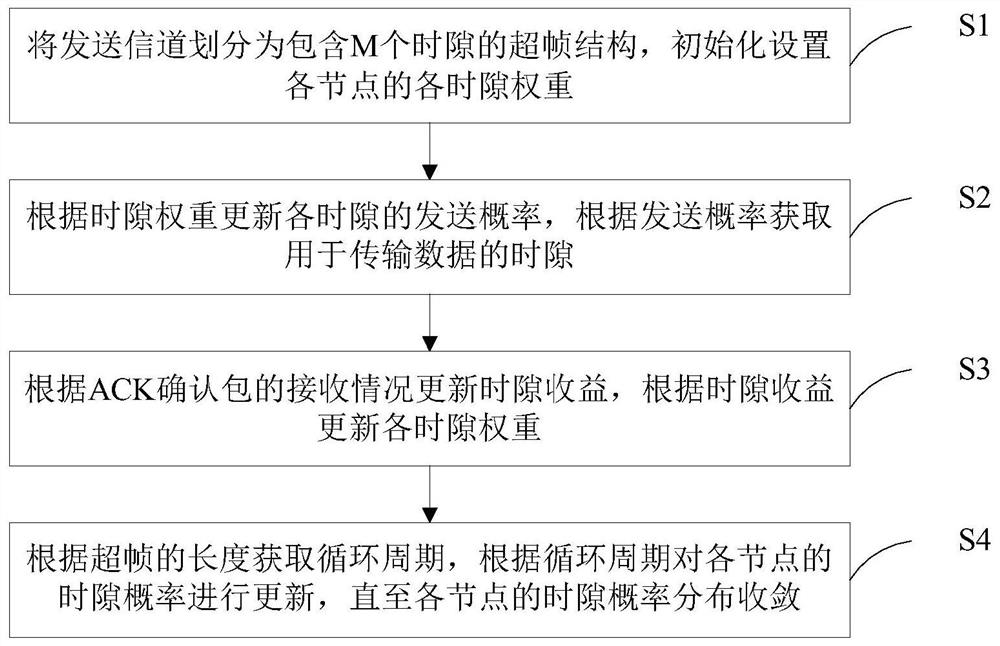
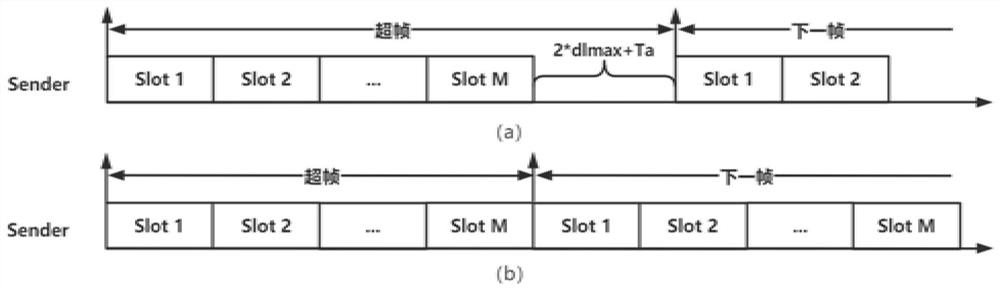
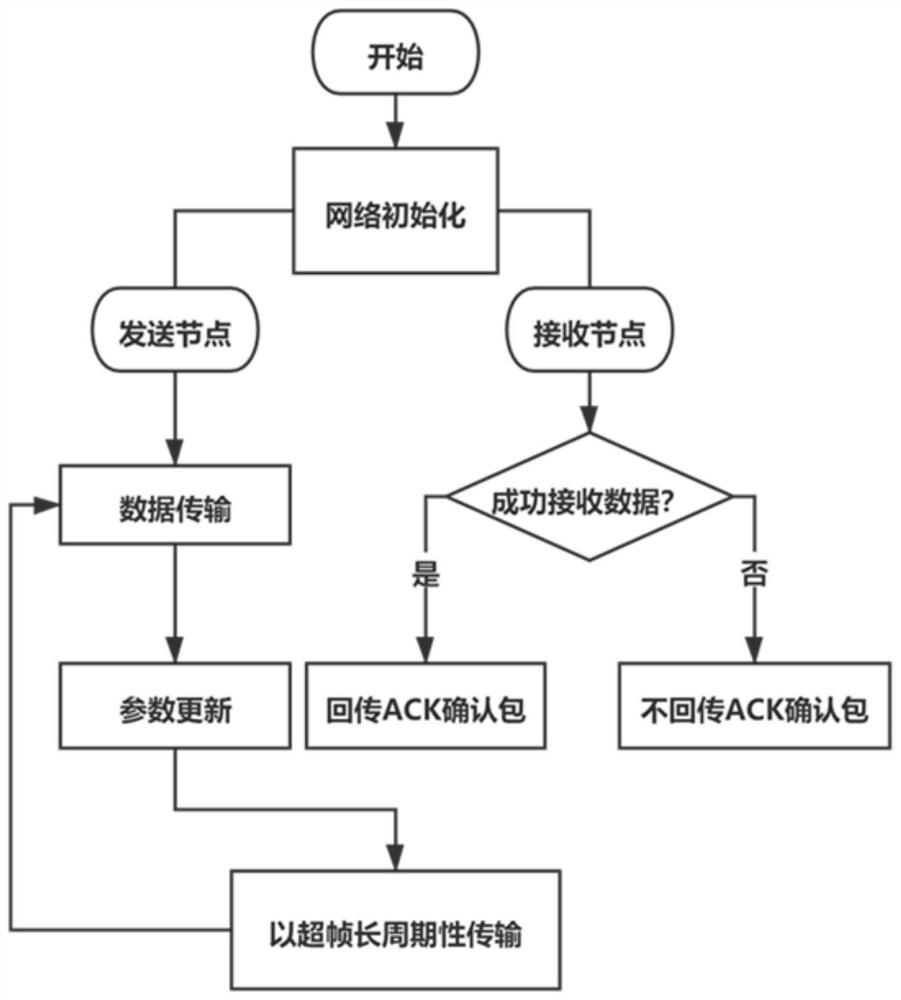
Underwater acoustic network time slot MAC protocol method, system, device and medium
ActiveCN113507328AReduce the probability of conflictHigh data delivery rateError prevention/detection by using return channelHigh level techniquesEngineeringAcknowledgement
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic network time slot MAC protocol method, system and device and a medium, and the method comprises the following steps: dividing a transmission channel into a superframe structure containing M time slots, and carrying out the initialization setting of the weight of each time slot of each node; updating the sending probability of each time slot according to the time slot weight, and obtaining the time slot for transmitting the data packet according to the sending probability; updating the time slot revenue according to the receiving condition of the ACK acknowledgement packet, and updating each time slot weight according to the time slot revenue; obtaining a cycle period according to the length of the superframe, and updating the time slot probability of each node according to the cycle period until the time slot probability distribution of each node converges. According to the method, the evolutionary game theory is simulated, the distributed underwater acoustic network MAC protocol which does not need time synchronization and only depends on local information to adaptively form the sending strategy of each node can be realized, the conflict probability of data transmission is reduced to a greater extent, so higher data delivery rate and throughput performance are realized, and the method can be widely applied to medium access control.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Distributed multi-channel underwater acoustic network communication method
ActiveCN110769519AImprove communication performanceReduce overheadWireless communicationInformation dispersalNetwork communication
The invention discloses a distributed multi-channel underwater acoustic network communication method. According to the method, parallel transmission of data is realized by simultaneously utilizing thecharacteristic of information propagation time delay of a plurality of communication channels and underwater acoustic channels; handshake signaling is sent by adopting an optimized time division multiplexing method in some communication channels, data is sent in parallel by adopting optimized sending time in other communication channels, and the handshake signaling and the data are transmitted inparallel in an assembly line mode. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that parallel transmission is carried out by fully utilizing the characteristic that the propagation timeof multi-channel and underwater acoustic channel information is prolonged, central node control is not needed, overhead caused by handshake can be reduced while transmission conflicts are completelyeliminated in a distributed network, and the communication efficiency of the underwater acoustic network is effectively improved. The method can be widely applied to distributed underwater acoustic communication networks, underwater acoustic sensor networks and other occasions.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
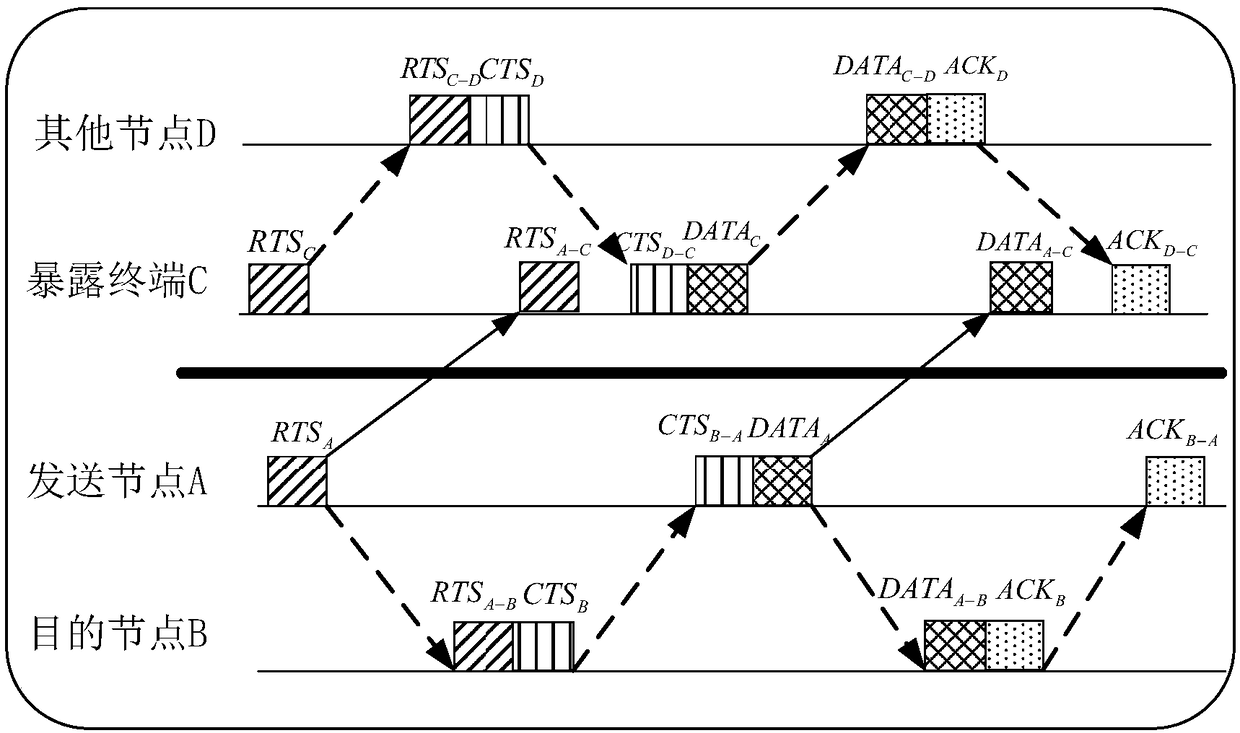
Underwater acoustic node exposed terminal solving method based on table mechanism and using propagation delay
ActiveCN108184250AImprove throughputReduce latencyPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementPropagation delayComputer science
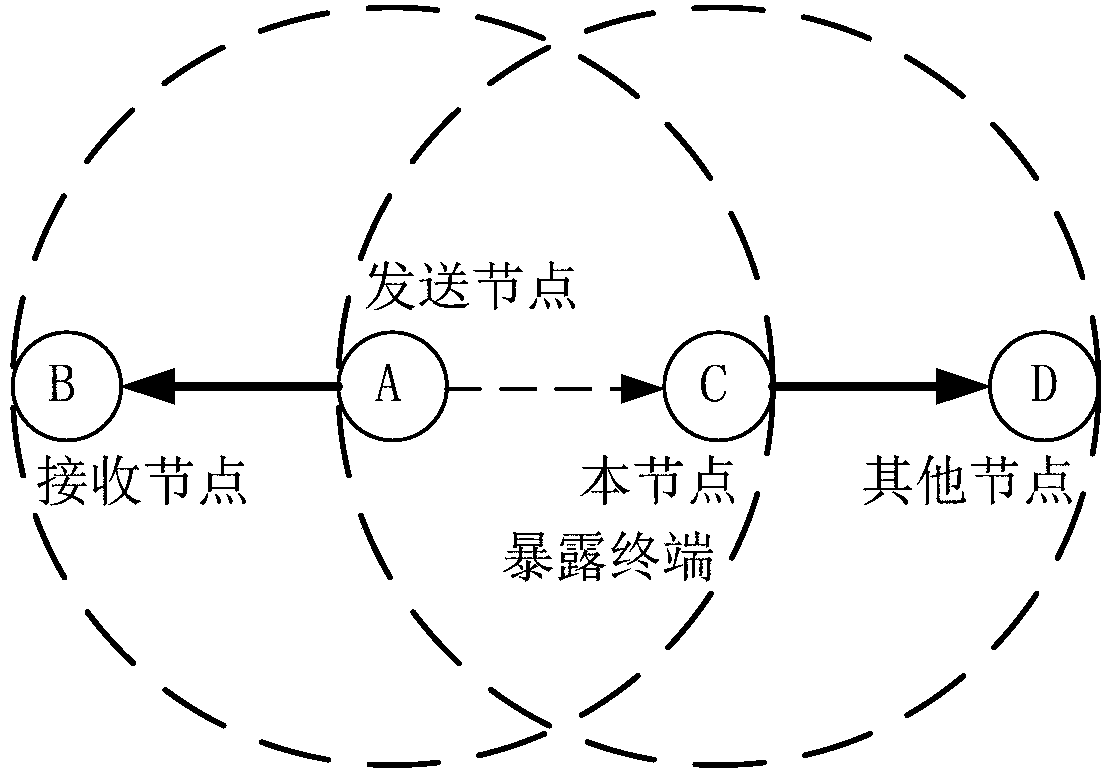
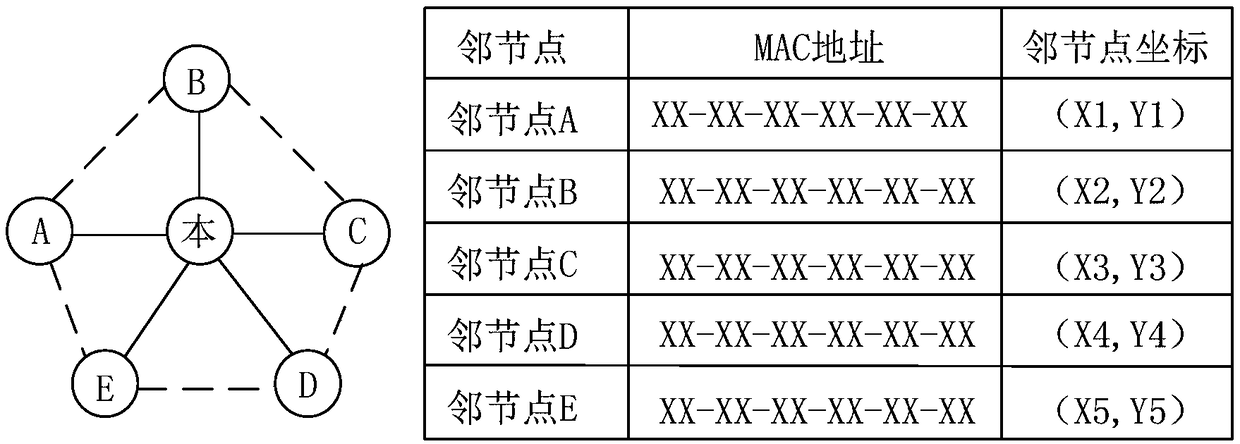
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic node exposed terminal solving method based on table mechanism and using propagation delay. The method is based on a handshaking mechanism, each underwater acoustic communication node obtains global node information in a network through self-learning of the table mechanism, and transmission tasks in the network are planned. The self-learning process ofthe table mechanism of the underwater acoustic node mainly comprises three parts which are respectively table initialization, table storage and table updating. The underwater acoustic node exposed terminal solving method provided by the invention has the advantages of searching for the exposed terminal in the network based on the table mechanism, being capable of effectively making use of communication propagation delay among the nodes to improve channel utilization rate and reduce collision among the nodes, thereby improving throughput of the network, reducing network average delay and improving quality of an underwater acoustic network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
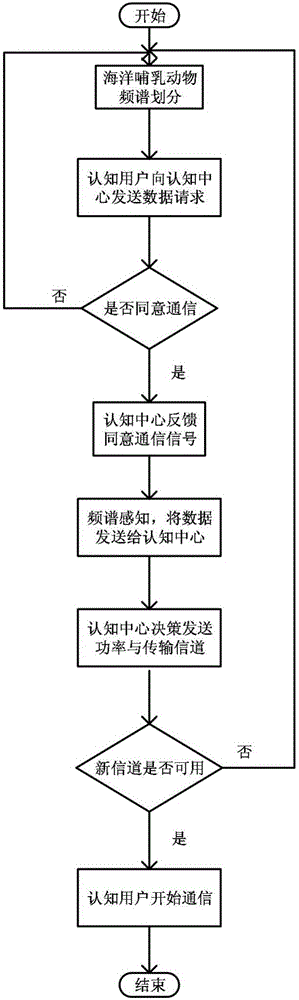
Biological-friendly cognitive underwater acoustic network communication method by efficiently utilizing spectrum resources
InactiveCN105898760AAvoid interferenceEfficient use ofSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionNetwork planningCognitive userFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a biological-friendly cognitive underwater acoustic network communication method by efficiently utilizing spectrum resources. The biological-friendly cognitive underwater acoustic network communication method comprises the following steps that: a primary user in UCANs is a marine mammal; a sensor node is a secondary user; a frequency band occupied by sound production of the marine mammal is used as an authorized frequency band; the authorized frequency band is divided into two parts; for the frequency band having high use frequency, the marine mammal has the prior use right; after receiving communication agreement information of a cognitive centre, a cognitive user performs spectrum sensing of a channel; the sending power is necessary to be lower than a hearing threshold of the marine mammal; the cognitive user performs communication according to distribution information of the cognitive centre; and spectrum sensing is still necessary to carry out in a communication process. According to the biological-friendly cognitive underwater acoustic network communication method disclosed by the invention, interference of communication of the sensor node to communication between marine mammals can be avoided; simultaneously, underwater spectrum resources are reasonably utilized and distributed; and high-efficiency utilization of the spectrum resources is realized based on a cognitive technology.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
MAC scheduling method of mesh underwater acoustic network
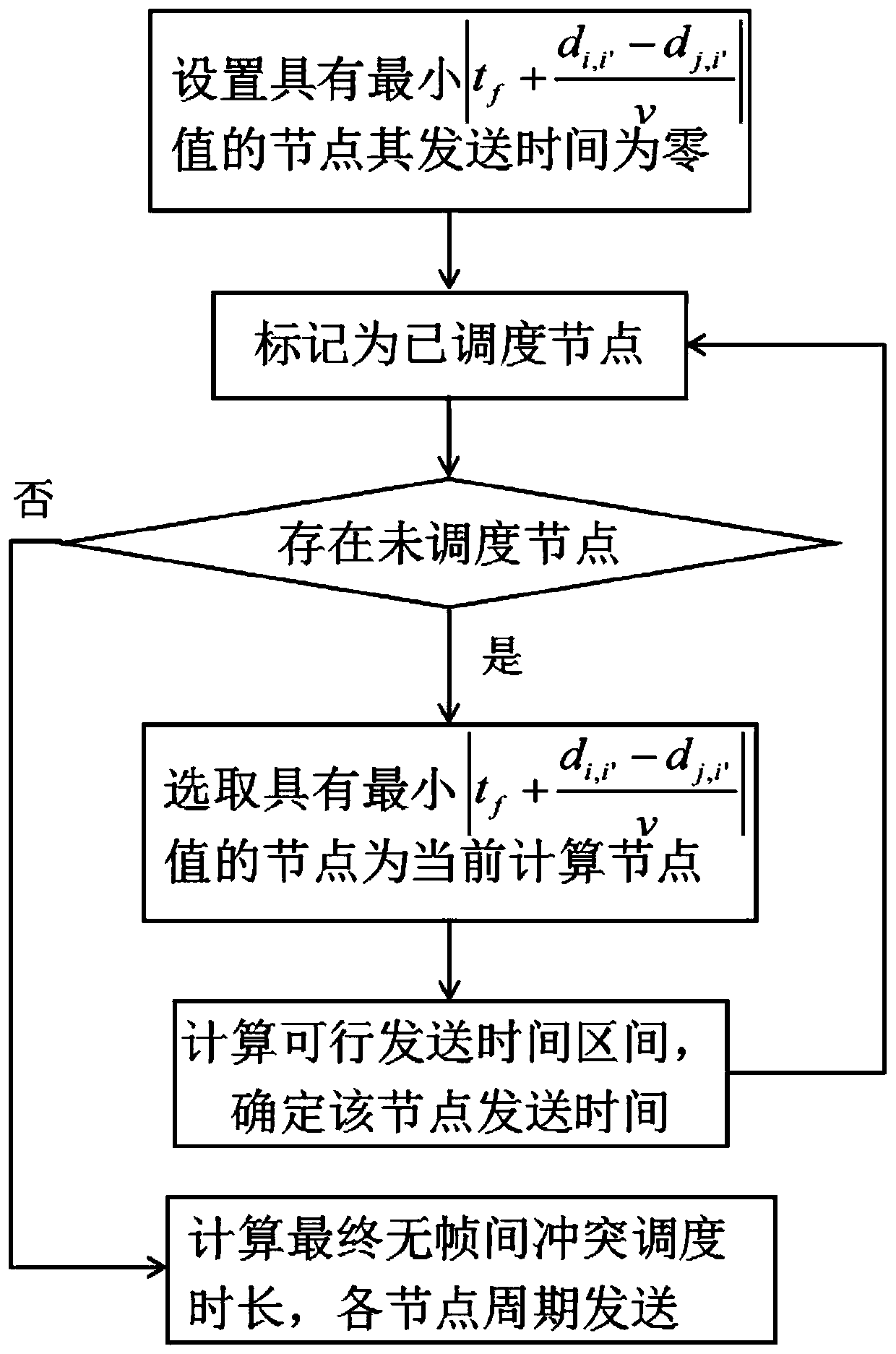
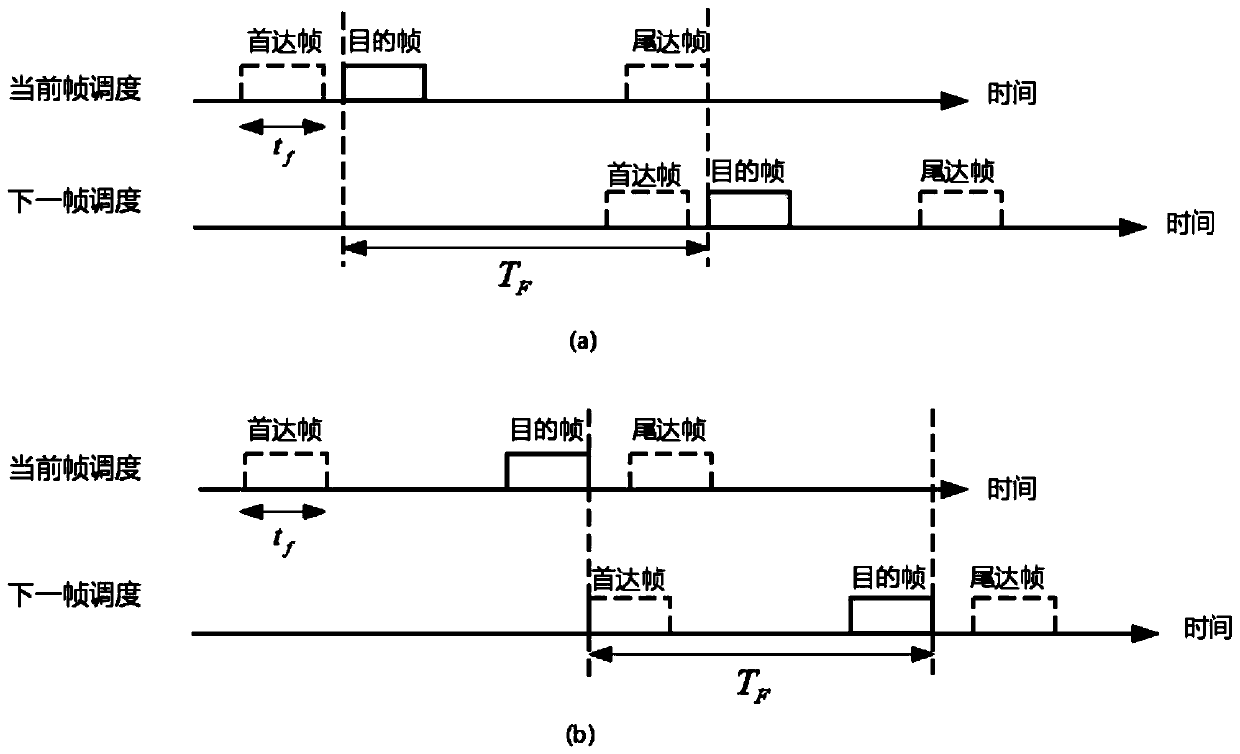
ActiveCN110691371ARaise priorityReduce overall dispatch timeNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionData packEngineering
The invention discloses an MAC (Media Access Control) scheduling method for a mesh underwater acoustic network, which comprises the following steps of: traversing all network nodes, calculating the minimum sending time difference of conflict-free transmission between each node and other nodes, sequentially arranging from small to large, and determining a scheduling sequence of each node; calculating the feasible sending time interval of each node, ensuring that the data packets sent by each sending end do not collide at the receiving end, and taking the minimum value of the feasible sending time interval as the sending time; and calculating the inter-frame conflict-free scheduling duration of each node, taking the maximum value of the scheduling duration of each node as the final scheduling duration, and enabling each node to perform sending by taking the final scheduling duration as a period. According to the invention, higher MAC scheduling capacity can be realized, and the maximum MAC scheduling capacity is approached to a greater extent.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Underwater acoustic cooperative communication routing method based on reinforcement learning Sarsa algorithm
ActiveCN112469103AReduce energy consumptionExtend the life cycleSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionHigh level techniquesAlgorithmEngineering
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic cooperative communication routing method based on a reinforcement learning Sarsa algorithm, and relates to an underwater acoustic network. The method comprises the steps: considering two aspects of reducing underwater acoustic data transmission energy consumption and complexity of a route selection algorithm, and providing route selection for an underwater acoustic multi-hop cooperative communication network by utilizing a reinforcement learning Sarsa algorithm according to an underwater acoustic communication energy consumption model; under the complex condition that a relay node and a cooperative node exist at the same time, rapidly carrying out the underwater acoustic multi-hop cooperative communication network route selection under the condition that the marine environment dynamically changes. A reinforcement learning algorithm is combined with cooperative communication, the operation complexity can be effectively reduced, the route selection stability is enhanced, and the transmission efficiency is improved, so that a cooperative route line enabling the total energy consumption of system transmission to be lowest is obtained, theenergy consumption of an underwater acoustic data transmission system is effectively reduced, and the life cycle of an underwater acoustic communication network is prolonged.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com