Underwater acoustic network routing method based on information importance and Q learning algorithm
A learning algorithm and underwater acoustic network technology, applied in the field of underwater acoustic network, can solve problems such as energy voids, long multi-hop transmission paths, and many dead relay nodes, and achieve the effects of shortening the range, reducing the number of explorations, and saving running time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0069] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
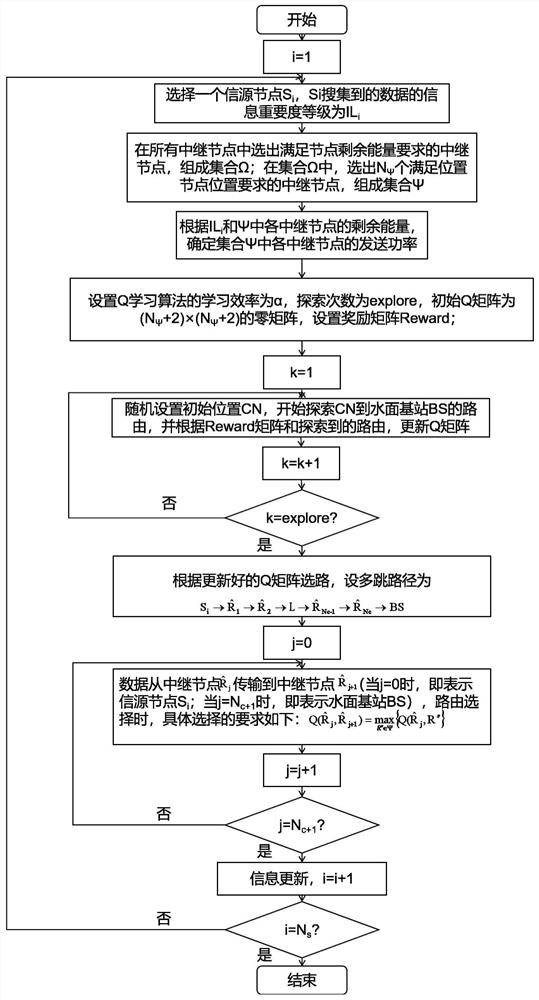
[0070] In the multi-diving underwater acoustic sensor network, the present invention takes the information importance level as the first priority condition and the remaining energy of the relay node as the second priority condition, and uses the Q learning algorithm to select the best route, on the one hand, it can balance the overall energy of the system consumption, avoiding the problem of energy holes, and prolonging the life cycle of the underwater acoustic communication network; on the other hand, it can ensure that important information can be transmitted to the surface base station in an accurate and timely manner. Specifically include the following steps:
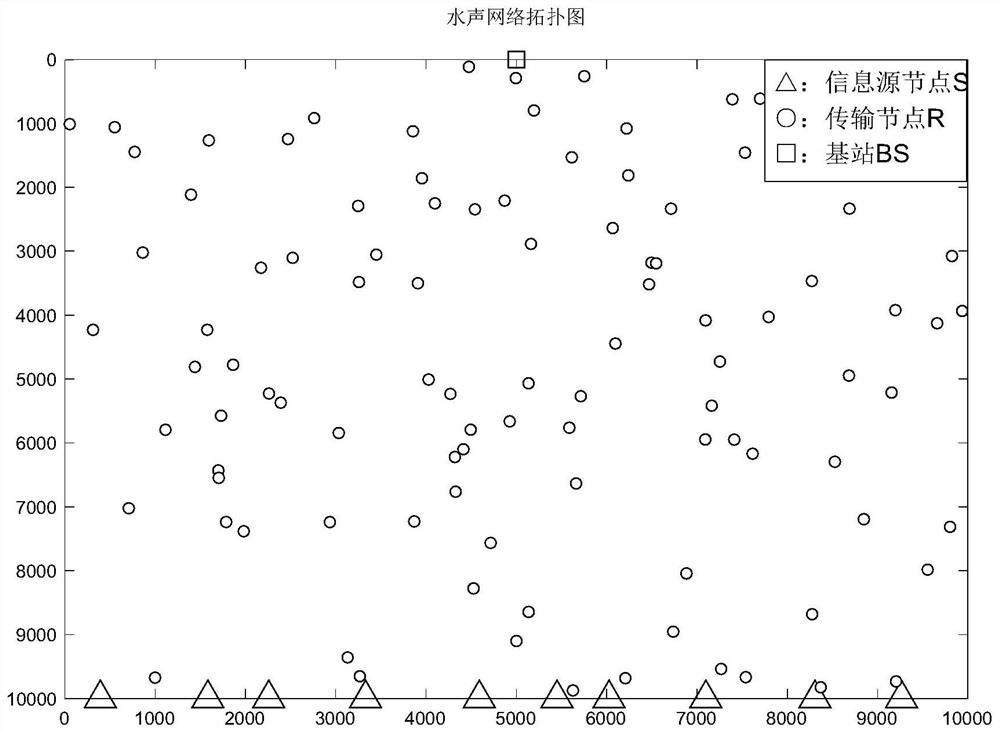
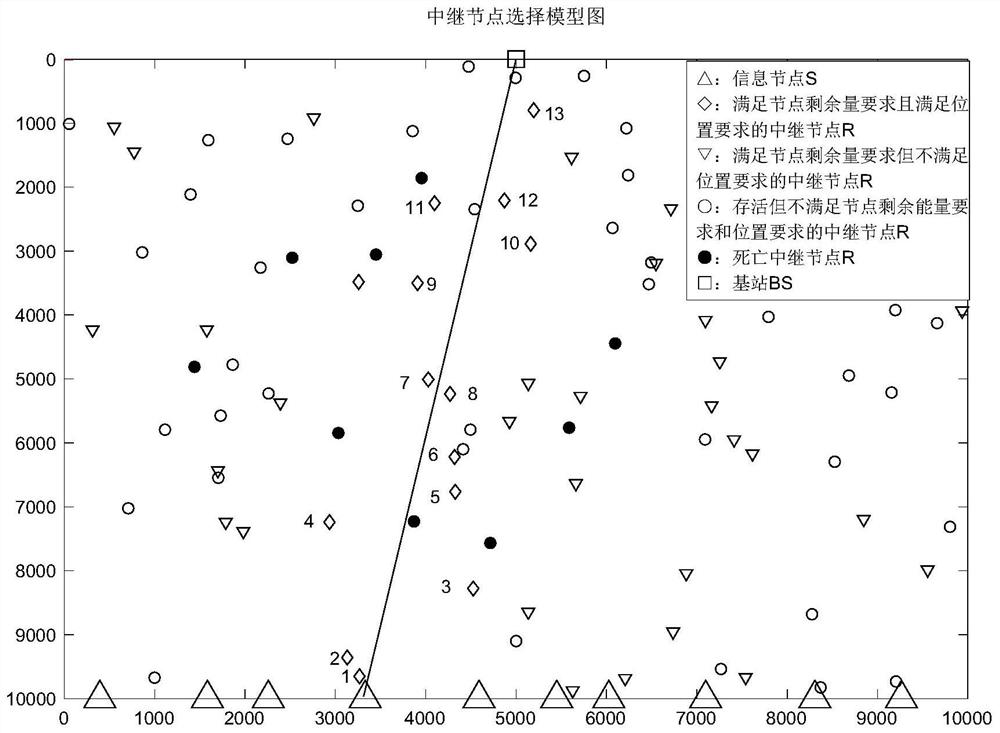
[0071] 1) In the underwater acoustic sensor network, including N s source node S i (i=1,2,...,N s ), N R relay node R i’ (i'=1,2,3,...,N R ) and 1 surface base station BS, su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com