A method for treating residual oil
A technology for residual oil and hydrotreating, which is applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, hydrotreating process, petroleum industry, etc. It can solve the problems of unfavorable device stable operation and unable to fundamentally change the pressure drop growth trend of the pre-reactor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
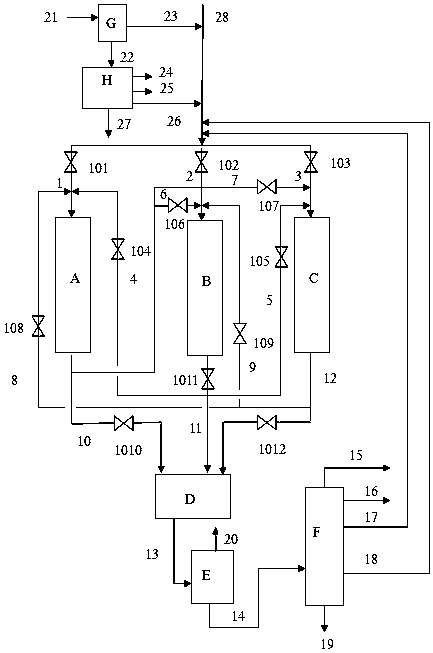
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
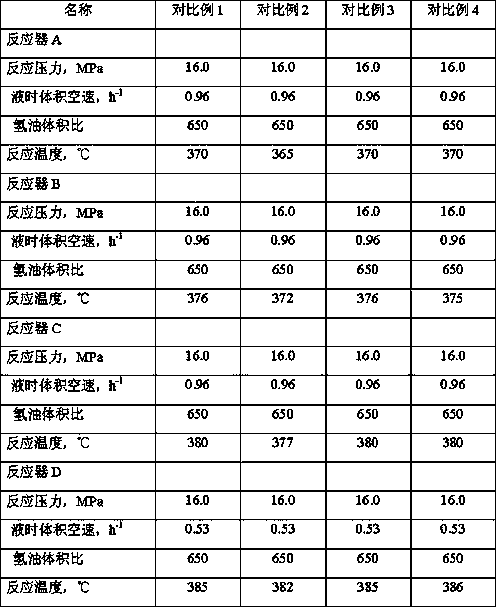
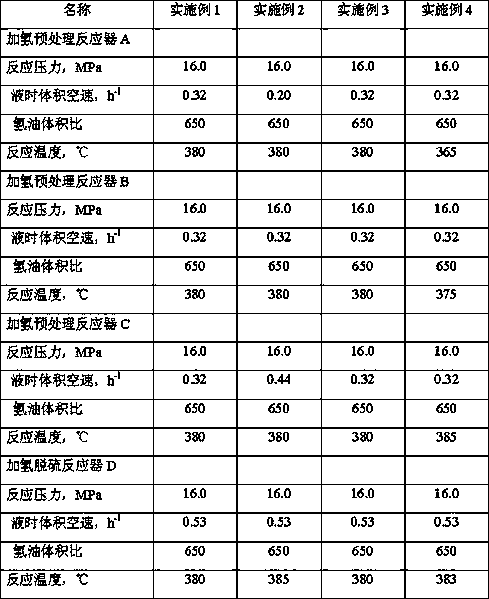
[0076] The raw material A (see Table 1 for properties) described in Example 1 was used to obtain light fractions and heavy fractions through separation, and the cut point was 600°C. The heavy fraction is processed through a coking unit, and then separated to obtain coked gasoline, coked diesel oil, coked wax oil and coke. The operating conditions of coking are: reaction temperature 505°C, pressure 170000Pa.
[0077] The coker wax oil and light fraction, 50% of the catalytic cracking diesel oil recycled from the catalytic cracking unit and all the catalytic cracking heavy cycle oil are sent to the hydrogenation pretreatment reaction zone. The total catalyst loading, feed properties and feed amount of the hydropretreatment reactor A, hydrogenation pretreatment reactor B, and hydrogenation pretreatment reactor C are exactly the same, and the hydrogenation pretreatment reactor A, Catalysts in Hydrogenation Pretreatment Reactor B, Hydrogenation Pretreatment Reactor C, and Hydrotre...
Embodiment 2
[0079] In Example 2, the properties of the raw material B used are shown in Table 1. After separation, the light fraction and the heavy fraction were obtained, and the cut point was 610°C. The heavy fraction is processed through a coking unit, and then separated to obtain coked gasoline, coked diesel oil, coked wax oil and coke. The operating conditions of coking are: reaction temperature 505°C, pressure 170000Pa.
[0080] Send coker wax oil and light fraction, 30% catalytic cracked diesel and all catalytic cracked heavy cycle oil to the hydrogenation pretreatment reaction zone. The total catalyst loading and feed properties of the hydrogenation pretreatment reactor A, hydrogenation pretreatment reactor B, and hydrogenation pretreatment reactor C are exactly the same, and the feed space velocity is different. The hydrogenation pretreatment reactor The hourly volume space velocity of liquid A is 0.20h -1 , the hourly volumetric space velocity of liquid B in the hydrogenation ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] In Example 3, raw materials A, B, and C were separated to obtain light fraction and heavy fraction, and the cut point was 600°C. The heavy fractions of raw materials A, B, and C are respectively processed through a coking unit, and then separated to obtain coked gasoline, coked diesel oil, coked wax oil and coke. The operating conditions of coking are: reaction temperature 505°C, pressure 170000Pa.
[0083] The hydrogenation pretreatment reactor A adopts the light fraction of raw material A and the coker gas oil of A, the hydrogenation pretreatment reactor B adopts the light fraction of raw material B and the coker gas oil of B, and the hydrogenation pretreatment reactor C adopts Feedstock C Light Ends and C Coker Wax Oil. The feed amount of described hydrogenation pretreatment reactor A, hydrogenation pretreatment reactor B, hydrogenation pretreatment reactor C is the same, and described hydrogenation pretreatment reactor A, hydrogenation pretreatment reactor B, hydro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com