Tilting bush thrust bearing with complex slip surface
A thrust bearing and sliding technology, applied in the direction of bearing components, shafts and bearings, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of tilting pad thrust bearing failure, not paying attention to pressure center offset, and inability to use tilting pad thrust bearings, etc. Achieve the effect of avoiding failure, high bearing capacity and low friction torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
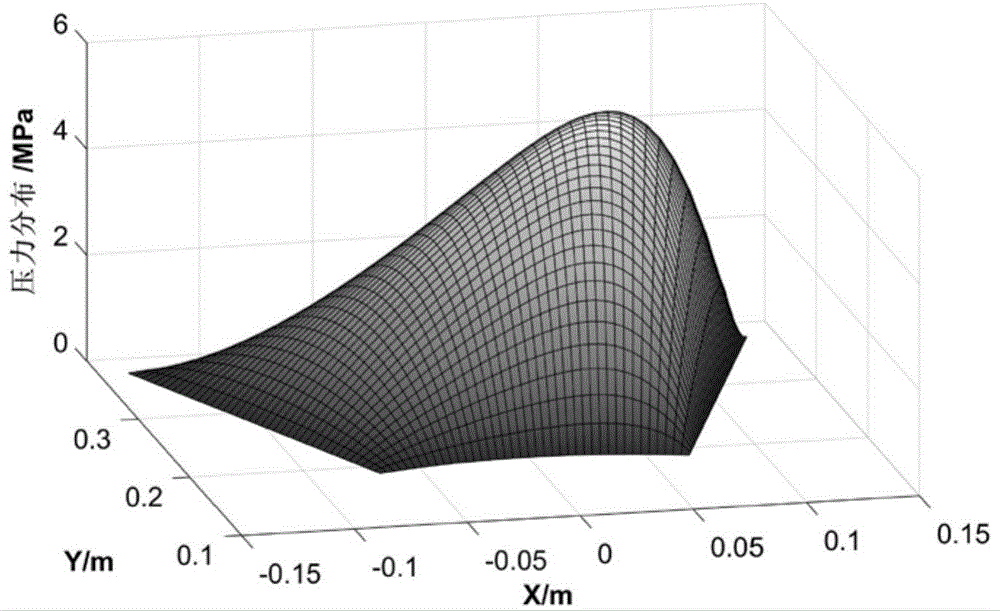
[0021] The thrust bearing optimized in this example has an outer diameter of 800 mm, an inner diameter of 400 mm, a wrap angle of 40°, a radial branching coefficient of 0.524, a circumferential branching coefficient of 0.609, a normal working speed of 1500 rpm, and an average working pressure of 0.544 MPa.
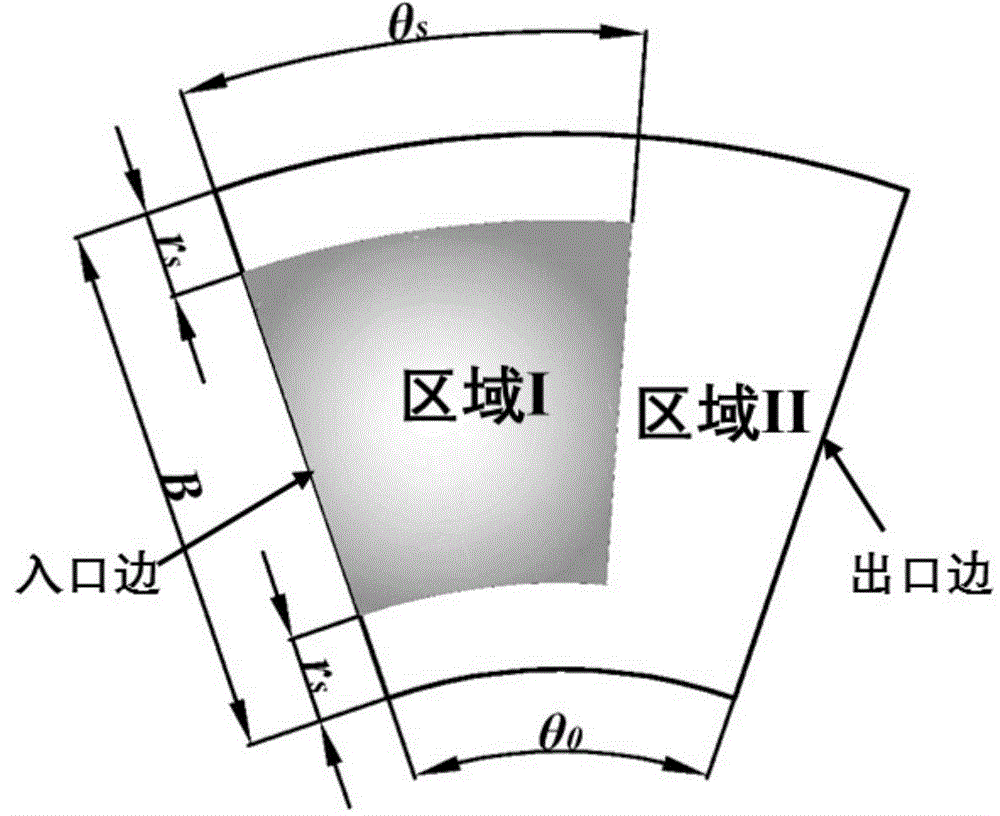
[0022] like figure 1 As shown in , the upper surface of the tile is divided into two regions: region I near the entrance region and the remaining region II, where region I is treated as a hydrophobic surface, which has a lower ultimate shear stress and is prone to interface Slip; area II is surface-treated as a hydrophilic surface, which has a higher ultimate shear stress and is less prone to interfacial slip.
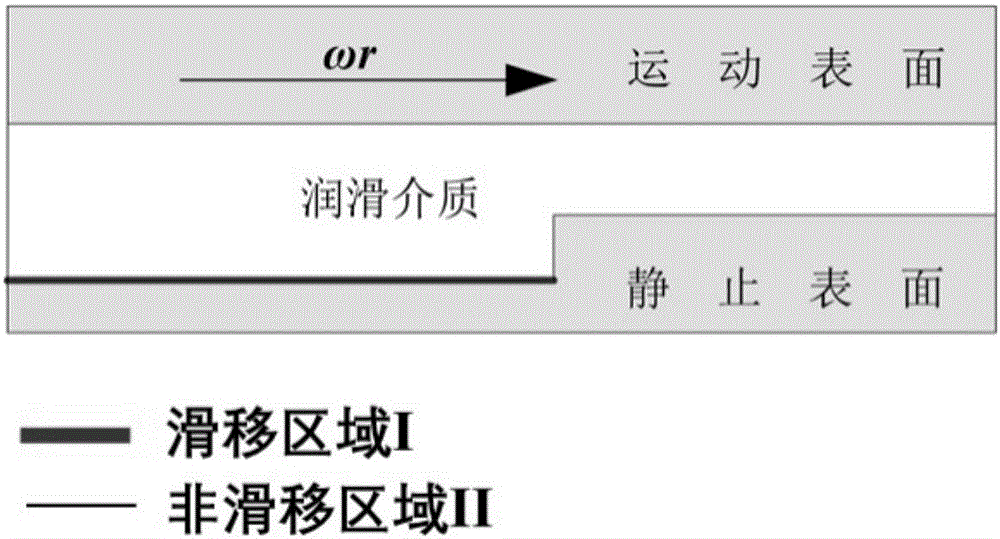
[0023] like figure 2 As shown, the height of region I is lower than that of region II. In this embodiment, the height of region I is 40 μm lower than that of region II, so as to protect the hydrophobic surface in region I from abrasion caused by the start and st...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The outer diameter of the optimized thrust bearing in this example is 800 mm, the inner diameter is 400 mm, the wrap angle is 40°, the radial branching coefficient is 0.524, the circumferential branching coefficient is 0.5, and the pads are pre-processed with 25 μm arc convex The normal working speed is 1500rpm, and the average working pressure is 0.544MPa.
[0029] like figure 1 As shown in , the upper surface of the tile is divided into two regions: region I near the entrance region and the remaining region II, where region I is treated as a hydrophobic surface, which has a lower ultimate shear stress and is prone to interface Slip; area II is surface-treated as a hydrophilic surface, which has a higher ultimate shear stress and is less prone to interfacial slip.
[0030] like figure 2 As shown, the height of region I is lower than that of region II. In this embodiment, the height of region I is 40 μm lower than that of region II, so as to protect the hydrophobic s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com