Gradient vector analysis-based retinal image micro-aneurysm automatic detection and identification method
A gradient vector and automatic detection technology, which is applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., to achieve easy operation and improve the effect of detection and recognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
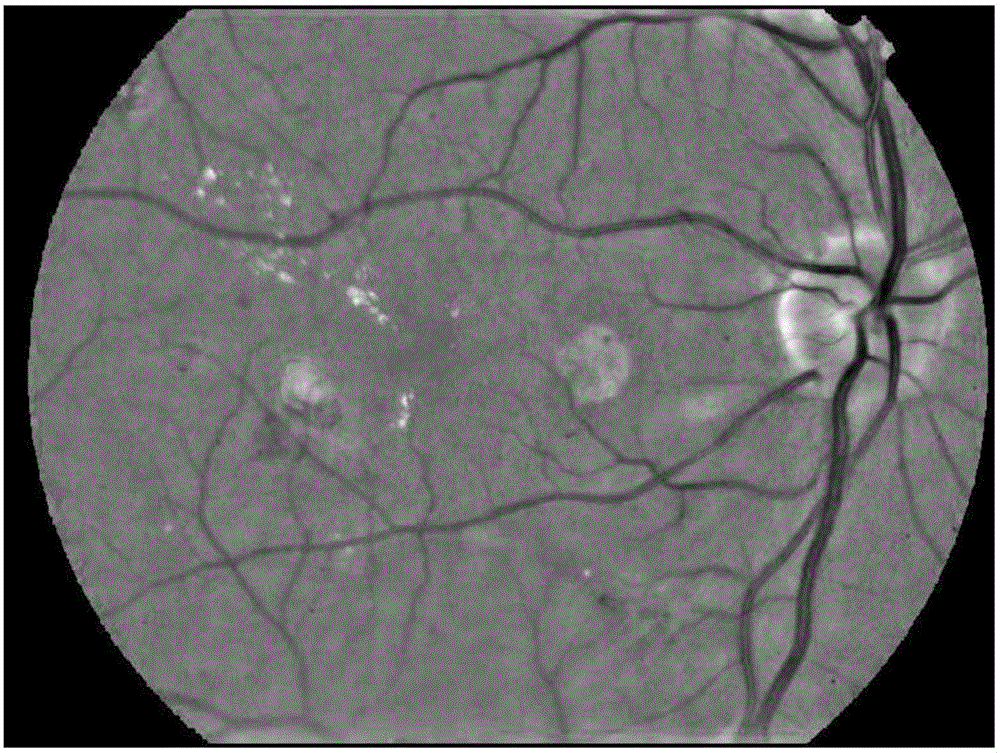
[0026] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment discloses a method for automatic detection and recognition of retinal image microaneurysms based on gradient vector analysis. The method includes the following steps:
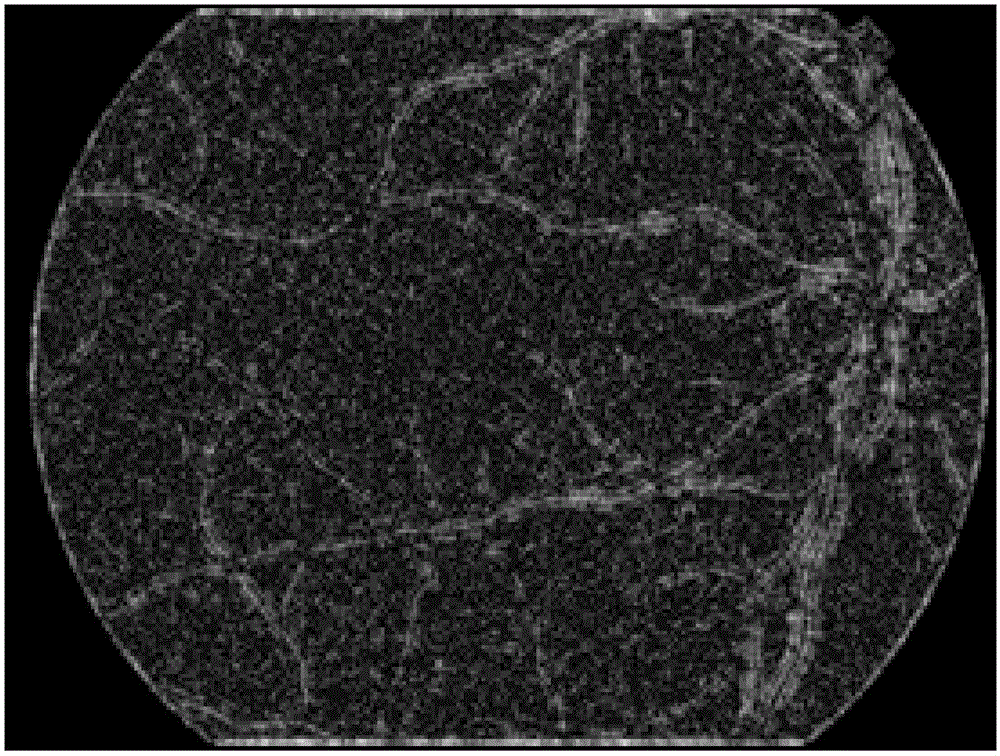
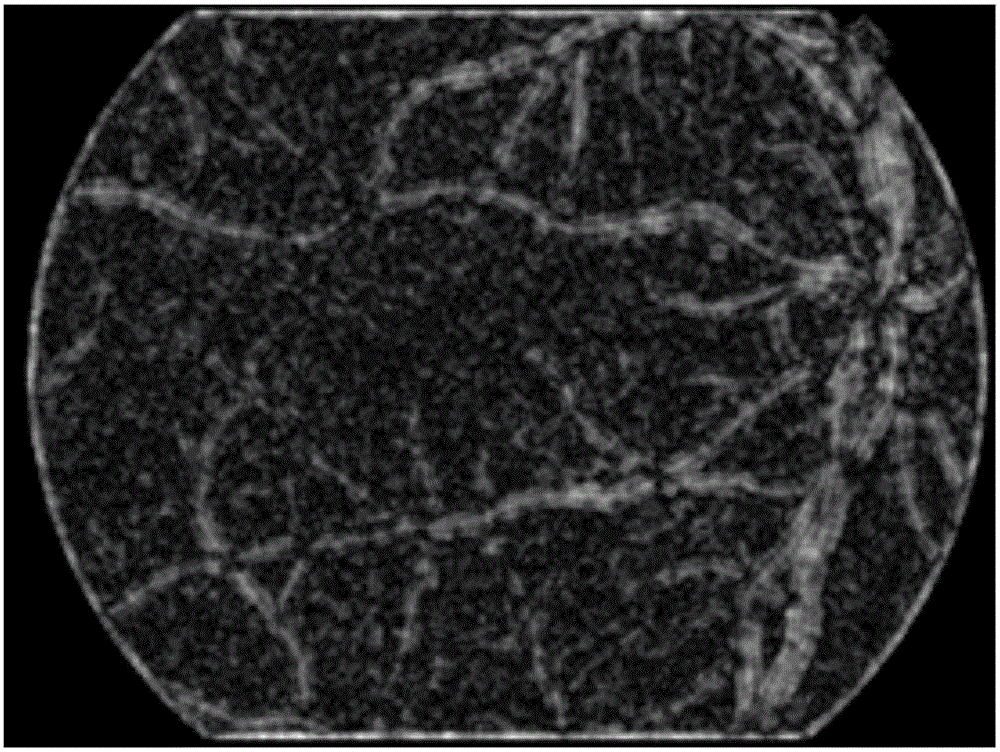
[0027] Step 1: Candidate microaneurysm detection; first microaneurysm extraction, the microaneurysm extraction mainly includes three steps of vessel removal, candidate microaneurysm location and segmentation;
[0028] Step 2: Extraction of candidate microaneurysm features;
[0029] Step 3: Microaneurysm identification.
[0030] Considering that the microaneurysm has the greatest contrast with the background in the green channel of the retinal image, the green channel will be used as the input image for subsequent operations. Before extracting candidate microaneurysms, in order to remove the noise of the fundus image while preserving the edge of the arteriole, the image was smoothed by edge-preserving filtering based on the weighted least squares framework. The sha...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific embodiment two: the method for automatic detection and recognition of retinal image microaneurysms based on gradient vector analysis described in specific embodiment one, in step one, the described blood vessel removal method is: by analyzing the different gradients between microaneurysms and blood vessels Distribution characteristics, to achieve the removal of blood vessels, and retain the real microaneurysms while removing blood vessels; the gradient vector x, y components are regarded as two random variables, by calculating and analyzing the correlation of all gradient vector components in the target area Variance matrix; for retinal vessels, the eigenvalues of the gradient component covariance matrix have a dominant eigenvalue; while for arterioles, the corresponding eigenvalues are approximately equal.
[0032] The capillaries in which microaneurysms are located are not visible in fundus retinal images; therefore, microaneurysms are usually isolated fro...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific embodiment three: the method for automatic detection and identification of retinal micro-targets (microaneurysms) based on gradient vector analysis described in specific embodiment one, in step one, the method for the location of candidate microaneurysms is: by calculating The second derivatives of candidate microaneurysms in multiple directions can be used to precisely locate microaneurysms.
[0041] After removing blood vessels, there will still be some tiny blood vessel fragments, background noise, and other fundus dark circular structures. Next, the present invention will locate candidate microaneurysms in the blood vessel removal image, while suppressing the appearance of non-microaneurysms. Considering that the above-mentioned non-microaneurysms and microaneurysms have similar gray values, it is not feasible to directly use gray-scale information to locate candidate microaneurysms.
[0042] Because the microaneurysm has a Gaussian shape distribution in g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com