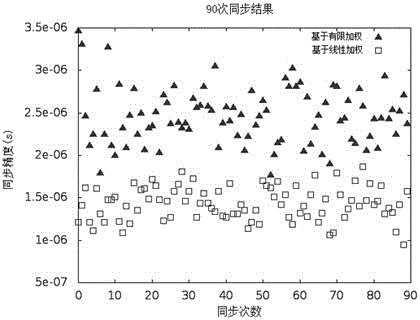
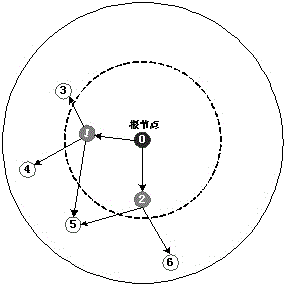
Time synchronization method based on linear weighted least square method
A least-squares, linear weighting technique, applied in time-division multiplexing systems, electrical components, multiplexing communications, etc., can solve problems such as unreasonable observations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be further elaborated below by describing a preferred specific embodiment in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
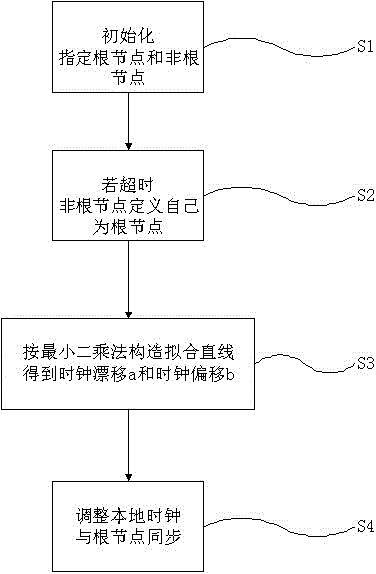
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, a time synchronization method based on the linear weighted least squares method includes the following steps:
[0038] S1. During initialization, a node is arbitrarily selected as the root node; the root node periodically broadcasts synchronization data packets, and the synchronization data packets include the time stamp TimeStamp of the MAC layer, the root node identification mark RootID, and the sequence number SeqNum of the synchronization data packets; The rest of the nodes are non-root nodes, and the non-root nodes record the number of the root node they belong to in the root node record myRootID, and their time stamp TimeStamp is synchronized with the time stamp TimeStamp of the root node they belong to.
[0039] S2. The non-root node starts a timeout timer when the networ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com