Lead-acid battery quick charging control method, variable-current control circuit and quick charging device
A lead-acid battery and fast charging technology, which is applied to battery circuit devices, secondary battery charging/discharging, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to precisely adapt to individuals, large deviations in battery acceptance capacity, and different degrees of inadaptability. Achieve the effects of improving charging speed and charging efficiency, improving current acceptance capacity, and flexible combination of functional circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
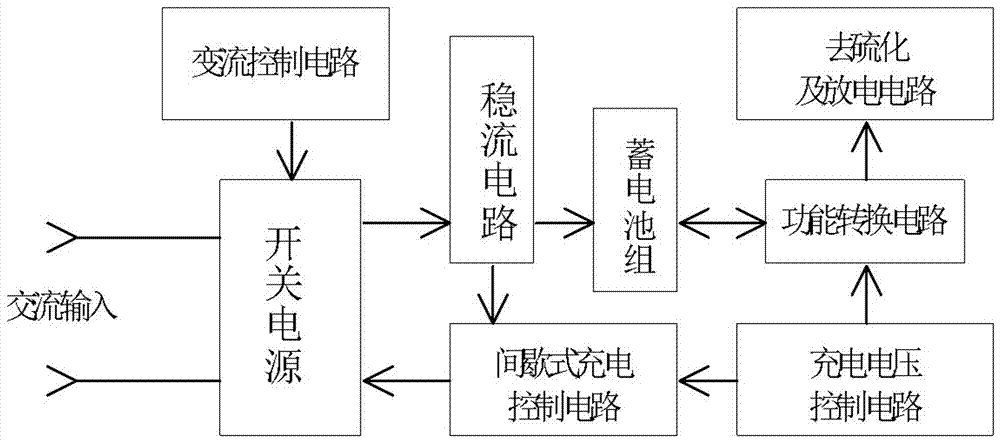
[0039] The fast charging control method of the lead-acid storage battery of the present invention, the realization mode comprises the following several stages:
[0040] 1) At the beginning of charging, the first is the charging stage of high-current variable current output:
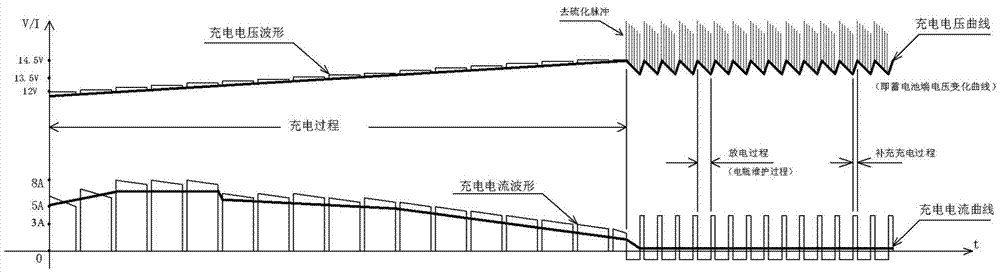
[0041] Adopt the variable current control circuit, set the maximum charging current based on the maximum current acceptance capacity of the battery during charging, and set the reference value of the voltage rising rate based on the voltage rising speed at the maximum charging current of the battery; detect the terminal voltage of the battery in real time , compare the measured rising speed of the battery terminal voltage with the set reference value of the voltage rising rate, and then perform segmental delay adjustment or linearly adjust the charging current, so that the charging current can always track and keep in sync with the immediate current acceptance capacity of the battery;
[0042] 2) When the...
Embodiment 2
[0047] see figure 2 The difference between the fast charging control method of the lead-acid battery in this embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the stage of charging with large current variable current output: when the rising rate of the battery terminal voltage is less than the set reference value of the voltage rising rate, the variable The current control circuit charges the battery with the maximum charging current;
[0048] When the rising rate of the battery terminal voltage is greater than the set reference value of the voltage rising rate, the charging current will be lowered by one gear through the variable current control circuit, and this state will be delayed, and the charging current will return to the original maximum after the delay is over. Current, if the rising speed of the terminal voltage of the battery is no longer greater than the reference rising rate, continue to charge with a high current, and if the rising speed of the terminal voltage is...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The difference between the fast charging control method of the lead-acid battery in this embodiment and the embodiment 1 or 2 is: further, when the terminal voltage of the battery rises to the highest voltage, the charging mode is switched to supplementary charging or the battery is maintained. In this embodiment, the micro-charging and discharging mode is used to supplement charge, activate and maintain the activity of the storage battery, that is, to maintain the storage battery by charging with a high current for a short time and discharging with a low current for a long time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com