Nonlinear coupled adaptive control method for multi-rotationally excited translational oscillator systems
A nonlinear coupling and adaptive control technology, applied in adaptive control, general control system, control/adjustment system, etc., can solve problems such as system chattering, unknown component size, equipment damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
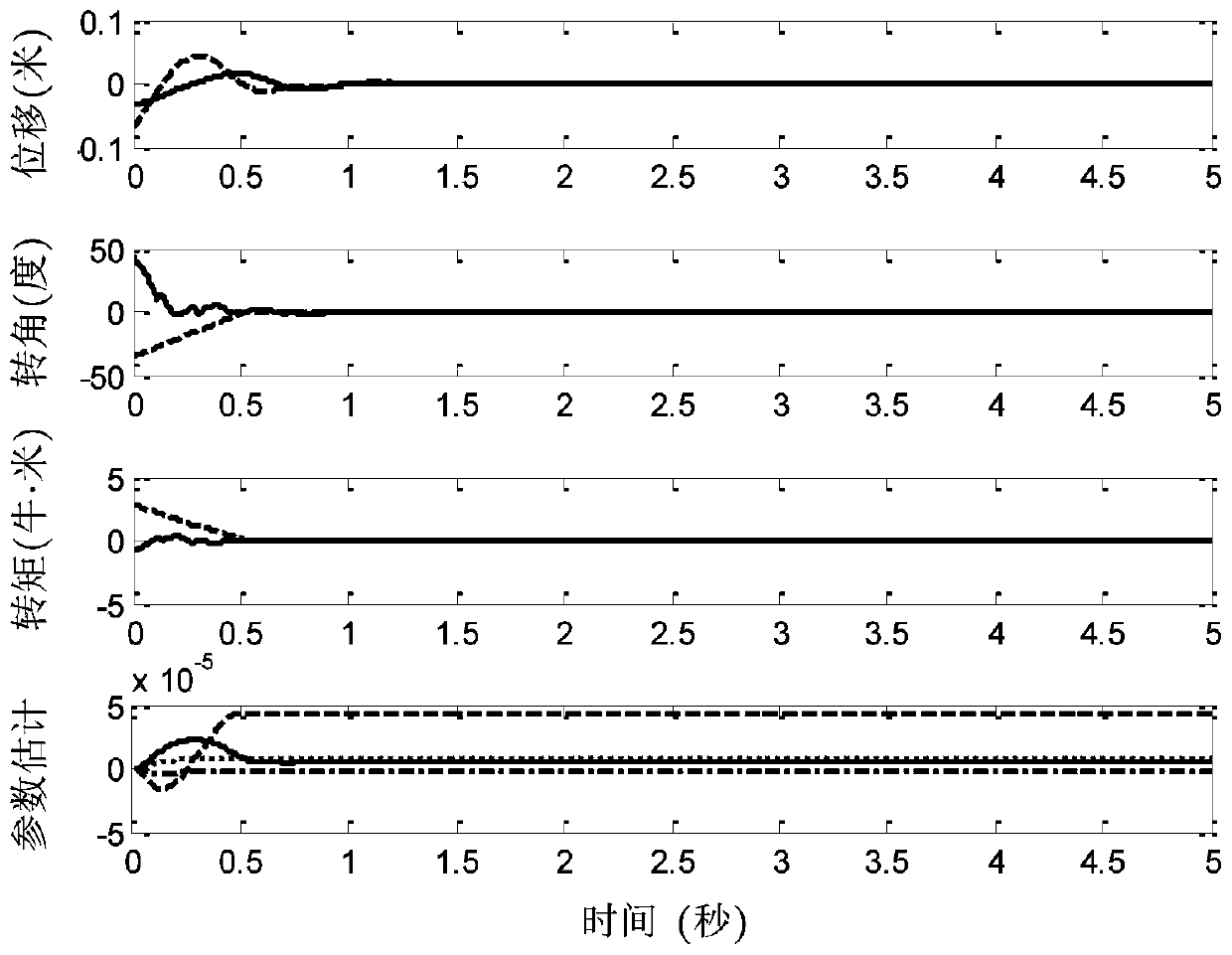
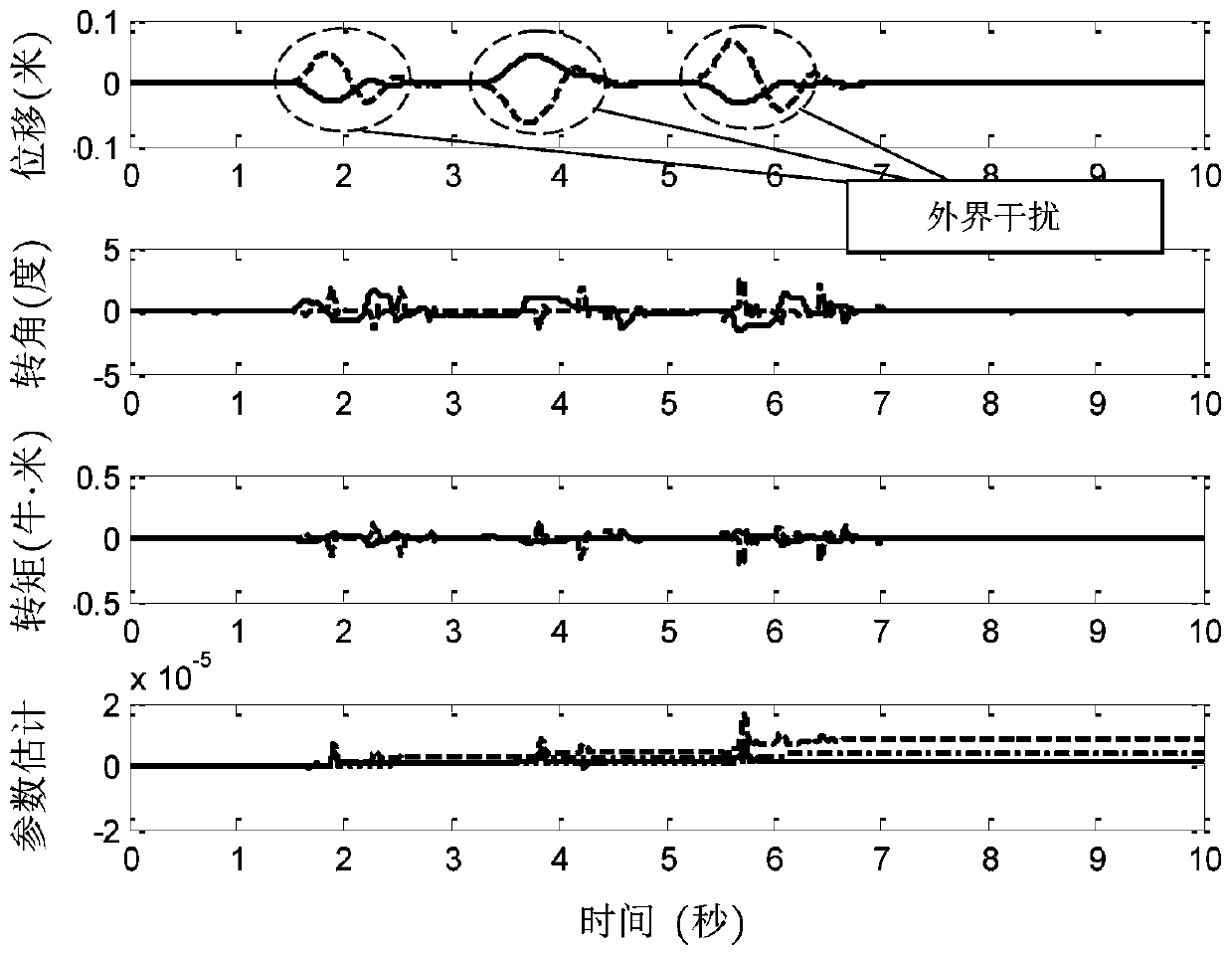
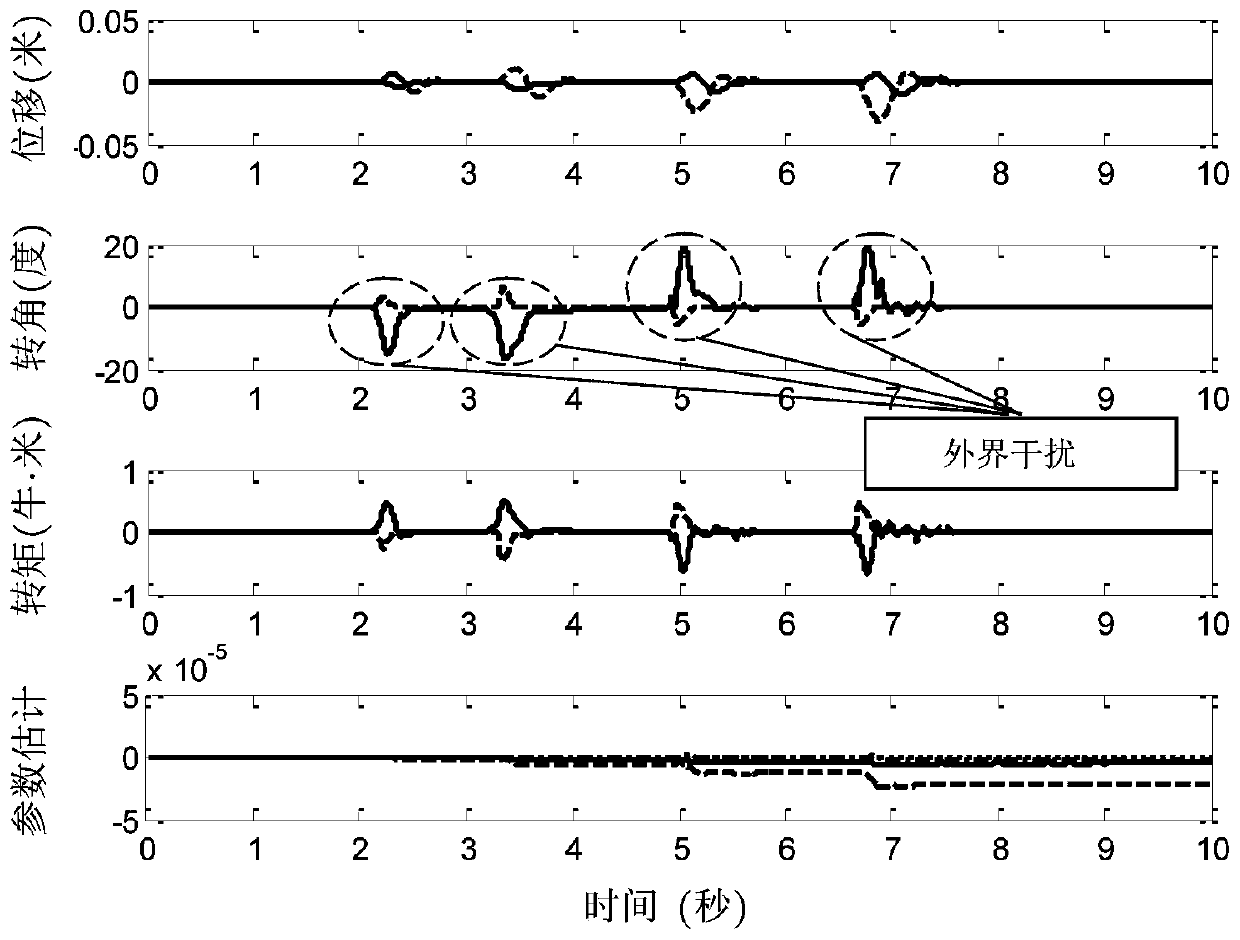
[0116] 1. Description of experimental steps
[0117] Section 1.1. Determining control objectives
[0118] The position vector of each TORA selected is The target position vector is where, for the i-th TORA in a multi-TORA system, x i is the displacement of the trolley, is the trolley speed, θ i is the rotor rotation angle, is the rotational angular velocity of the rotor, θ di is the target angle of the rotor, and the total number of single TORAs in the system is N, then i=1,2,...,N.
[0119] Section 1.2, define error signal, parameter vector and measurable vector
[0120] Define the rotor swing angle error e of each TORA in a multi-TORA system θi (t) for
[0121] e θi = θ di -θ i (4)
[0122] Among them, θ i is the rotor rotation angle, θ di is the target angle of the rotor. define unknown parameter vector measurable vector Among them, the symbol " "Represents the matrix / vector transpose, the element ω in the vector i1 ,ω i2 ,ω i3 ,y i1 ,y i2 ,y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com