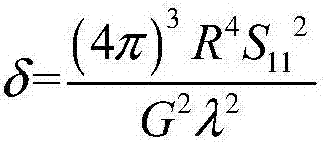Method for measuring radar cross section by using extrapolation method
A radar scattering and cross-sectional area technology, applied in the radar field, can solve the problems of lack of RCS measurement system calibration information, large measurement result uncertainty, and small electromagnetic wave reflection, etc., to achieve rich RCS measurement information, comprehensive measurement result information, and small measurement The effect of uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
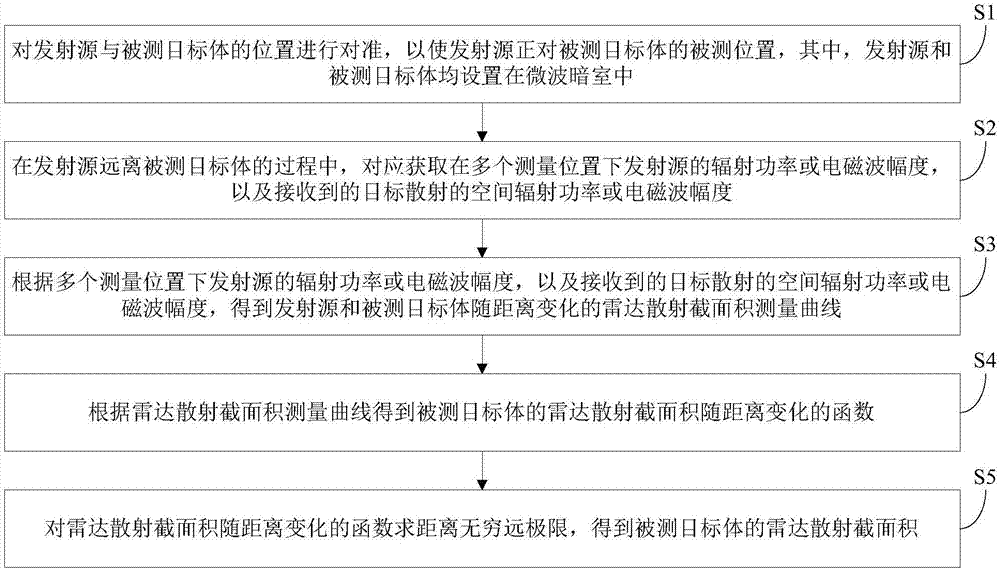
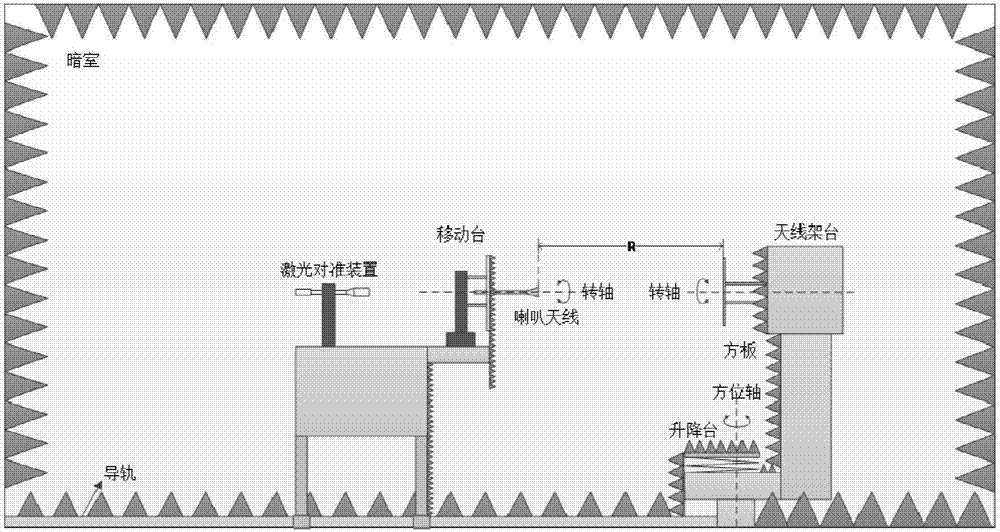
[0019] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below. Examples of the embodiments are shown in the accompanying drawings, in which the same or similar reference numerals indicate the same or similar elements or elements with the same or similar functions. The embodiments described below with reference to the drawings are exemplary, and are only used to explain the present invention, but should not be understood as limiting the present invention.
[0020] In the description of the present invention, it should be understood that the terms "center", "longitudinal", "transverse", "upper", "lower", "front", "rear", "left", "right", " The orientation or positional relationship indicated by "vertical", "horizontal", "top", "bottom", "inner", "outer" etc. is based on the orientation or positional relationship shown in the drawings, and is only for the convenience of describing the present invention and The description is simplified, rather than indicating or impl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com