Method and device for biologically treating organic wastewater
A biological treatment, waste water technology, applied in the direction of sustainable biological treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain dissolution efficiency, and achieve the prevention of excessive adhesion and efficient biological treatment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
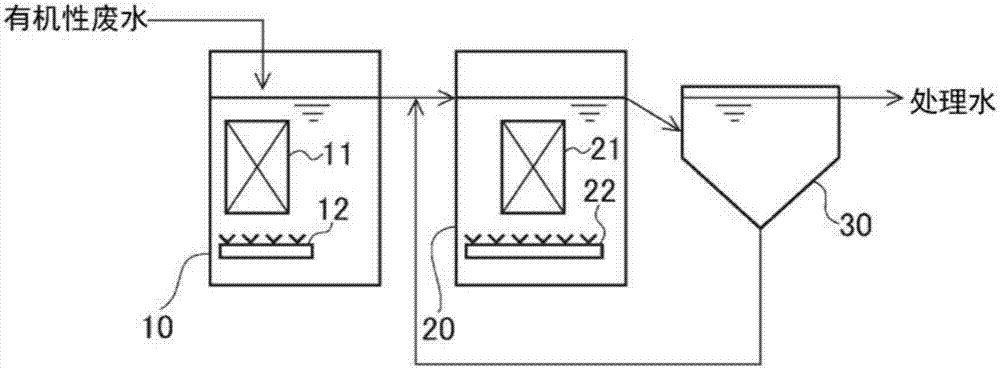
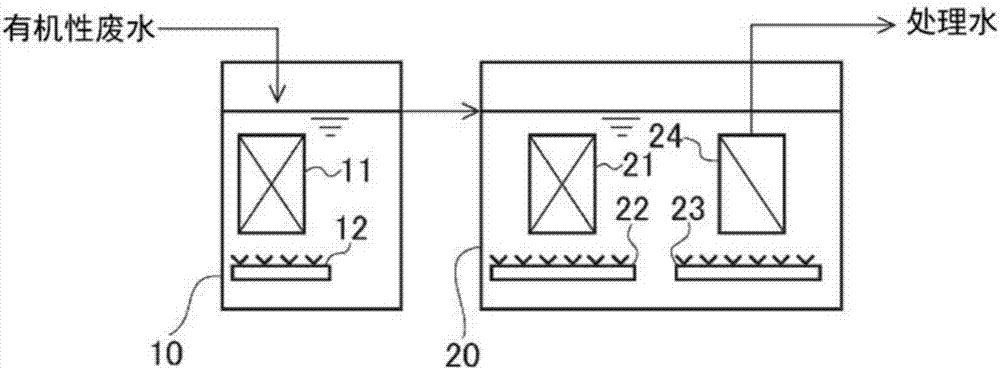
[0085] use image 3 The shown apparatus having the first biological treatment tank 10 and the second biological treatment tank 20 (equipped with a UF membrane separation device 24 ) is used to treat organic waste water. will contain COD Cr : 1000mg / L, BOD: 640mg / L artificial matrix aqueous solution prepared as simulated wastewater of easily decomposable sugary wastewater as organic wastewater (raw water).
[0086] The treatment conditions of each biological treatment tank were set as follows. The overall BOD volume load of the device is 0.73kg-BOD / m 3 / day, the overall HRT of the device is 21h.
[0087]
[0088] Capacity 105L
[0089] DO: 0.5mg / L
[0090] BOD volume load: 3.85kg-BOD / m 3 / sky
[0091] HRT: 4h
[0092] pH: 7.0
[0093]
[0094] Capacity 450L
[0095] DO: 4mg / L
[0096] Dissolved TOC sludge load: 0.01kg-dissolved TOC / kg-MLSS / day
[0097] HRT: 17h
[0098] pH: 7.0
[0099] SRT: 30 days
[0100] In the first and second biological treatment tanks, i...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Raw water was treated in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a polyethylene plate-shaped carrier (the same size as in Example 1) was used as a carrier. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0133] [embodiment 3, comparative example 5,6]
[0134] Raw water was treated in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the amount of aeration was changed (increased) as shown in Table 4. The results are shown in Table 4.
[0135] As shown in Table 4, it was confirmed that the aeration ratio (the aeration amount of the first biological treatment tank / the aeration amount of the second biological treatment tank) was preferably 1.5 to 3 times. In addition, although the aeration rate ratio of the comparative example 6 was 3 times, since the aeration rate of the 1st biological treatment tank was too much, sludge did not adhere to the 1st fixed bed, and it was difficult to treat.
[0136] [Table 4]
[0137] ◆Influence of aeration volume ratio
[0138]
[0139] (bubble diameter = 1mm)
[0140] [Example 4,5, Comparative Example 7,8]
[0141] Raw water was treated in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the distance between carriers was set as shown in Table 5. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com