Omnidirectional chipless RFID tag based on angle positioning
An RFID tag and angle positioning technology, applied in the field of the Internet of Things, can solve the problems of polarization mismatch, difficult to adapt to the complex and changeable environmental requirements of the tag position, etc., and achieve the effect of changing the angle sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
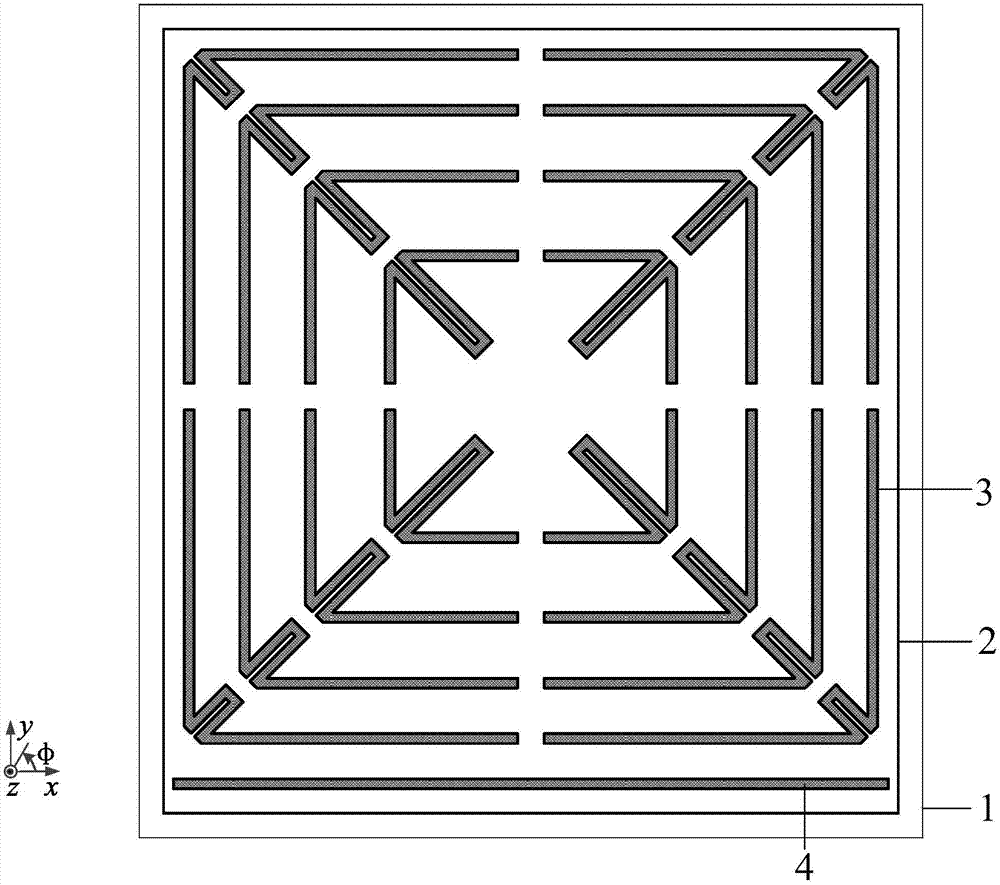
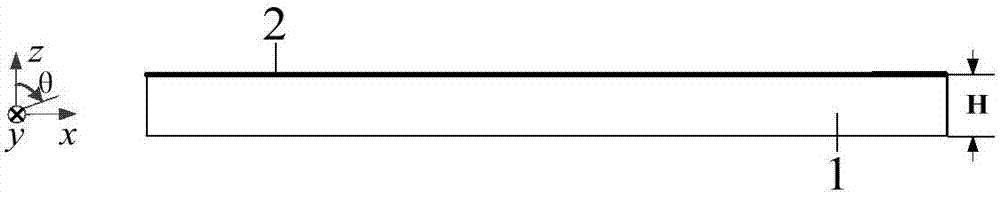
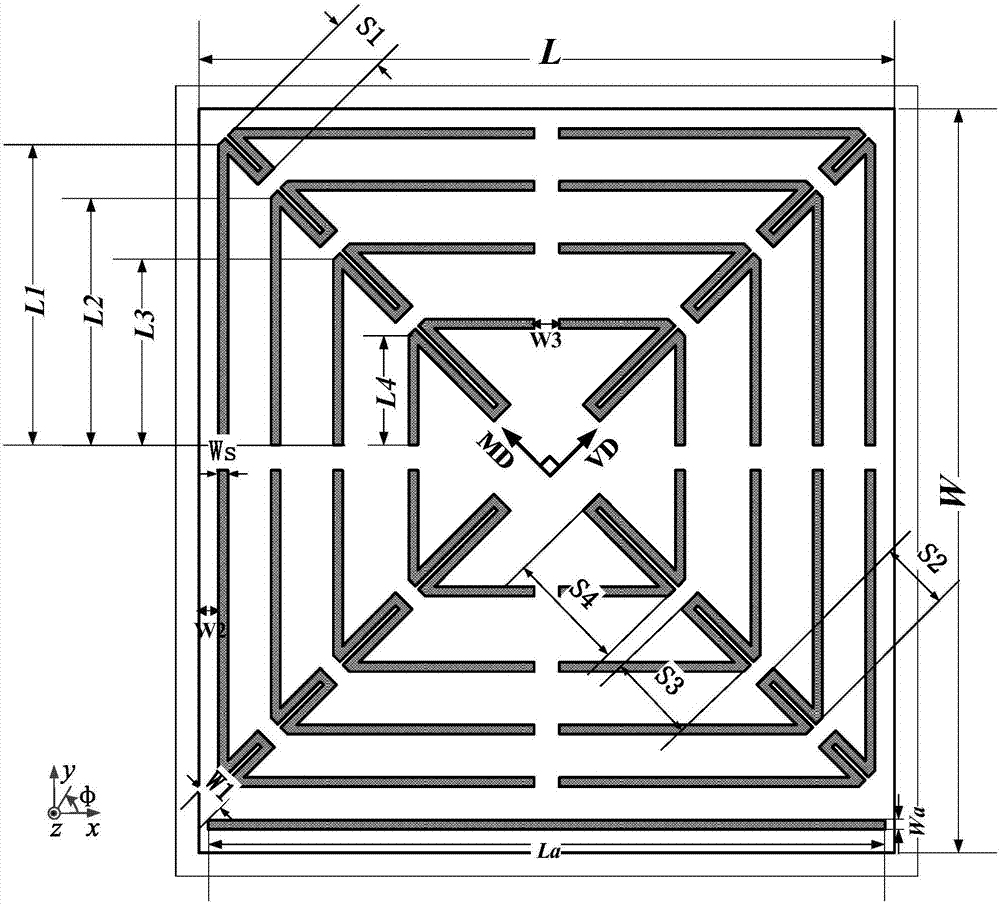
[0035] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, an omnidirectional chipless RFID tag based on angle positioning, the tag is a symmetrical structure, including an antenna radiation patch structure 2 and a dielectric substrate structure 1, and the antenna radiation patch structure is located on the dielectric substrate structure On the surface, the antenna radiation patch structure is composed of a rectangular patch, and the rectangular patch is printed with an upper coding unit 3 and a lower positioning unit 4, and the lower positioning unit is located directly below the upper coding unit.
[0036] The upper coding unit is composed of four groups of arrow-shaped slots with the same structural size, and the four groups are respectively slotted symmetrically along the main and auxiliary diagonals. Adjacent two groups of arrow-shaped grooves are separated by a certain distance, and the four groups are respectively located at the four corners of the rectangular patch, of which two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com