A PSF Inverse Transform Method Based on Parallel Lu Decomposition
An inverse transformation and block technology, applied in complex mathematical operations and other directions, can solve problems such as time-consuming, difficult to obtain results, serious time consumption, etc., to reduce time consumption, high memory reuse rate, parallelism high degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and in combination with preferred embodiments.
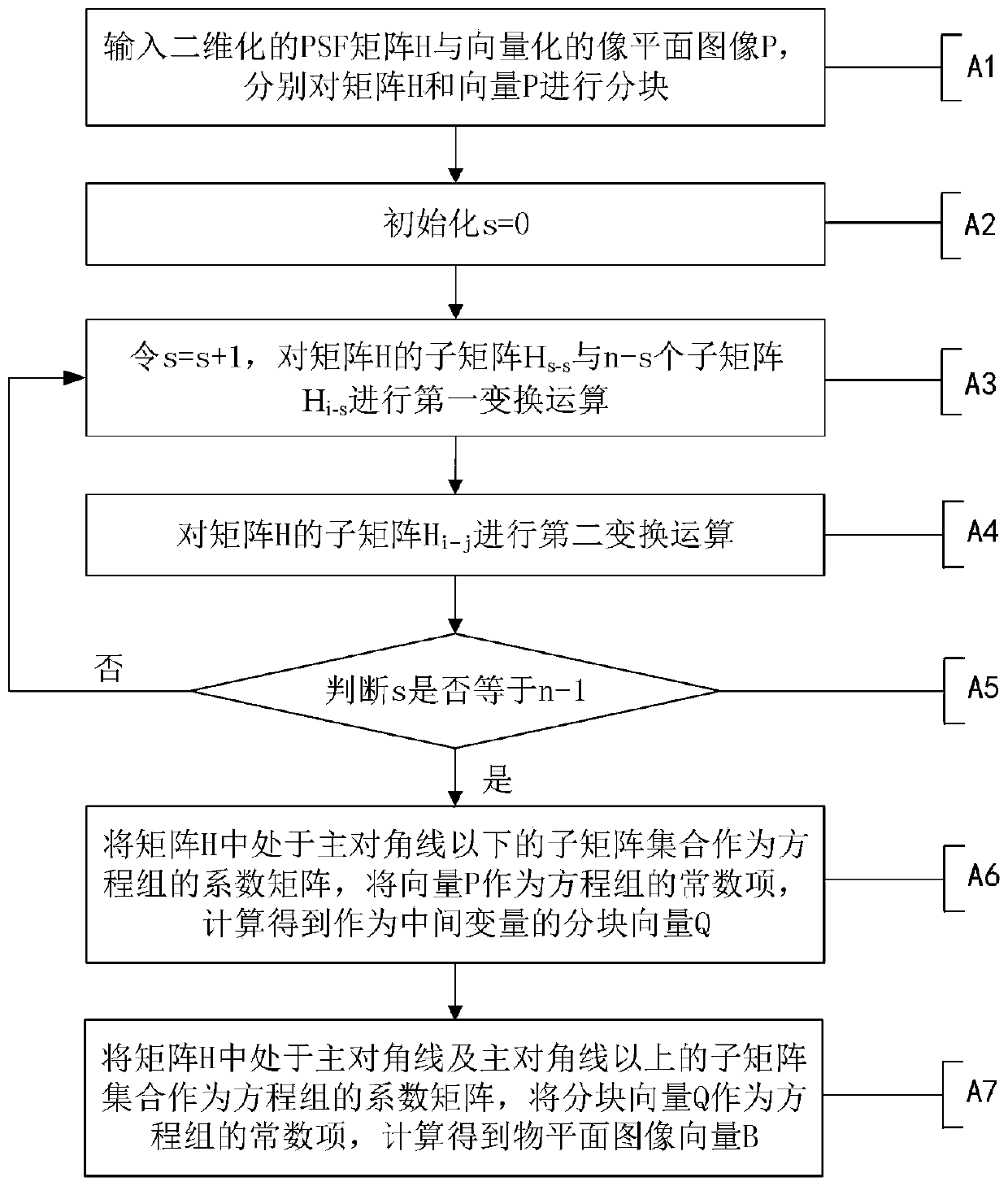
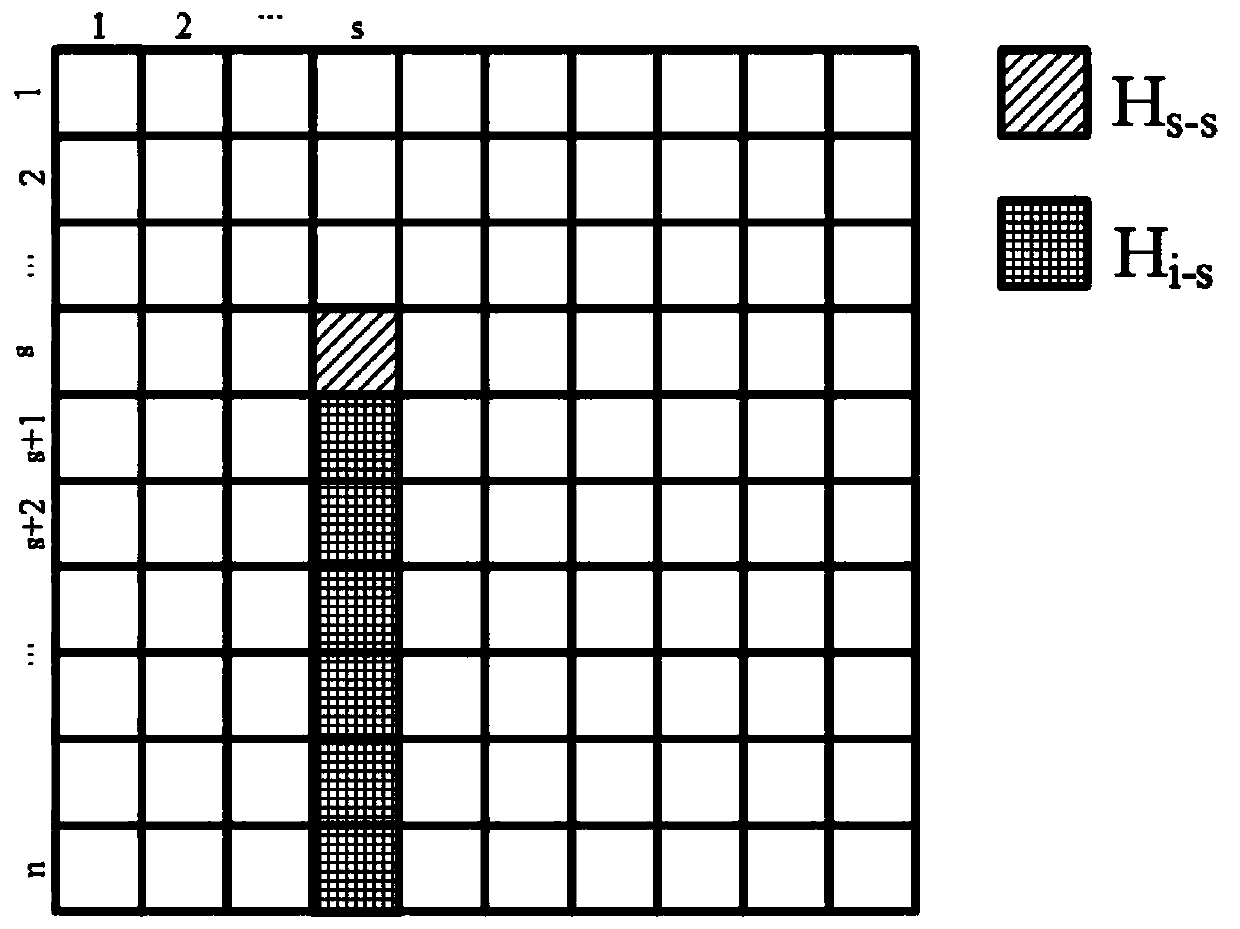
[0048] In order to improve the efficiency of PSF inverse transformation, try to keep the scalability of the algorithm, such as figure 1As shown, the preferred embodiment of the present invention discloses a PSF inverse transformation method based on parallel LU decomposition. The idea of the present invention is based on the convenience of LU decomposition in solving linear equations, and utilizes the method of matrix partitioning to make LU It is possible to use parallel processing in the decomposition, and use parallelized LU decomposition technology and Gaussian elimination method to effectively reduce the time consumed by PSF inverse transformation; specifically, the following steps are included:
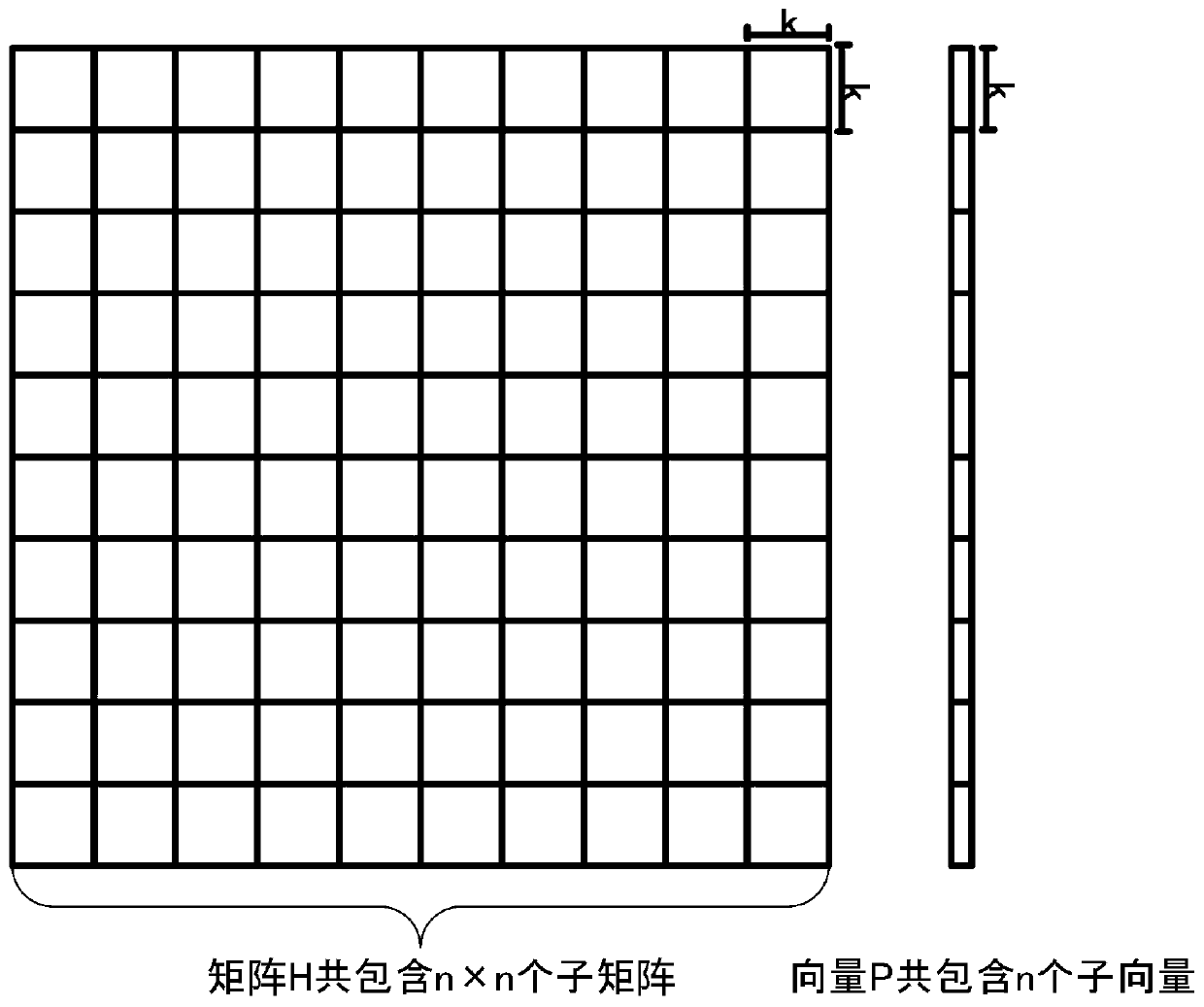
[0049] A1: Input the two-dimensional joint PSF matrix H and the vectorized image plane image P, respectively block the matr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com