Fine-grain emotion element extracting method based on local information representation
A technology of element extraction and local information, applied in neural learning methods, biological neural network models, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of wrong part-of-speech judgment of phrases, many missing extraction results, and difficulty in judging whether the current word is part of the evaluation object, etc. achieve high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0024] Specific Embodiment 1: The fine-grained emotional element extraction method based on local information representation in this embodiment includes:
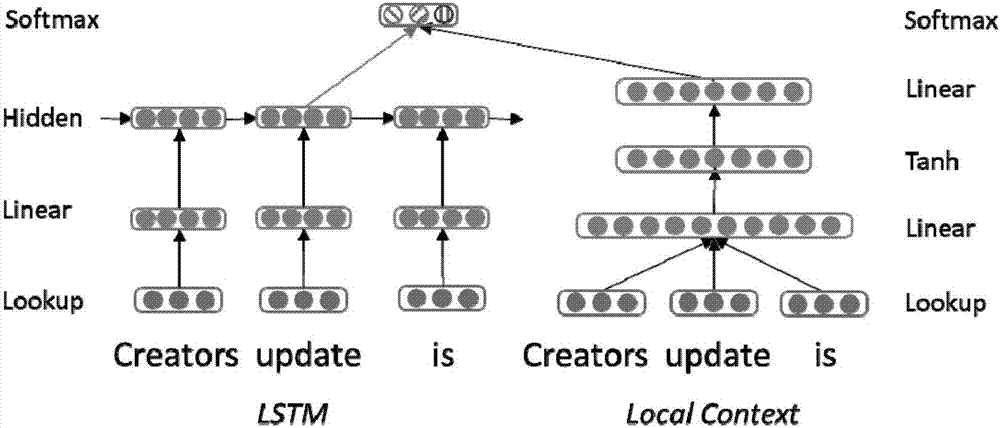
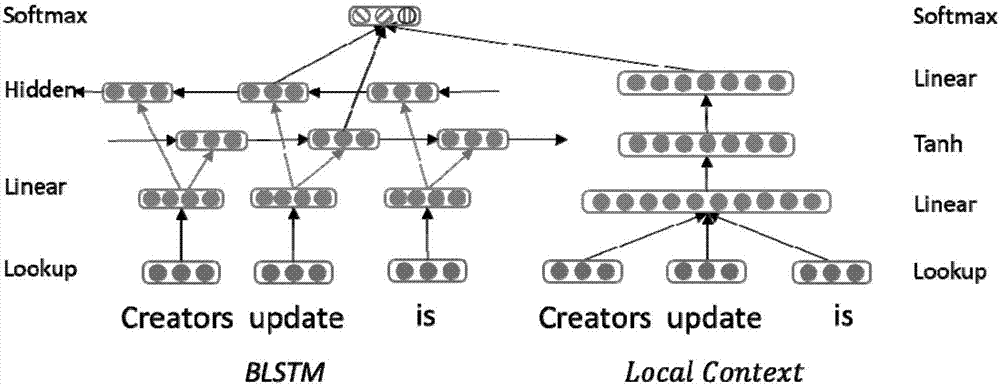
[0025] Step 1. Each word in the preset window size is searched for the vector representation of the word feature through the Lookup Table, and the obtained word vectors are respectively input into the LSTM model; and the obtained word vectors are combined into a vector input to the front Feed the neural network model;
[0026] Step 2: Represent the hidden layer features of the LSTM model as h t And the local contextual feature representation h of the feed-forward neural network model lr Perform splicing to obtain the spliced result h con :
[0027] h con =[h t , h lr ]
[0028] Step 3, put h con Send it to the output layer and use the softmax function for label classification to obtain the classification result.
[0029] The method in this paper also treats the evaluation object extraction as a sequence labeling ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in the softmax function, each label calculation result P(y t =k|s,θ) is expressed as:
[0035]
[0036] in, Represents the weight from the last hidden layer to the output layer, k represents a certain label category, K represents all possible label sets, s, θ represent the current sentence and model parameters respectively, y t Indicates the current predicted label result.
[0037] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that: the size of the preset window is 3. For the feed-forward neural network used to learn local information, the word vector input with different window sizes was tested, and it was found that the extraction effect was the best when the window size was 3 (previous word, current word, next word). Therefore, for the local information representation model, the window size is uniformly set to 3.
[0039] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com