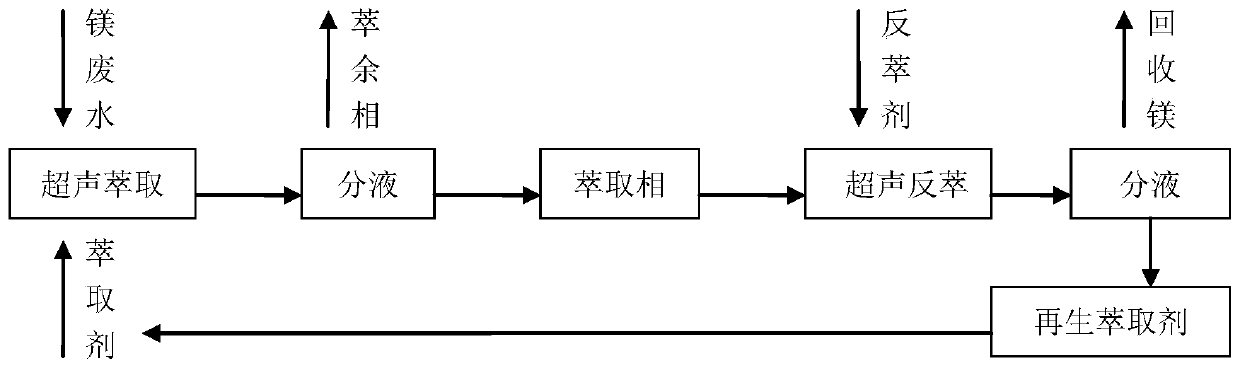
A method for extracting magnesium from metallurgical wastewater
An extraction and waste water technology, applied in the field of magnesium extraction, can solve the problems of low single-stage extraction rate and total recovery rate of magnesium, inability to realize continuous feed extraction, limitation of magnesium ion extraction, etc., and achieve simple and feasible production process, extraction and reaction. The effect of short extraction time and fast extraction speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The initial concentration of magnesium ions in wastewater is 19.81g·L -1 , the volume is 100ml, the extraction temperature is normal temperature (25°C), sulfonated kerosene is used as a dilution solvent, and the volume ratio of the compound extractant is dinonylnaphthalenesulfonic acid: diisooctyl phosphate: n-decyl alcohol=80:15:5, compound The amount of extractant is 200ml, the organic phase is composed of sulfonated kerosene and compound extractant in a volume ratio of 1.5:1, the amount of organic phase is 500ml, the ultrasonic extraction power is 100-300W, the ultrasonic frequency is 20-25KHZ, and the ultrasonic extraction time is selected at 4min, the depth of immersion of the horn is about 5mm, and the liquid separation time is 3min, the single-stage extraction rate of magnesium is 86.59%. The concentration of loaded magnesium in the extracted organic phase was 7.81g L -1 , at room temperature (25°C), using sulfuric acid as the stripping agent, the stripping agen...
Embodiment 2
[0021] The initial concentration of magnesium ions in wastewater is 20.59g L -1 , the volume is 100ml, the extraction temperature is normal temperature (20°C), sulfonated kerosene is used as the dilution solvent, and the volume ratio of the compound extractant is dinonylnaphthalenesulfonic acid: diisooctyl phosphate: n-decyl alcohol=80:15:5, compound The amount of extractant is 200ml, the organic phase is made of sulfonated kerosene and compound extractant in a volume ratio of 1:1, the amount of organic phase is 400ml, the ultrasonic extraction power is 100-300W, the ultrasonic frequency is 20-25KHZ, and the ultrasonic extraction time is selected at 4 minutes, the depth of immersion of the horn is about 5mm, and the liquid separation time is 5 minutes, the single-stage extraction rate of magnesium is 85.21%. The concentration of loaded magnesium in the extracted organic phase was 7.79g L -1 , at room temperature (20°C), using sulfuric acid as the stripping agent, the strippin...
Embodiment 3
[0023] The initial concentration of magnesium ions in wastewater is 20.81g L -1 , the volume is 100ml, the extraction temperature is normal temperature (23°C), sulfonated kerosene is used as the dilution solvent, and the volume ratio of the compound extractant is dinonylnaphthalenesulfonic acid: diisooctyl phosphate: n-decyl alcohol=80:15:5, compound The amount of extractant is 200ml, the organic phase is composed of sulfonated kerosene and composite extractant in a volume ratio of 0.5:1, the amount of organic phase is 300ml, the ultrasonic extraction power is 100-300W, the ultrasonic frequency is 20-25KHZ, and the ultrasonic extraction time is selected at 3min, the depth of immersion of the horn is about 5mm, and the liquid separation time is 4min, the single-stage extraction rate of magnesium is 83.27%. The concentration of loaded magnesium in the extracted organic phase was 7.76g L -1 , at room temperature (23°C), using sulfuric acid as the stripping agent, the stripping a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com