Glass mat reinforcement
A technology of glass mat and glass fiber, applied in the direction of textiles, papermaking, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problem that formaldehyde-free binders cannot provide all the necessary properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
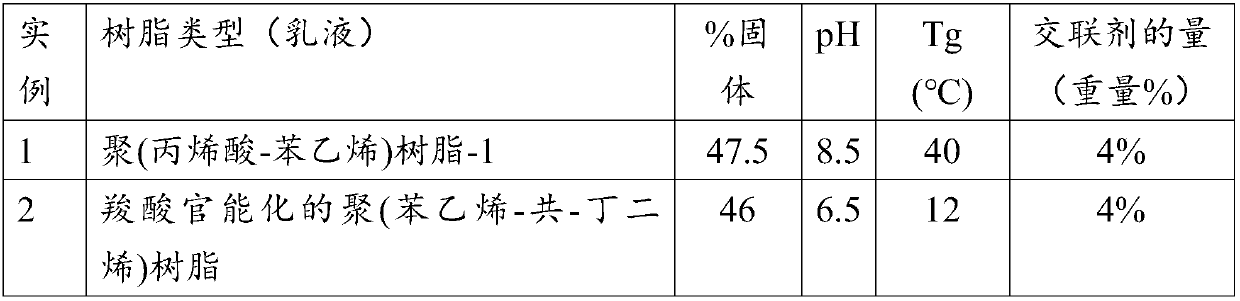
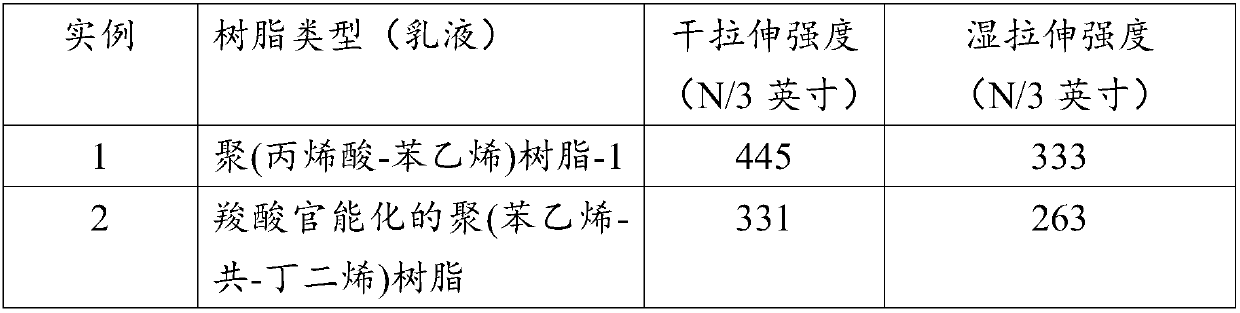
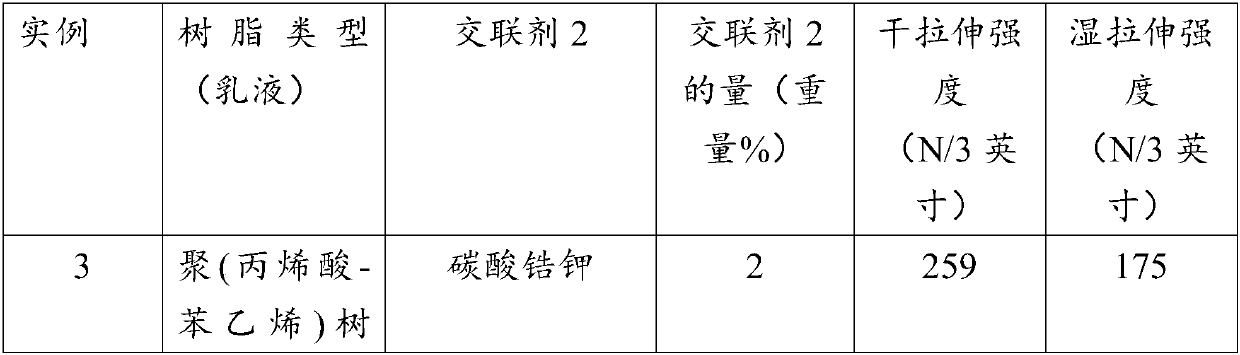
[0039] Embodiment 1. A glass mat comprising: a glass fiber assembly; and a binder composition comprising a polymeric resin having a pH of at least about 5.0 and a crosslinking agent, wherein The polymer resin includes a styrenic copolymer, an acrylic copolymer, or a combination thereof having at least one functional group of carboxylic acid, a salt of a carboxylic acid, an acid anhydride, a salt of an anhydride, or a combination thereof; the crosslinking agent includes a polyhydric alcohol , polyepoxides, polycarbodiimides, polyethylenimides, divalent metal carbonates, or combinations thereof.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2. A method of making a glass mat, the method comprising providing a glass mat, wherein the glass mat comprises: a fiberglass assembly; and a binder composition comprising A polymer resin and a crosslinking agent at a pH of 1, wherein the polymer resin comprises a styrenic copolymer, an acrylic copolymer having at least one functional group of a carboxylic acid, a salt of a carboxylic acid, an anhydride, a salt of an anhydride, or a combination thereof or a combination thereof; the crosslinking agent includes polyhydric alcohol, polyepoxide, polycarbodiimide, polyaziridine, divalent metal carbonate or a combination thereof.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3. The glass mat or method of any one of the preceding embodiments, wherein the styrenic copolymer is prepared from a styrenic monomer and at least one ethylenically unsaturated monomer, the ethylenically unsaturated monomer Including aromatic, carboxylic acid, carboxylic anhydride, acrylic acid, acrylate ester, conjugated diene functional groups or combinations thereof.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com