Improved two-step linear discriminant analysis method
A linear discriminant analysis, singularity technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of no contribution to classification performance, increased algorithm complexity and training time, and unfavorable eigenvectors for classification. The effect of improved classification performance and training speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
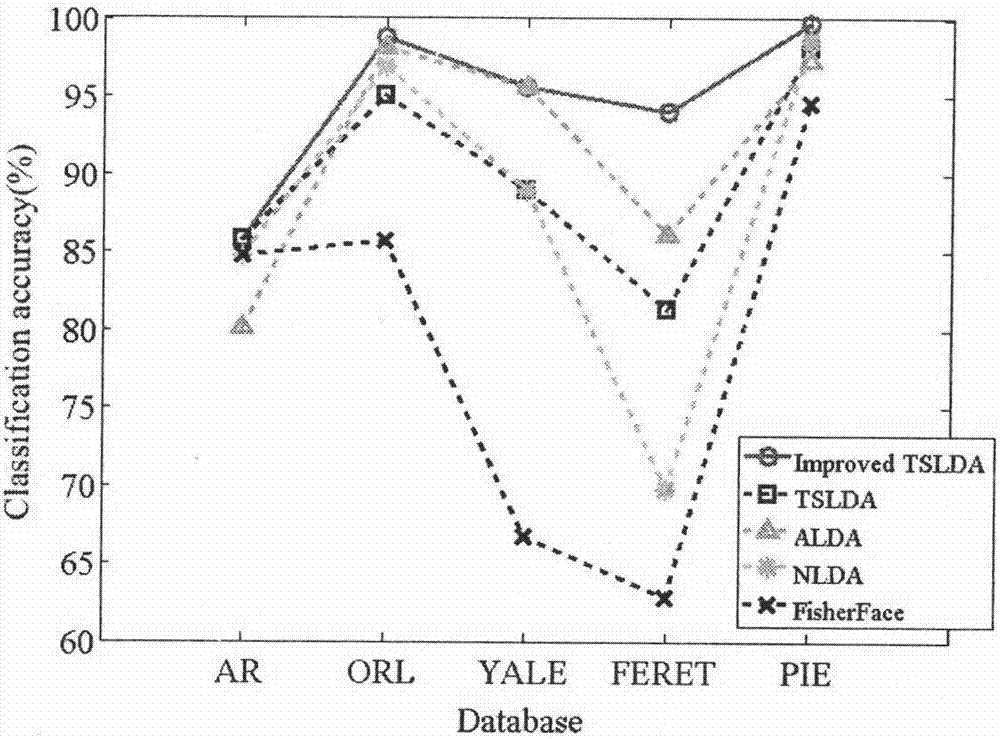
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in further detail below through embodiments in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
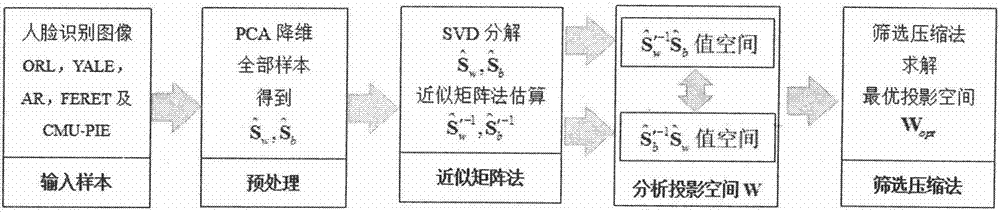
[0036] figure 1 It is an implementation flow chart of an improved two-step linear discriminant analysis method of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0037] Step A: Preprocessing: Perform PCA dimensionality reduction on the original samples to simplify operations. Specifically, for the overall dispersion matrix S t Perform SVD decomposition:
[0038]
[0039] in is its eigenvalue matrix, r t = n-1 is S t rank of U t =[U TR , U TN ] is its feature space, and for S t value space, for S t null space. Select U TR All samples are projected as a transformation matrix, and all samples are reduced from d to r t (d>r t ), the intra-class dispersion matrix after projection is The between-class dispersion matrix is
[0040] Step B: Approximate matrix method eliminat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com