Uplink non-orthogonal scheduling-free method and device
A non-orthogonal, base station technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve the problem of inability to reduce adjacent cell interference, and achieve the effect of reducing adjacent cell interference and reducing multiple access resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
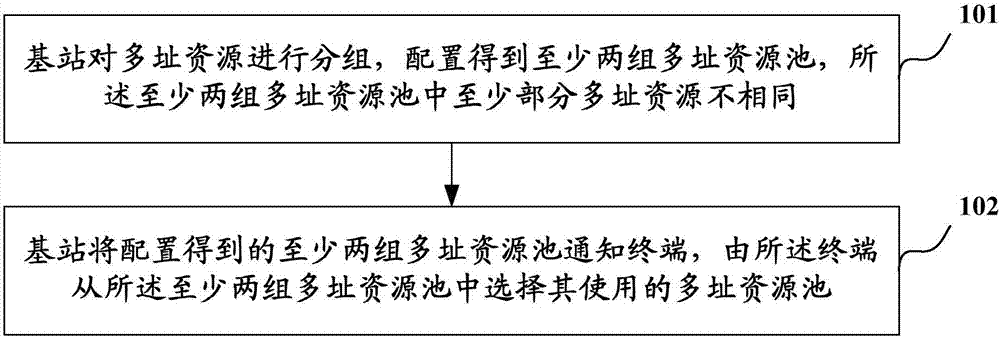
[0049] see figure 1 , the figure shows an uplink non-orthogonal scheduling-free method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0050] Step 101, the base station groups the multiple access resources, configures at least two sets of multiple access resource pools, and at least some of the multiple access resources in the at least two sets of multiple access resource pools are different;
[0051] Take two groups of multiple-access resource pools as an example: the first multiple-access resource pool and the second multiple-access resource pool, wherein, part of the multiple-access resource in the second multiple-access resource pool is the same as the multiple-access resource in the first multiple-access resource pool different.
[0052] Take three sets of multiple-access resource pools as an example: the first multiple-access resource pool, the second multiple-access resource pool, and the third multiple-access resource pool, wherein the second multiple-access resource pool is th...
Embodiment 2
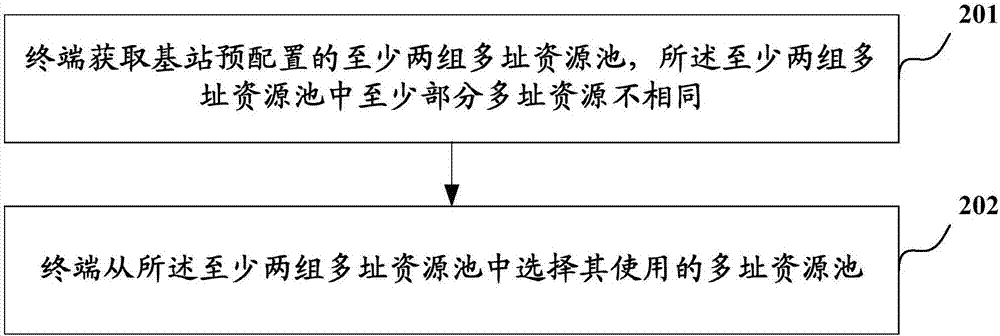
[0060] see figure 2 , the figure shows an uplink non-orthogonal scheduling-free method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0061] Step 201, the terminal acquires at least two sets of multiple access resource pools pre-configured by the base station, and at least some of the multiple access resources in the at least two sets of multiple access resource pools are different;
[0062] In this embodiment, the above-mentioned multiple access resources include: any one or more of time domain resources, frequency domain resources, air domain resources, and code domain resources, wherein the code domain resources include but are not limited to: codebook (codebook) Any one or more of , codeword (codeword), sequence (sequence), interleaver (interleaver) and mapping pattern (mapping pattern).
[0063] In this embodiment, optionally, at least two groups of multiple-access resource pools include: a first multiple-access resource pool and a second multiple-access resource pool, wherein t...
Embodiment 3
[0069] The implementation of the present invention will be described below by taking PDMA (Pattern Division Multiple Access) uplink scheduling-free transmission as a specific example.
[0070] PDMA technology adopts the design idea of joint optimization of the sending end and the receiving end, divides the information of multiple users at the sending end with unequal diversity, and maps it to the same time domain resource, frequency domain resource or air domain resource, using different codes Patterns are used to distinguish different users with overlapping resources; high-performance and low-complexity multi-user detection techniques, such as the belief propagation algorithm, are used at the receiving end to approach the maximum a posteriori probability detection performance. The characteristic of multiple access resources of PDMA technology is that different pattern resources share the same time domain resources, frequency domain resources, air domain resources and other r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com