A full-terminal reliability calculation method for dividing communication communities based on modularity
A calculation method and modularity technology, applied in calculation, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient consideration of full-scale reliability calculation methods, inapplicability to large and complex networks, slow calculation speed, etc., and achieve less analysis time consumption , reducing the time spent, reducing the effect of the state space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
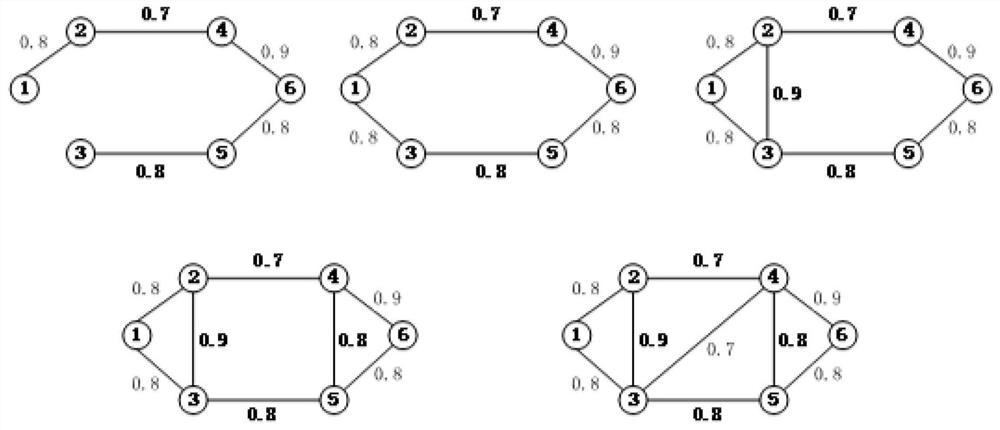
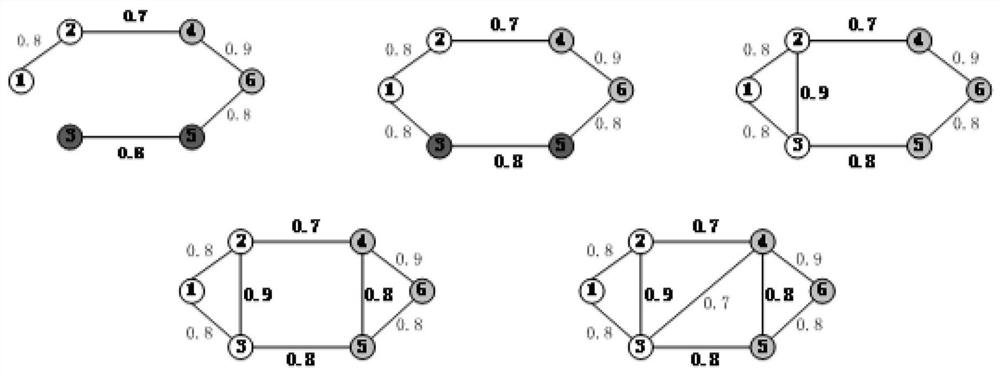
[0039] Embodiment 1, a full-terminal reliability calculation method based on modularity division of communication communities, including modularity-based power communication network community division and full-terminal reliability calculation based on minimum path sets,
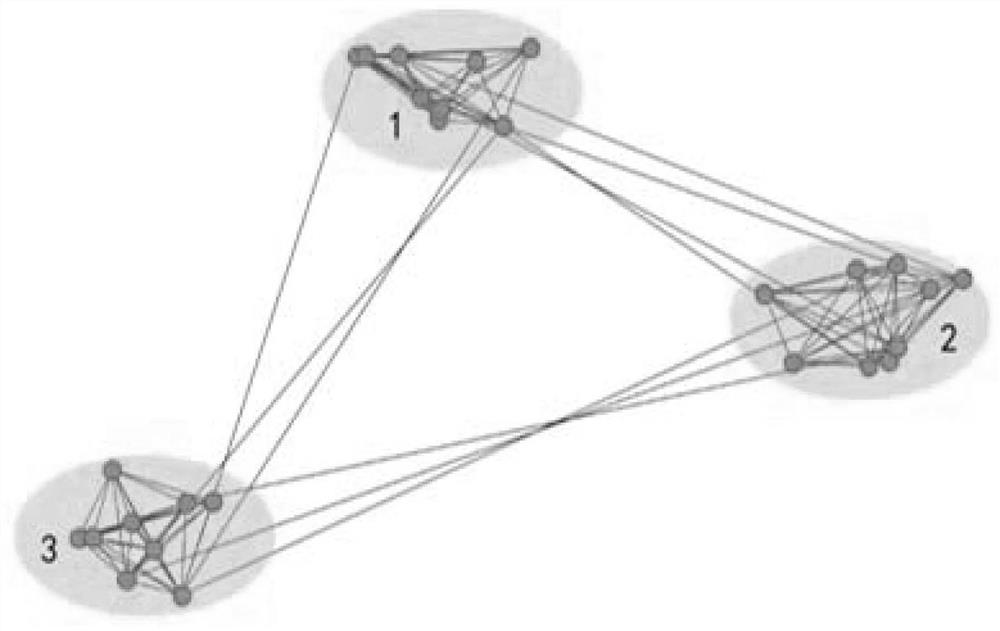
[0040] S1, there is no generally accepted formal definition for the concept of community, but in essence, all definitions of community have such a consensus: the connection between nodes within the community is relatively close, while the connection between nodes in different communities is relatively close. Sparse, borrowing the formal definition of community proposed by Radichi. The definition looks like this:
[0041] In the network G, record the degree of any node i as k i =∑ j A ij , where A represents the adjacency matrix of graph G. C represents a community containing node i, then the degree of node i can be divided into two parts:
[0042]
[0043] in, Indicates the number of connecting edges ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2. On the basis of Embodiment 1, the specific steps of calculating the full-terminal reliability based on the minimum road set are as follows;
[0064] A. Based on the small-world network characteristics of the power communication network, the entire complex network is decomposed into multiple smaller and independent networks by using the "community" structure of the complex network, and the internal full-terminal reliability of these networks is solved, and then These small-scale networks are noded, and the node weight is the value of the full-terminal reliability of the small-scale network, and then the full-terminal reliability between the small-scale networks is solved, and the final full-terminal reliability represents the entire network. All-round reliability.
[0065] When analyzing the full-terminal reliability within the "community" and the full-terminal reliability between "communities", since the network scale has been greatly reduced, the traditio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com