Chimeric antigen receptor specific for tumor cells
A chimeric antigen receptor, specific technology, applied in the direction of receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant, for targeting specific cell fusion, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can solve the unsatisfied medical treatment of other cancer types demand and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Example 1: Expression of targets on pancreatic cancer
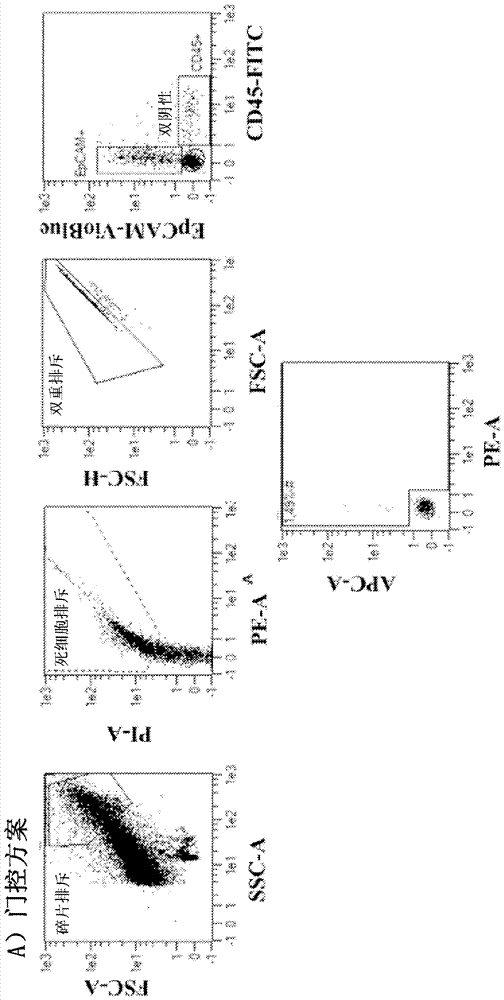
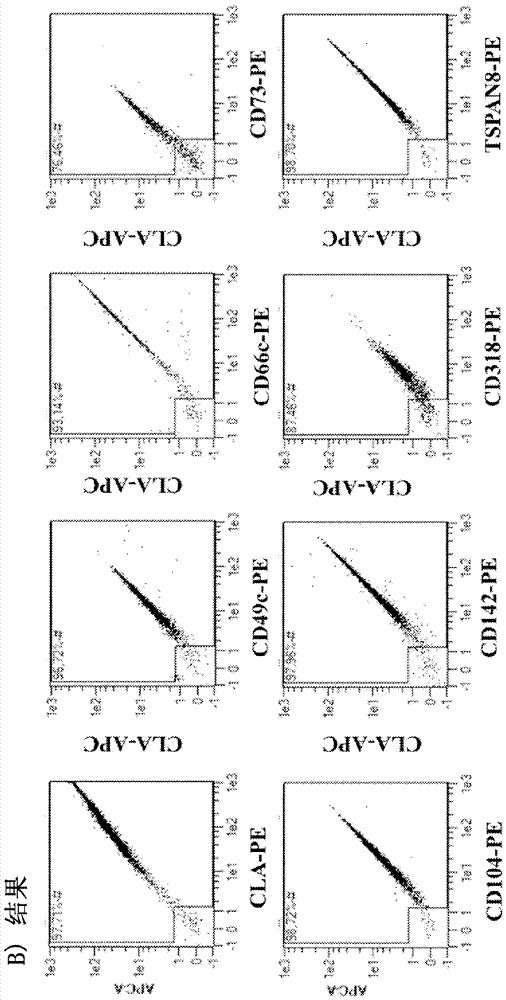
[0123] Expression of CLA, CD142, CD73, CD49c, CD66c, CD104, CD318, and TSPAN8 on xenografted human pancreatic cancer cells indicated a strong abundance of these markers on pancreatic cancer cells, independent of the tumor microenvironment ( image 3 ). Furthermore, all markers were also reproducibly expressed at high levels on primary human pancreatic cancer cells (labeled Epcam+), but not on cells of healthy tumor-infiltrating leukocytes (labeled CD45+) or other healthy tissue-resident cell types (labeled is not double negative) on ( Figure 4 ). These results were further validated using immunohistochemistry-based detection of target expression in human pancreatic carcinoma ( Figure 5 ).
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: Structure of a CAR that recognizes a pancreatic cancer-specific target
[0125] Adapters used can contain epitopes / tags that allow detection of the CAR, such as figure 1 shown in . Examples of epitopes / tags are YOL, cMYC or HIS. The pancreatic cancer target-specific binding fragment is derived from one or several antibodies specific for CLA, CD142, CD73, CD49c, CD66c, CD104, CD318 and / or TSPAN8. The hinge region may be derived from, for example, an IgG domain, CD8α or CD28, and may contain an epitope / tag that allows detection of the CAR. The transmembrane domain may be derived from eg CD8α or CD28, followed by one to three signaling domains. These domains may be derived from, for example, CD28, 4-1BB, OX40 or CD3ζ.
Embodiment 3
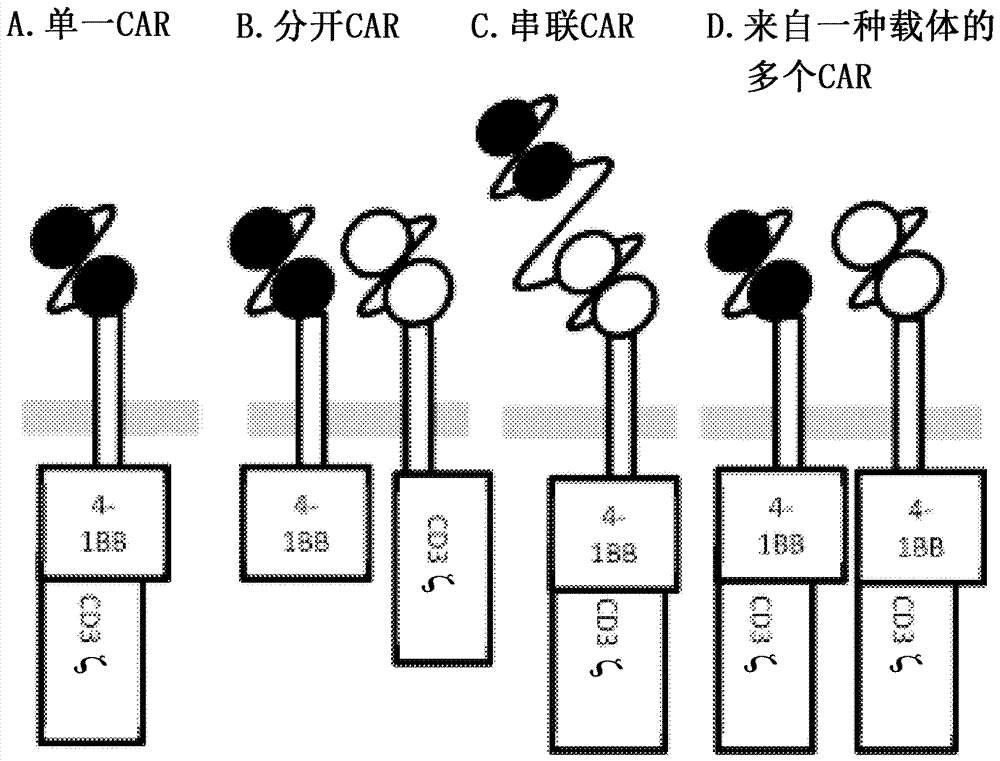
[0126] Example 3: Structure of a Dual CAR Recognizing a Pancreatic Cancer-Specific Target
[0127] This can be done by combining multiple antigen binding sites on one CAR molecule or by using multiple CAR molecules that are expressed in one cell and only function in combination, for example by using each CAR construct that is ineffective for cell activation when used alone signaling domains to address the recognition of two or more targets ( figure 2 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com