Method for splicing printed board in frequency selective radome processing technology
A technology of processing technology and frequency selection, applied in the direction of antenna, radiation unit cover, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of FSS screen performance degradation and difficulty reaching designers.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be further described below by examples in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0021] The method for splicing printed boards in the frequency selective radome processing process of the present invention includes the following elements:
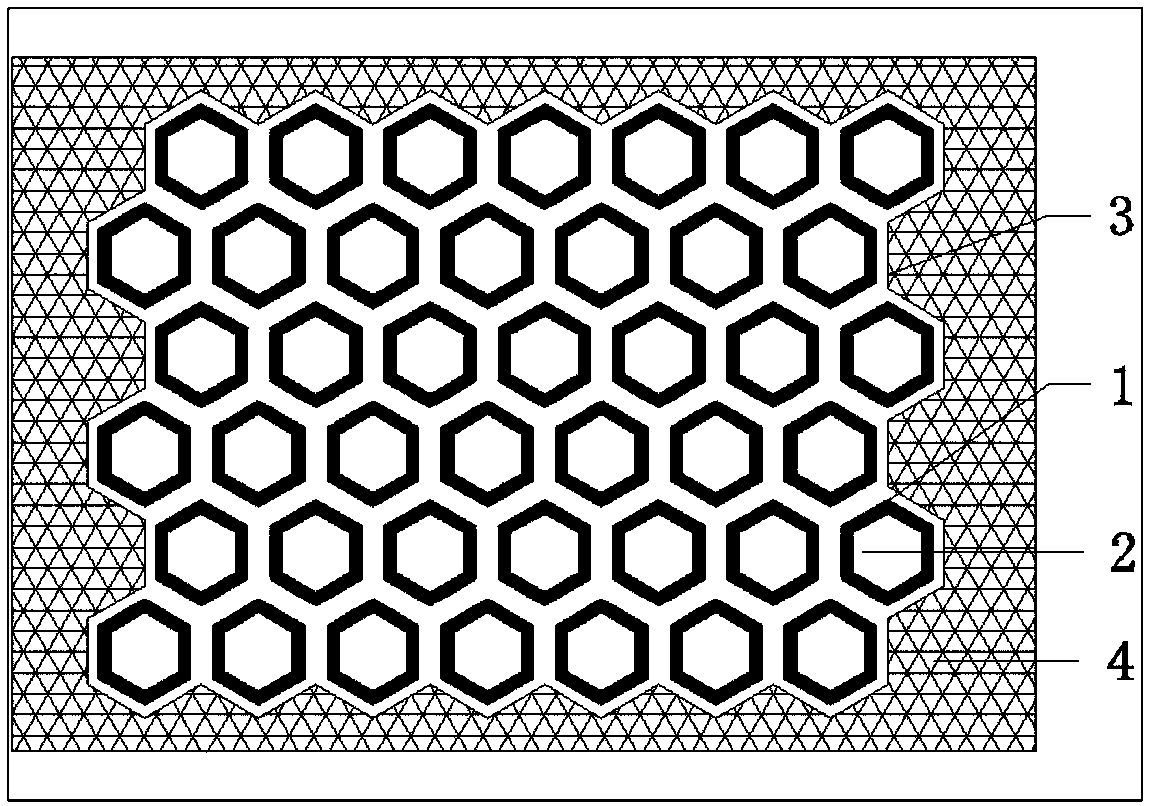
[0022] According to the size and structure of the radome, the FSS screen is divided into various sub-modules.
[0023] Wherein, the area of each sub-module should be as large as possible, and the number of sub-modules should be as small as possible, so as to reduce the number of seams. The sub-module should be producible by engineering. At present, the maximum size of the hard board processing of domestic printed boards does not exceed 1200mm.
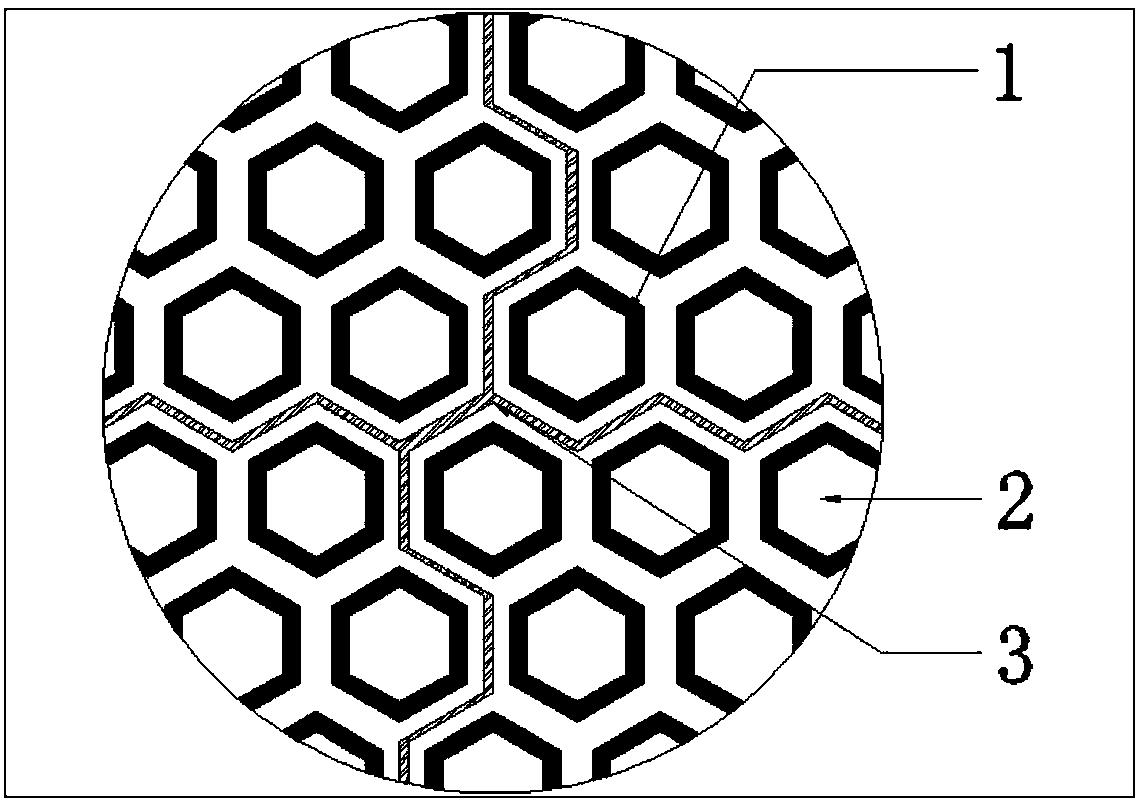
[0024] Further, according to the size and shape of each divided sub-module, the number and arrangement position of the periodic units 1 on the module are determined.
[0025] E.g figure 2 As shown in a rectangular FSS screen sub-module, the periodic unit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com