Hyperspectral hyperpixel segmentation method based on principal component weighted false color synthesis and color histogram driving
A technology of false color synthesis and color histogram, applied in image enhancement, image data processing, image analysis, etc., can solve problems such as large data redundancy, difficult real-time image segmentation, and high data dimensionality of hyperspectral images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
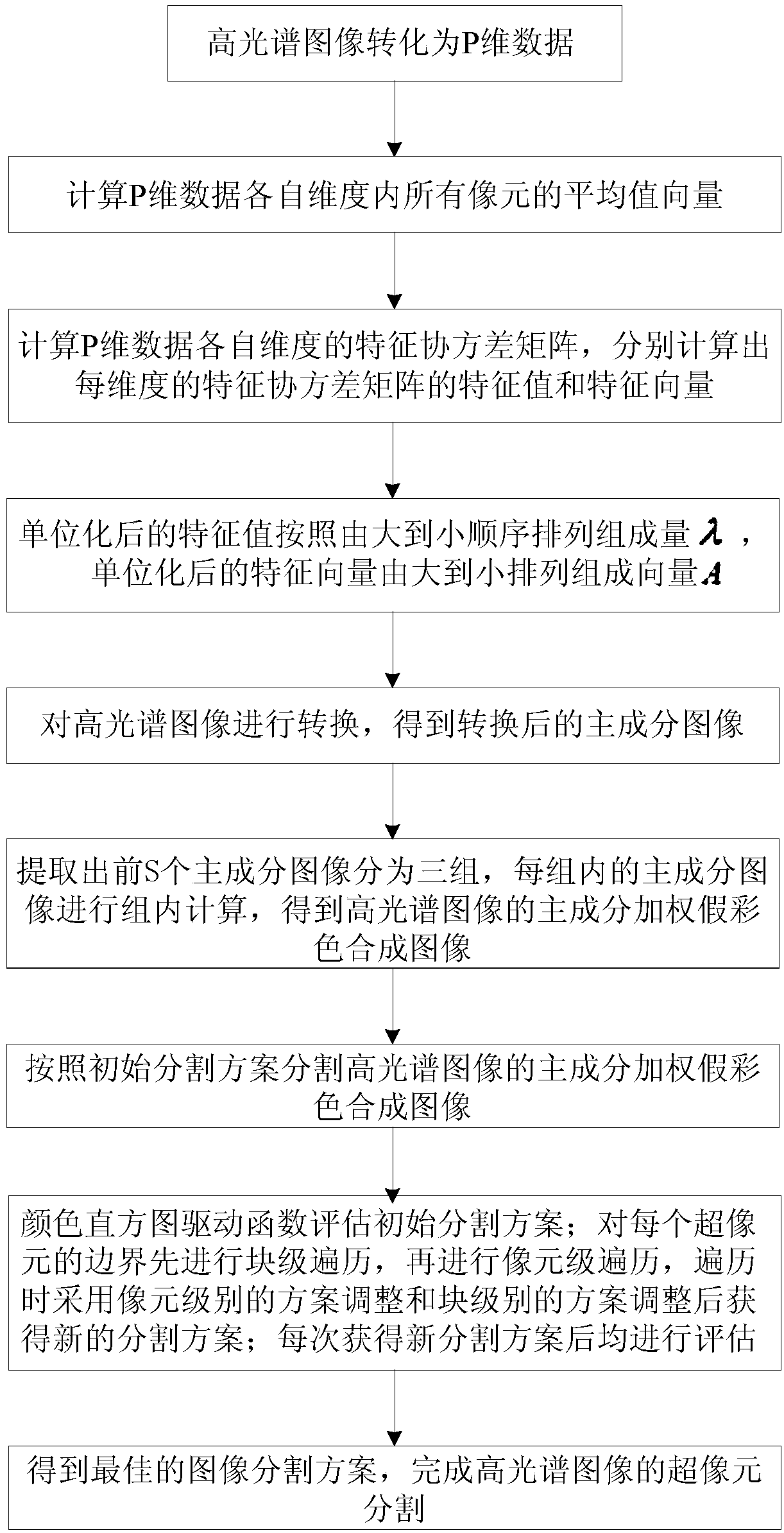
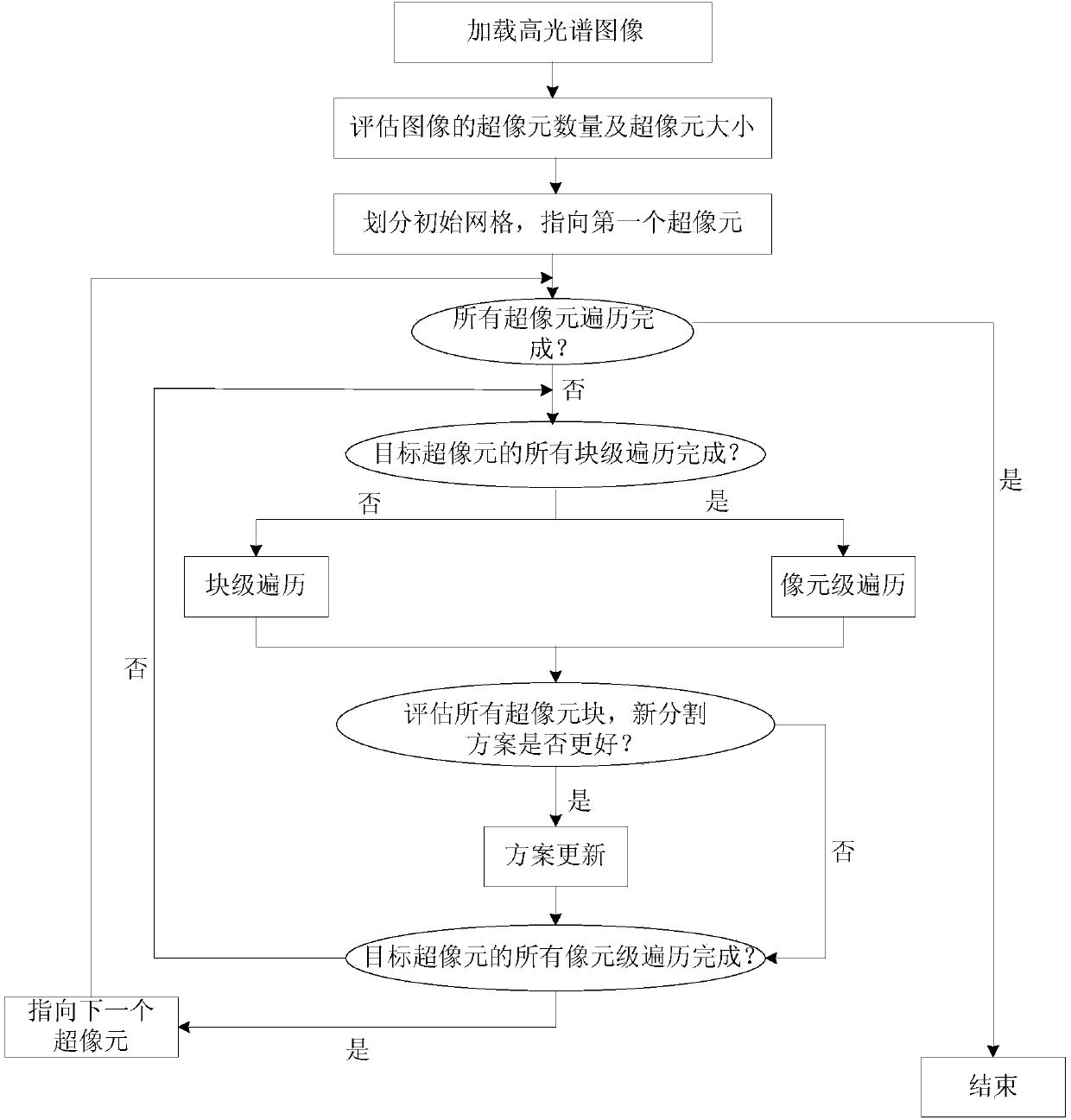
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 and 2 As shown, a hyperspectral super-pixel segmentation method based on principal component weighted false color synthesis and color histogram driving described in this embodiment is specifically carried out in accordance with the following steps:
[0023] Step 1: Perform principal component weighted false-color synthesis on the hyperspectral image data X of P-band M×N pixels, and convert the hyperspectral image into P-dimensional data; respectively calculate the average vector of all pixels in each dimension of the P-dimensional data ;
[0024] Step 2. Use the P-dimensional data obtained in step 1 and the average vectors of all pixels in the respective dimensions of the P-dimensional data to calculate the characteristic covariance matrix of the respective dimensions of the P-dimensional data, and calculate the characteristics of the characteristic covariance matrix of each dimension Values and eigenvectors; unitize the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033]Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of step one is:
[0034] For hyperspectral image data X=(x 1 ,x 2 ,...x i ,...,x M×N )=(X 1 ,X 2 ,...,X j ,...,X P ) T Perform principal component weighted false color synthesis, where X is a (M×N)×P dimensional matrix, x i Represents the i-th pixel in the hyperspectral image, i=1,2,...,M×N, that is, convert the M×N pixel matrix into a (M×N)×1 pixel column vector, X j Indicates the jth dimension of the image, where j=1,2,...,P;
[0035] Calculate the mean vector of all pixels in the respective dimensions of the P-dimensional data:
[0036]
[0037] Represents the mean vector of all pixels in the hyperspectral image data in each dimension.
[0038] In this embodiment, the hyperspectral image is converted into P-dimensional high-dimensional data, and by calculating the M×N groups of data relative to the mean The a...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode two is: the specific process of step two is:
[0040] The feature covariance matrix of each dimension of hyperspectral image data is:
[0041]
[0042] The diagonal elements of the characteristic covariance matrix C represent the variance of each dimension; the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the covariance matrix C of each dimension are calculated respectively, and the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the characteristic covariance matrix C of each dimension are unitized, and the unit The transformed eigenvalue λ j and the eigenvector a j Arrange according to the order from large to small to obtain the vector λ=(λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ P ) and the vector A=(a 1 ,a 2 ,...,a P ).
[0043] The off-diagonal elements of the covariance matrix measure the degree of simultaneous change between different bands. The larger the correlation coefficient, the gre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com