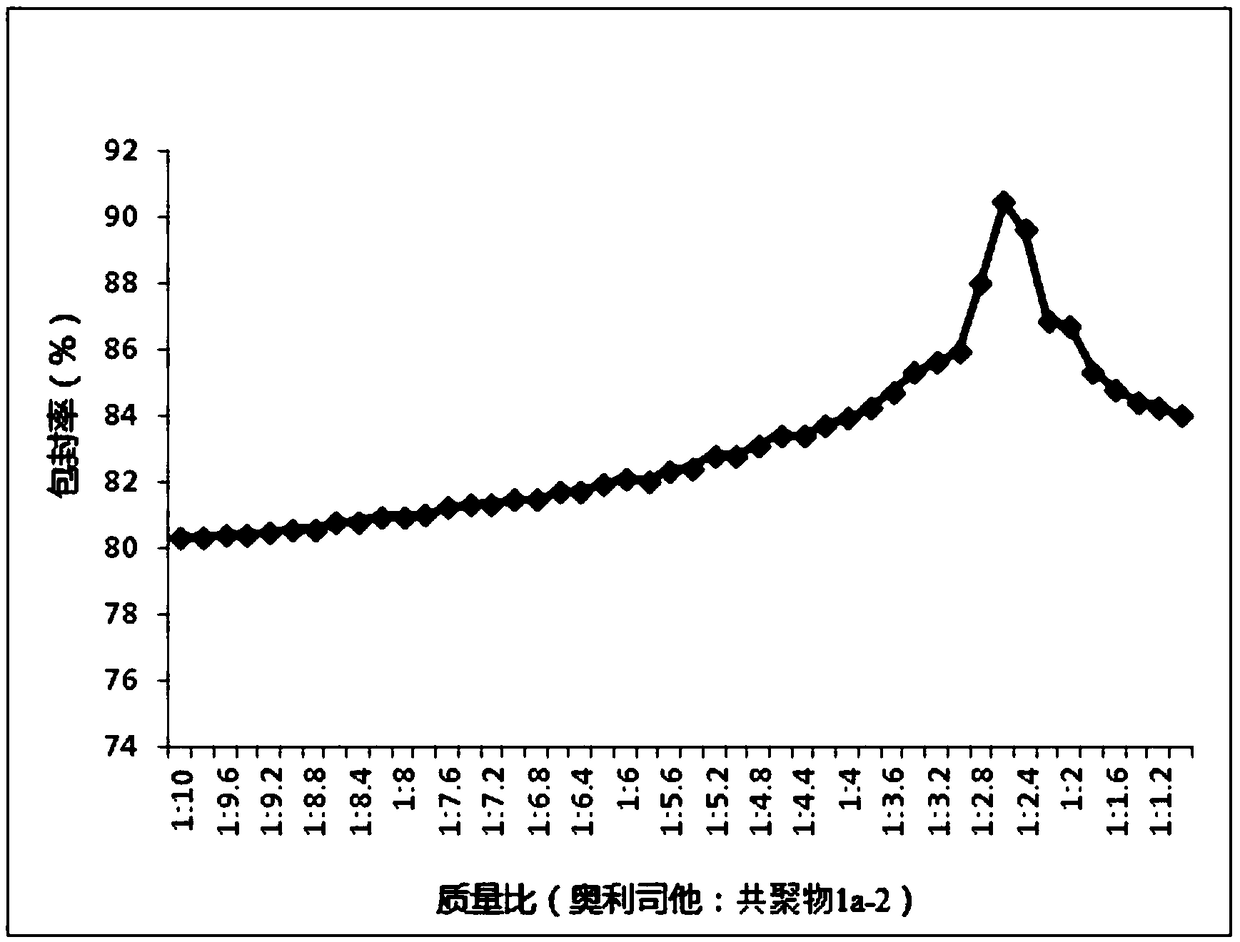
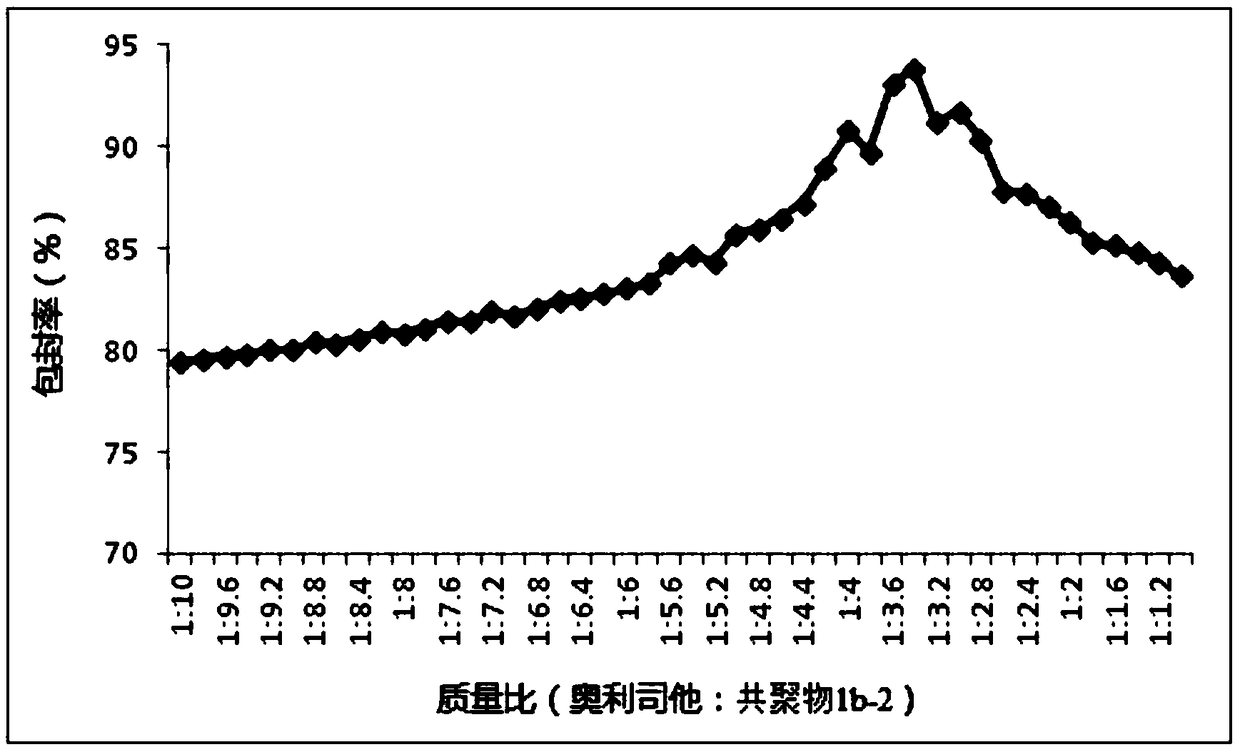
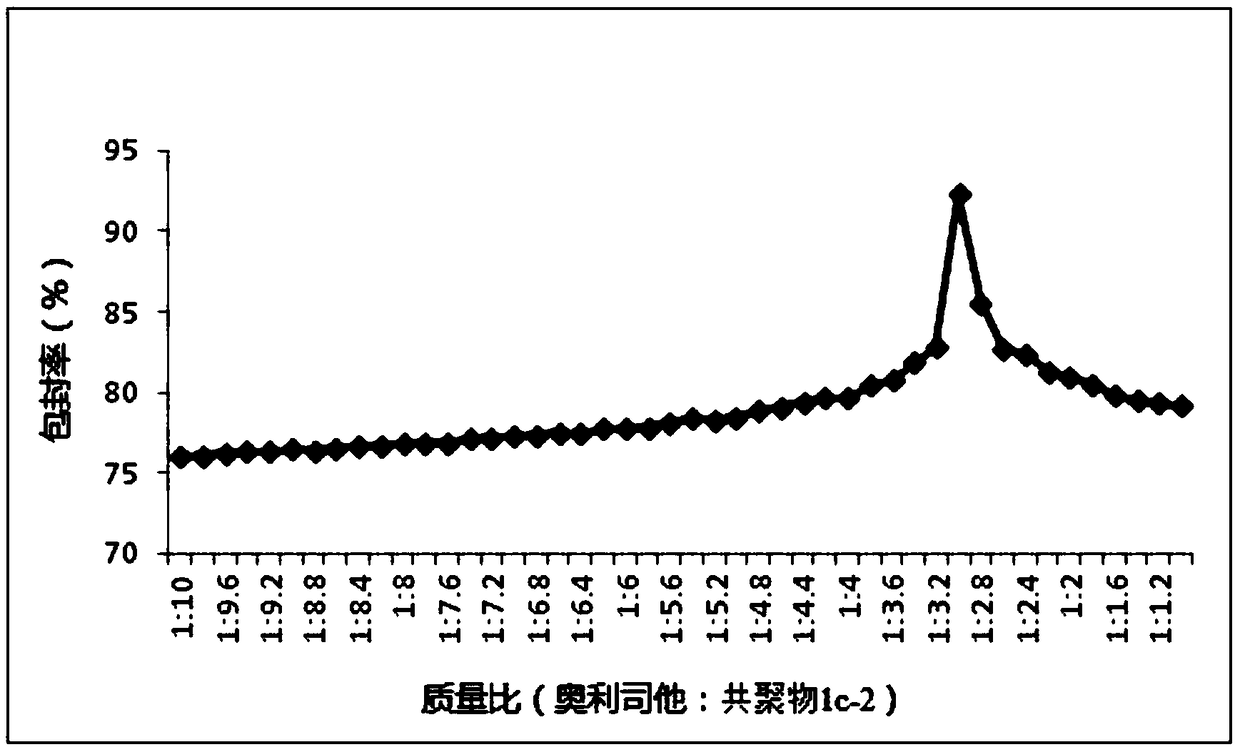
Use of nano-microspheres containing orlistat in the preparation of anti-hepatitis B virus drugs
A technology of orlistat and nano-microspheres, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of low bioavailability of orlistat, low solubility of orlistat, and inability to be administered orally
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1 Preparation and Structure Confirmation of Vitamin A Methacrylate (Compound 3a)
[0064]
[0065] Preparation: Take 28.65g vitamin A (0.100mol), put it in a 500mL three-necked flask, add petroleum ether to it under stirring, until vitamin A is completely dissolved, then add 5mg DCC (N,N'-dicyclohexyldi imine), and then add 13.21g of methacrylic acid (Compound 2, 0.15mol) in saturated petroleum ether solution, slowly raise the temperature to 50°C under stirring for reaction, and use high performance liquid chromatography to track the reaction to the end. Petroleum ether was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the resulting solid was washed with water and freeze-dried to obtain 31.55 g (0.089 mol) of a light yellow solid with a melting point of 51-52° C. and a yield of 89%.
[0066] Structural Confirmation:
[0067] Compound 2: 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 ) δ (ppm): 6.69 (1H, s), 6.55 (1H, s), 2.03 (3H, s).
[0068] Vitamin A: 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 )δ (ppm): 6.55 (1...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 Preparation and Structure Confirmation of Vitamin E Methacrylate (Compound 3b)
[0071]
[0072] Preparation: Take 43.72g of vitamin E (0.100mol), put it in a 500mL three-necked flask, add ether to it under stirring until the vitamin E is completely dissolved, then add 5mg of DMAP (4-dimethylaminopyridine) to it, and then add 13.23 g of methacrylic acid (compound 2, 0.16 mol) in saturated ether solution was slowly raised to 50° C. for reaction under stirring, and the reaction was tracked to the end point by high performance liquid chromatography. Ethyl ether was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the resulting solid was washed with water and then freeze-dried to obtain 45.39 g (0.091 mol) of off-white solid with a melting point of 42-43°C and a yield of 91%.
[0073] Structural Confirmation:
[0074] Compound 2: 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 ) δ (ppm): 6.69 (1H, s), 6.55 (1H, s), 2.03 (3H, s).
[0075] Vitamin E: 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 )δ(ppm): 2.74(2H, t), 2.12(3H...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3 Vitamin D 2 Preparation and Structure Confirmation of Methacrylate (Compound 3c)
[0078]
[0079] Preparation: Take 36.69g vitamin D 2 (0.101mol), placed in a 500mL three-necked flask, added diethyl ether therein under stirring until the vitamin E was completely dissolved, then added 5mg DMAP (4-dimethylaminopyridine), and then added 13.22g methacrylic acid (compound 2, 0.15 mol) of saturated ether solution, the temperature was slowly raised to 50°C under stirring for reaction, and the reaction was tracked to the end point by high performance liquid chromatography. Diethyl ether was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the obtained solid was washed with water and then freeze-dried to obtain 44.15 g (0.095 mol) of an off-white solid with a melting point of 85-87° C. and a yield of 95%.
[0080] Structural Confirmation:
[0081] Compound 2: 1H-NMR (CDCl 3 ) δ (ppm): 6.69 (1H, s), 6.55 (1H, s), 2.03 (3H, s).
[0082] Vitamin D 2 : 1 H-NMR (CDCl ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| encapsulation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com