Electro-hydraulic servo valve with acceleration bias drift inhibition function
An electro-hydraulic servo valve, zero offset drift technology, applied in the direction of servo motor components, valve details, valve devices, etc., can solve the problems of high computational complexity, unsuitable for production application, high hardware cost, etc., to achieve simple calculation method and structure Simple, low-cost-to-manufacture effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
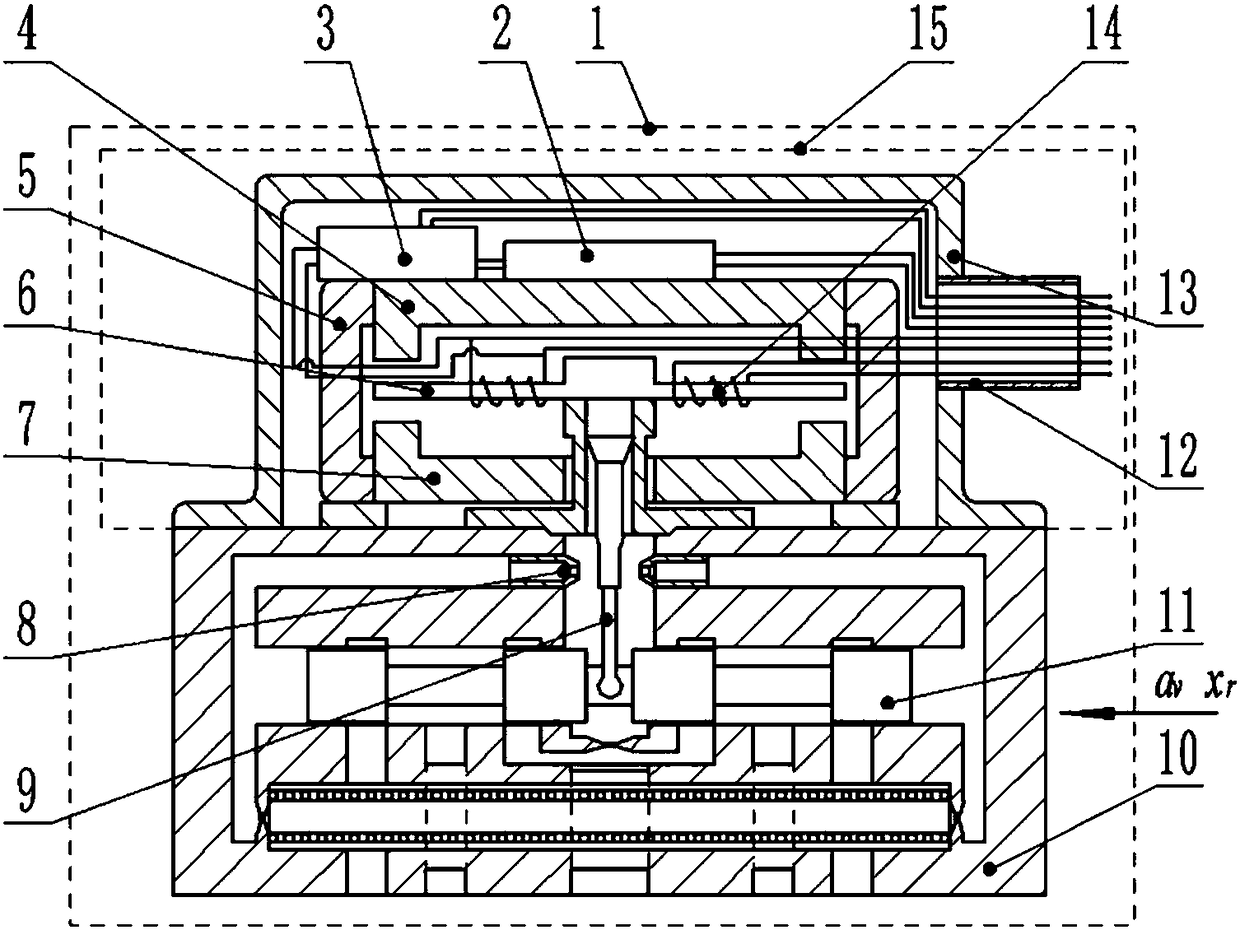
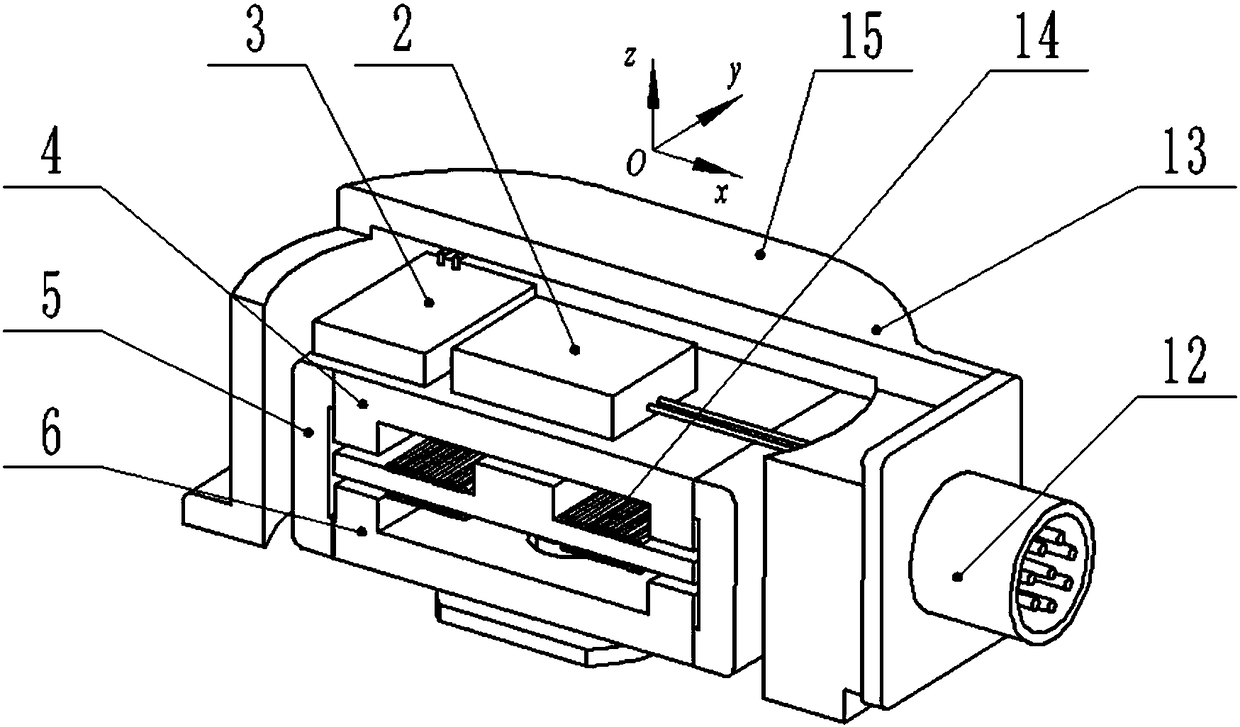
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides an electro-hydraulic servo valve with acceleration zero offset drift suppression function, including an electro-hydraulic servo valve body 1, an accelerometer 2, and a current amplifier 3. The electro-hydraulic servo valve body in this embodiment 1. The nozzle baffle type electro-hydraulic servo valve is used, mainly including: upper guide magnet 4, permanent magnet 5, armature baffle assembly 6, lower guide magnet 7, nozzle 8, feedback lever 9, valve body 10, main valve core 11. Current input port 12, torque motor cover 13 and control coil 14. The upper magnet guide 4 , the permanent magnet 5 , the armature baffle 6 , the lower magnet guide 7 , the current input port 12 , the torque motor cover 13 and the control coil 14 constitute the torque motor 15 of the electro-hydraulic servo valve body 1 . The accelerometer 2 and the current amplifier 3 form a zero offset drift suppression device.
[0047] The accelerometer 2...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The structure of the electro-hydraulic servo valve in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the body 1 of the electro-hydraulic servo valve is connected in series with double coils. At this time, the superposition relationship between the control current and the feedback current is as follows Figure 5 shown. Pin A of the current terminal is the positive pole of the control current Δi, pin D is the negative pole of the control current Δi, pin B and pin C are short-circuited. At this time, the positive pole of the amplifier feedback current Δi" is connected to pin D, and the negative pole of the amplifier feedback current Δi" is connected to pin A.
Embodiment 3
[0067] The structure of the electro-hydraulic servo valve in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the body 1 of the electro-hydraulic servo valve adopts a double-coil parallel connection method. At this time, the superposition relationship between the control current and the feedback current is as follows Figure 6 shown. Pin A of the current terminal is the positive pole of the control current Δi, pin D is the negative pole of the control current Δi, pin B and pin D are short-circuited, and pin A and pin C are short-circuited. At this time, the positive pole of the amplifier feedback current Δi" is connected to pin D, and the negative pole of the amplifier feedback current Δi" is connected to pin A.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com