Method for large-area preparation of hydrophobic/hydrophilic Janus composite fiber membrane with function of efficient catchment under drive of directional capillary force through electrostatic spinning
A composite fiber membrane, electrospinning technology, applied in electrospinning, fiber processing, filament/line forming and other directions, can solve problems such as restricting application and not yet reported, and achieve easy capture and absorption, low cost, high efficiency high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The first step is to prepare precursor solution A: polyvinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF-HFP) solution:
[0042] Weigh a certain amount of PVDF-HFP of pure grade after vacuum drying, select N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as the organic solvent A, and prepare a DMF solution with a mass fraction of PVDF-HFP of 15wt%. At a heating temperature of 60°C, heat and stir until the polymer is completely dissolved, and then set aside for later use.
[0043] The second step, electrospinning to prepare hydrophobic PVDF-HFP electrospun membrane:
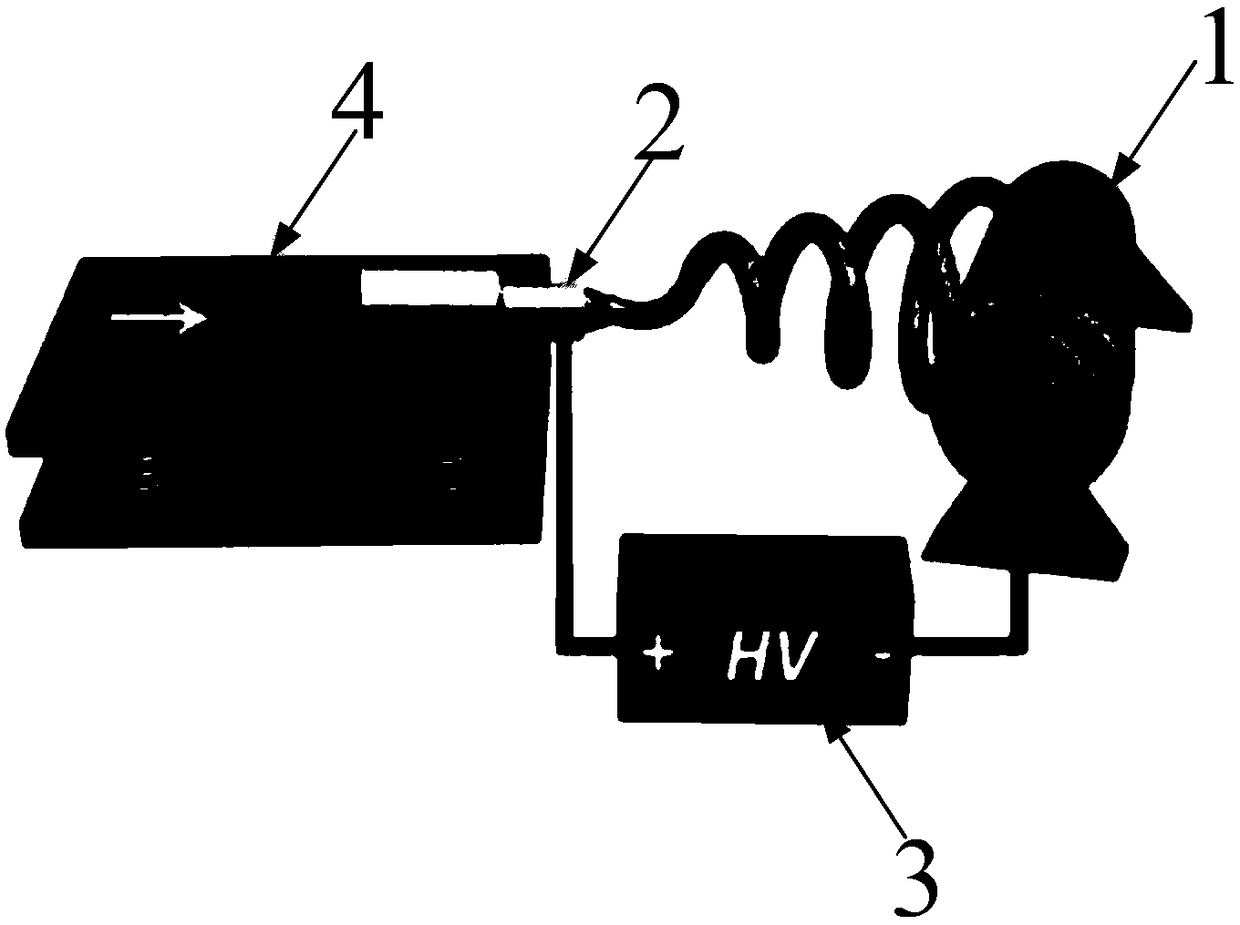
[0044] Select a non-woven fabric with the same width as the collecting drum as the receiving substrate A, and inject the PVDF-HFP / DMF precursor solution with a concentration of 15wt% configured in the first step into the syringe for electrospinning. Spinning device such as figure 1 As shown, it mainly includes a receiving drum 1, a metal spinneret 2, a high-voltage electrostatic positive and negative electrode 3, and a solution i...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The first step is to prepare electrospinning precursor solution A—polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) solution:
[0053] Weigh a certain amount of pure grade PVDF after vacuum drying, select N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) as a mixed solvent with a mass ratio of 4:1, and configure DMF with a mass fraction of PVDF of 30wt% / THF solution. At a heating temperature of 80° C., heat and stir until the polymer is completely dissolved, and set aside for later use.
[0054] The second step, electrospinning to prepare hydrophobic PVDF electrospun membrane:
[0055] Select a non-woven fabric with the same width as the collecting drum as the receiving substrate A, and inject the PVDF / (DMF / THF) precursor solution with a concentration of 30wt% configured in the first step into the syringe for electrospinning.
[0056] Regulate the metal spinneret of injector and apply high-voltage electrostatic field between the drum receiving substrate A, the high-voltage electros...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The first step is to prepare the electrospinning precursor polystyrene (PS) solution:
[0064] Weigh a certain amount of PS that has been vacuum-dried and analytically pure, select N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as a solvent, and prepare a DMF solution with a mass fraction of 10 wt% PS. At a heating temperature of 25°C, heat and stir until the polymer is completely dissolved, and then set aside for later use.
[0065] The second step, electrospinning to prepare hydrophobic PS electrospun membrane:
[0066] A non-woven fabric with the same width as the collecting drum was selected as the receiving substrate, and the PS / DMF precursor solution with a concentration of 10 wt% prepared in the first step was injected into the syringe for electrospinning.
[0067] A high-voltage electrostatic field is applied between the metal spinneret of the injector and the receiving base of the drum. The high-voltage electrostatic field voltage is 35kV, the diameter of the metal spinneret is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap