A method for recovering palladium from palladium-containing waste catalyst
A waste catalyst and palladium ion technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of palladium scarce resource waste, complex process flow, environmental pollution, etc., to avoid high energy consumption and environmental pollution, short process flow, and high recovery rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
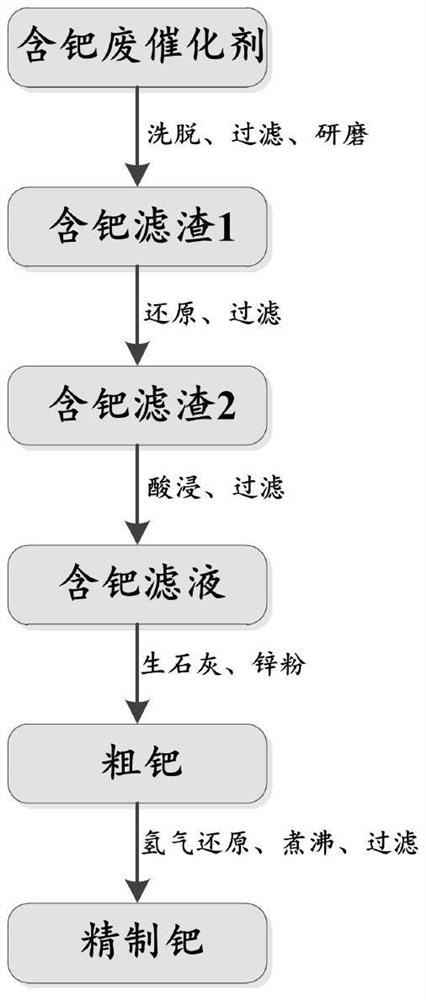
[0023] 100g of palladium-containing waste catalyst was added to a 1000mL flask, and 300mL of a composite solution was added. The composite solution included carbon tetrachloride, ethanol, methanol, petroleum ether, glacial acetic acid, carbon disulfide, chloroform and ether. Each component in the composite solution was added The ratio is the same, washed 3 times for 30 minutes each time; after filtration, the palladium-containing waste catalyst is ground and pulverized into powder with a particle size of 20-200 mesh, and 100 mL of hydrazine hydrate is added to reduce it at 80 ° C for 30 min. Filter, carry out acid leaching of filter residue with 100mL aqua regia for 30min, then add 30g quicklime, 4g zinc powder successively, obtain sponge palladium after passing hydrogen for 10min, finally boil it, filter to obtain refined palladium, and its recovery of palladium The rate reached 99.4%.
Embodiment 2
[0025] 100g of palladium-containing waste catalyst was added to a 1000mL flask, and 300mL of a composite solution was added for washing 3 times for 25 minutes each time. The composite solution included carbon tetrachloride, ethanol, methanol, glacial acetic acid, carbon disulfide, chloroform and ether. The addition ratio of each component in the liquid is the same; after filtration, the palladium-containing waste catalyst is ground and pulverized, and 100 mL of sodium borohydride-methanol solution (mass fraction is 40%) is added to reduce it for 30 min at 80 ° C, and after filtration, The filter residue was subjected to acid leaching with 100 mL of aqua regia for 30 min, then 30 g of quicklime and 5 g of tin powder were added successively, and palladium sponge was obtained after passing in hydrogen for 10 min. Finally, it was boiled and filtered to obtain refined palladium, and its recovery rate to palladium reached 99.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0027] In a 1000mL flask, 100g of palladium-containing waste catalyst was added, and 300mL of a composite solution was added. The composite solution included carbon tetrachloride, ethanol, methanol, carbon disulfide, chloroform and diethyl ether, and each component was added in the same proportion in the composite solution. Washed 3 times for 50 minutes each time; after filtration, the palladium-containing waste catalyst was ground and pulverized, 100 mL of formic acid was added at 80°C, and the mixture was reduced for 30 min. After filtration, the filter residue was acid leached with 100 mL of aqua regia for 30 min. Then 25g of quicklime and 6g of magnesium powder were added successively, the palladium sponge was obtained after passing hydrogen for 20min, and finally it was boiled and filtered to obtain refined palladium, and its recovery rate to palladium reached 99.3%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com