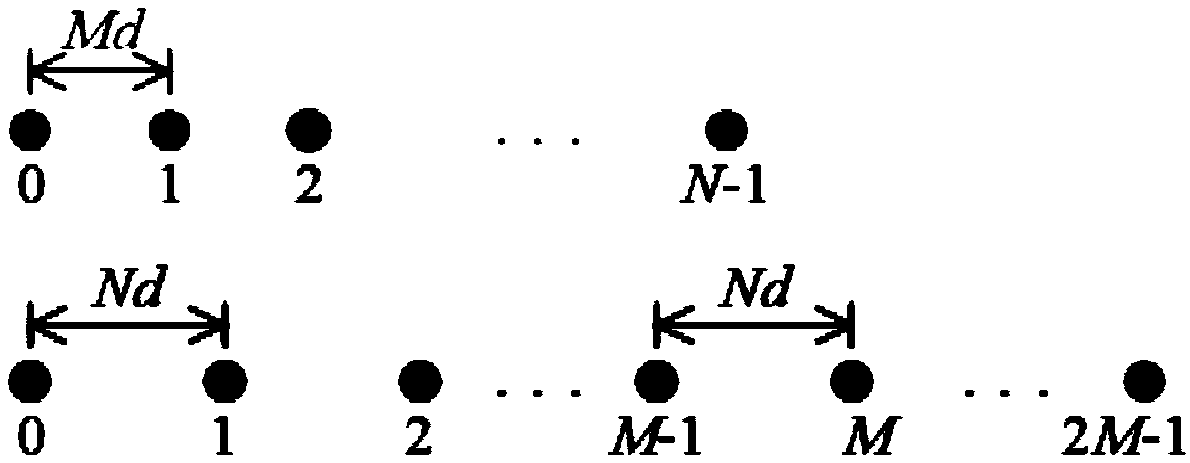
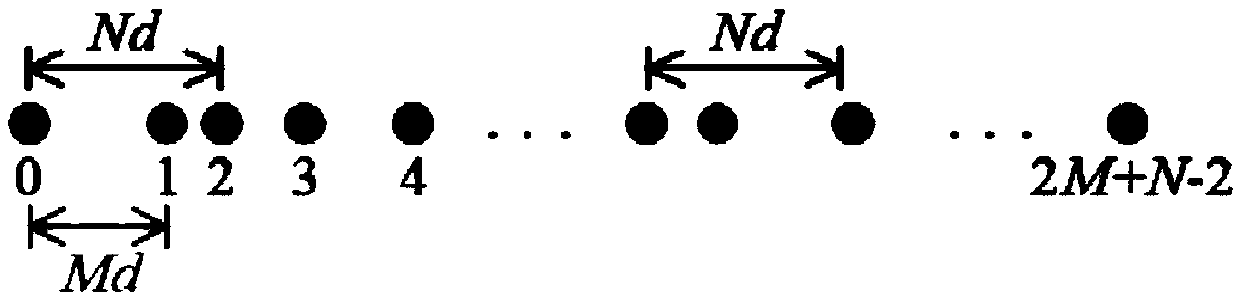Direction of arrival estimation method based on relatively prime array second-order equivalent virtual signal disperse Fourier inversion
A direction-of-arrival estimation and discrete Fourier technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as high computational complexity, inability to obtain signal power information, and hardware implementation difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0096] Simulation example 1: A coprime array is used to receive incident signals, and its parameters are selected as M=9, N=10, that is, the coprime array of the structure contains a total of 2M+N−1=27 physical array elements. Fixed sampling snapshot number T=1000, respectively test under different signal-to-noise ratios, the power estimation accuracy of the method proposed in the present invention is expressed by root mean square error (RMSE) to a single signal source and 30 signal sources, and its calculation The formula is:
[0097]
[0098] Among them, Q is the number of Monte Carlo trials, Indicates the power estimate of the l-th signal in the q-th Monte Carlo trial, is the actual power of the lth signal. In this simulation, Q=1000. For the case of a single signal source, the incident direction of the signal source in each Monte Carlo test satisfies the Gaussian distribution For the case of 30 signal sources, the incident directions of the signal sources are eve...
example 2
[0099] Simulation example 2: adopt the same coprime array as simulation example 1 to receive the incident signal, the signal-to-noise ratio is set to 10dB, test respectively in the case of different sampling snapshots, the method proposed by the present invention is for a single signal source and 30 signals The power estimation accuracy of the source, other simulation conditions remain the same as simulation example 1. The accuracy of power estimation in the case of a single signal source and 30 signal sources under the condition of different sampling snapshots is as follows: Figure 5 shown. It can be seen that in the case of a single signal source, the root mean square error of power estimation is less than 1dB; in the case of 30 signal sources, when the number of sampling snapshots is greater than 300, the root mean square error of power estimation is reduced to below 1dB . Therefore, the method proposed in the present invention can estimate signal power more accurately. ...
example 3
[0100] Simulation example 3: The same coprime array as simulation example 1 is used to receive the incident signal, the signal-to-noise ratio is set to 10dB, and the number of sampling snapshots is set to T=500. Assume that the number of incident narrowband signals is 30, and the incident directions are evenly distributed in the spatial angle range of 45° to 135°. The spatial power spectrum obtained by the proposed method of the present invention is as Figure 6 , where the vertical dotted line represents the true direction of the incident signal source. It can be seen that the method proposed in the present invention can effectively distinguish the 30 incident signal sources. For the traditional direction of arrival estimation method using a uniform linear array, only 26 incident signals can be resolved at most by using 27 physical array elements. The above results show that the method proposed in the present invention has achieved an increase in the degree of freedom.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com