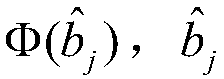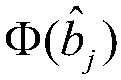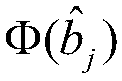Wavelength division multiple access ultra-wideband multiuser detection method based on Gaussian mixture model clustering
A Gaussian mixture model, multi-user detection technology, applied in the field of ultra-broadband communication, can solve the problems of low detection performance and poor real-time performance, and achieve the effect of solving excessive computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0017] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 As shown, a WDM multi-user detection method based on Gaussian mixture model clustering comprises the following steps:
[0018] Step 1: Obtain WDM UWB signals under Gaussian channels, input the UWB signals into K matched filters for preliminary detection, and obtain the matched filter result y=[y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y K ] T , where y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y K is the matched filtering result from the first user to the Kth user;
[0019] Step 2: Perform symbol judgment and symbol mapping on the matched filter result y of K users, and map the matched filter result y to a symbol mapping result conforming to the Gaussian mixture model The result of symbol judgment for the matched filter result y of the jth user;
[0020] Step 3: Map the code element to the result Gaussian mixture model clustering is carried out, and after the error symbols are corrected, the WDM ultra-wideband multi-user detection result is output.
[0021] In the case ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0023] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the cross-correlation coefficient matrix R=(r of the K matched filters described in the step one ij ) K×K , satisfy and r ii >>|r ij |, r ii ≈1, i,j=1,2,…,K, i≠j; where r ii is the i-th row and i-column element in the cross-correlation coefficient matrix R, r ij is the element in row i and column j in the cross-correlation coefficient matrix R.
[0024] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step two, the matched filtering results y of the K users are j Carry out symbol judgment and symbol mapping, and match the filter result y j Mapped to the symbol mapping result conforming to the Gaussian mixture model The specific process is:
[0026] Step 21: Let the initial mapping function in Is the result of the sign judgment of the matched filtering result y; where A is a diagonal matrix, The result of symbol judgment for the matched filter result y from the first user to the Kth user;
[0027] Step two two: Yes Taking the partial derivative, we get:
[0028]
[0029] Step 23: Let the mapping equation be:
[0030]
[0031] where A j is the amplitude value of the jth ultra-wideband signal received;
[0032] according to The mapping equation is rewritten as:
[0033]
[0034] where b i is the sending symbol, n j Gaussian whit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com