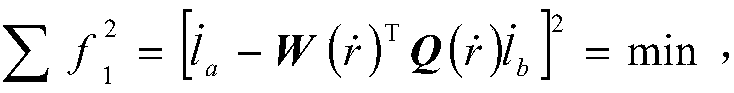Non-initial value solving method for three-dimensional spatial similarity transformation model parameters based on linear feature constraints
A technology of similarity transformation and straight line feature, applied in the field of surveying and mapping, it can solve problems such as unsatisfactory initial value, influence on reliability of calculation results, and non-convergence of results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] Embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawings:
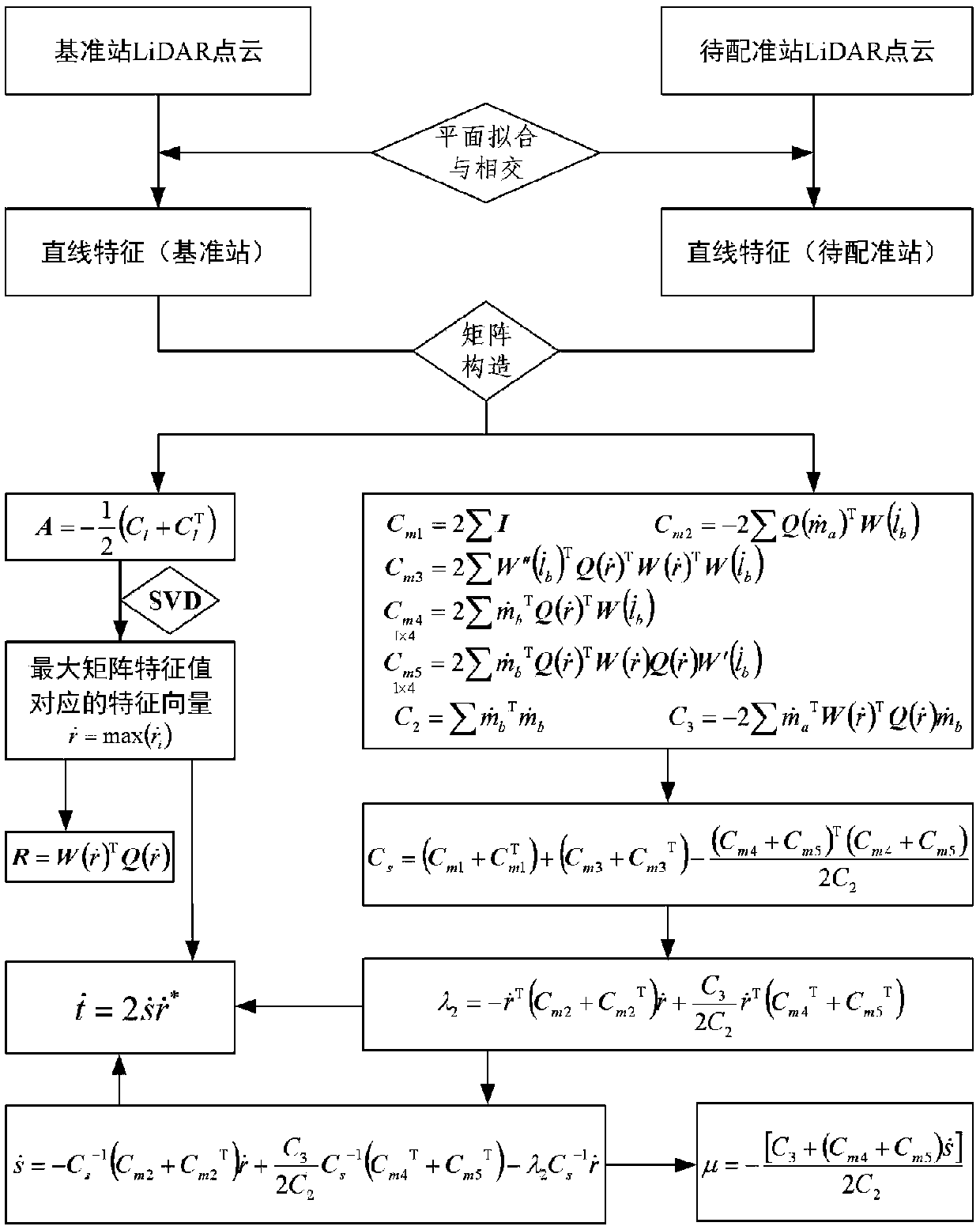
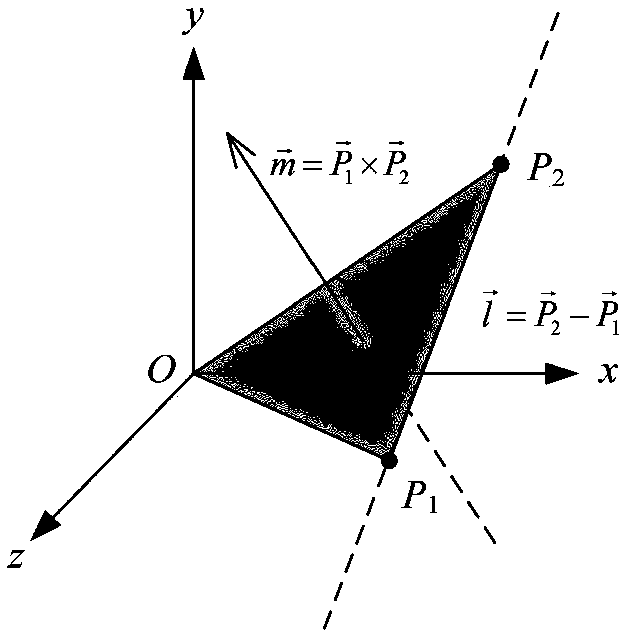
[0062] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for solving the parameters of the three-dimensional similar transformation model based on linear feature constraints in the present invention without an initial value, for the same measured area, selects different viewing angles to arrange two adjacent measuring stations, and uses two adjacent measuring stations The surface feature LiDAR point cloud of the measured target is collected by the station. There is overlap between two adjacent station point clouds, and there are three or more sets of straight line features with the same name in the overlapping area. Select one of the station as the reference station , take another measuring station as the station to be registered, and take the complete coincidence of features of the same name as the constraint condition, solve the conversion parameters of the coordinate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com