Multidimensional joint nonuniformity correction method for infrared imaging system
A non-uniformity correction, infrared imaging system technology, applied in the field of infrared imaging, can solve problems such as large computational load, increased hardware overhead of imaging system, and impact on imaging quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
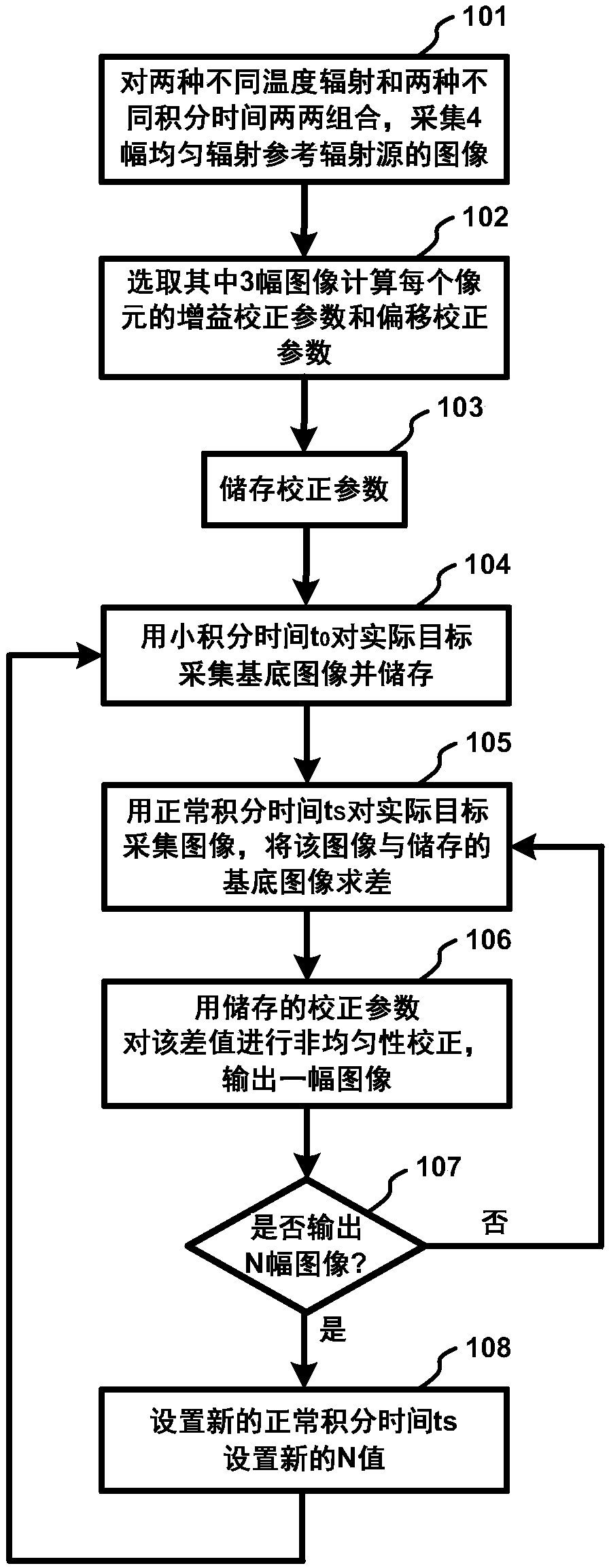
[0070] Such as figure 2 As shown, the method for multi-dimensional joint non-uniformity correction in the embodiment of the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0071] (1) Collect 3 corrected images for the black body (as a reference radiation source for uniform radiation), including: setting the black body temperature to T H , set the integration time to t C , collect the first corrected image D(T H ,t C ); keep the blackbody temperature T H , set the integration time to t 0 (t 0 C ), the second corrected image D(T H ,t 0 ); reduce the blackbody temperature to T L , set the integration time to t C , collect the third corrected image D(T L ,t C ); the gray value of the pixel (i, j) in these three images is
[0072] D. i,j (T H ,t C ) = t C ×[G i,j ×L(T H )+B i,j ]+[V×A i,j +O i,j ] (11)
[0073] D. i,j (T H ,t 0 ) = t 0×[G i,j ×L(T H )+B i,j ]+[V×A i,j +O i,j ] (12)
[0074] D. i,j (T L ,t C ) = t C ×[G i,j ×L(T ...
Embodiment 2
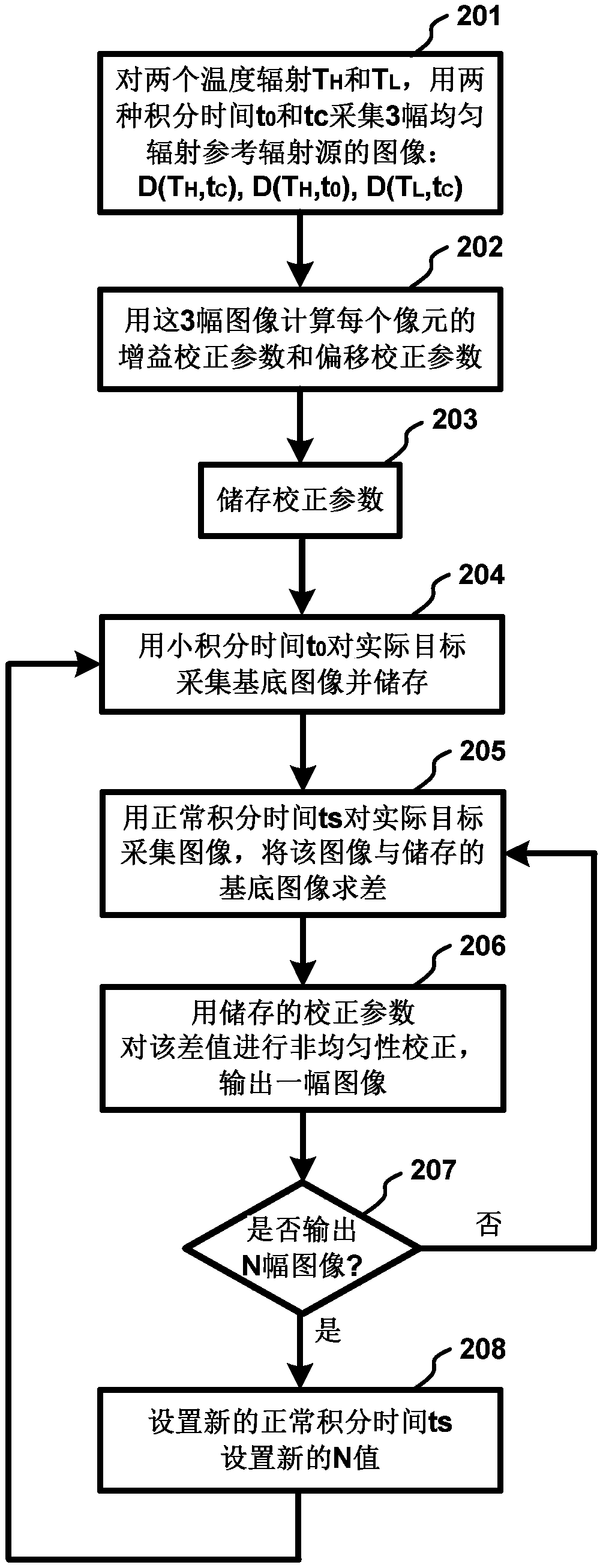
[0103] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the method for multi-dimensional joint non-uniformity correction in the embodiment of the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0104] (1) Collect 3 corrected images for the black body (as a reference radiation source for uniform radiation), including: setting the black body temperature to T H , set the integration time to t C , collect the first corrected image D(T H ,t C ); keep the blackbody temperature T H , set the integration time to t 0 (t 0 C ), the second corrected image D(T H ,t 0 ); reduce the blackbody temperature to T L , set the integration time to t 0 , collect the third corrected image D(T L ,t 0 ); the gray value of the pixel (i, j) in these three images is
[0105] D. i,j (T H ,t C ) = t C ×[G i,j ×L(T H )+B i,j ]+[V×A i,j +O i,j ] (25)
[0106] D. i,j (T H ,t 0 ) = t 0 ×[G i,j ×L(T H )+B i,j ]+[V×A i,j +O i,j ] (26)
[0107] D. i,j (T L ,t 0 ) = t 0 ×[G i,j ×L(T ...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the method for multi-dimensional joint non-uniformity correction in the embodiment of the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0139] (1) Collect 3 corrected images for the black body (as a reference radiation source for uniform radiation), including: setting the black body temperature to T L , set the integration time to t C , collect the first corrected image D(T L ,t C ); keep the blackbody temperature T L , set the integration time to t 0 (t 0 C ), the second corrected image D(T L ,t 0 ); Raise the blackbody temperature to T H , set the integration time to t C , collect the third corrected image D(T H ,t C ); the gray value of the pixel (i, j) in these three images is
[0140] D. i,j (T L ,t C ) = t C ×[G i,j ×L(T L )+B i,j ]+[V×A i,j +O i,j ] (39)
[0141] D. i,j (T L ,t 0 ) = t0 ×[G i,j ×L(T L )+B i,j ]+[V×A i,j +O i,j ] (40)
[0142] D. i,j (T H ,t C ) = t C ×[G i,j ×L(T H ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com