A Method for Ionospheric Clutter Suppression of High Frequency Ground Wave Radar
A high-frequency ground wave radar and clutter suppression technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to suppress ionospheric interference well, missing Bragg peak information, and not being suitable for wide beam radar, etc. Achieve the effects of reducing energy decline, improving detection performance, and suppressing strong ionospheric clutter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0035] Specific embodiment one: a kind of high-frequency ground wave radar ionospheric clutter suppressing method comprises the following steps:
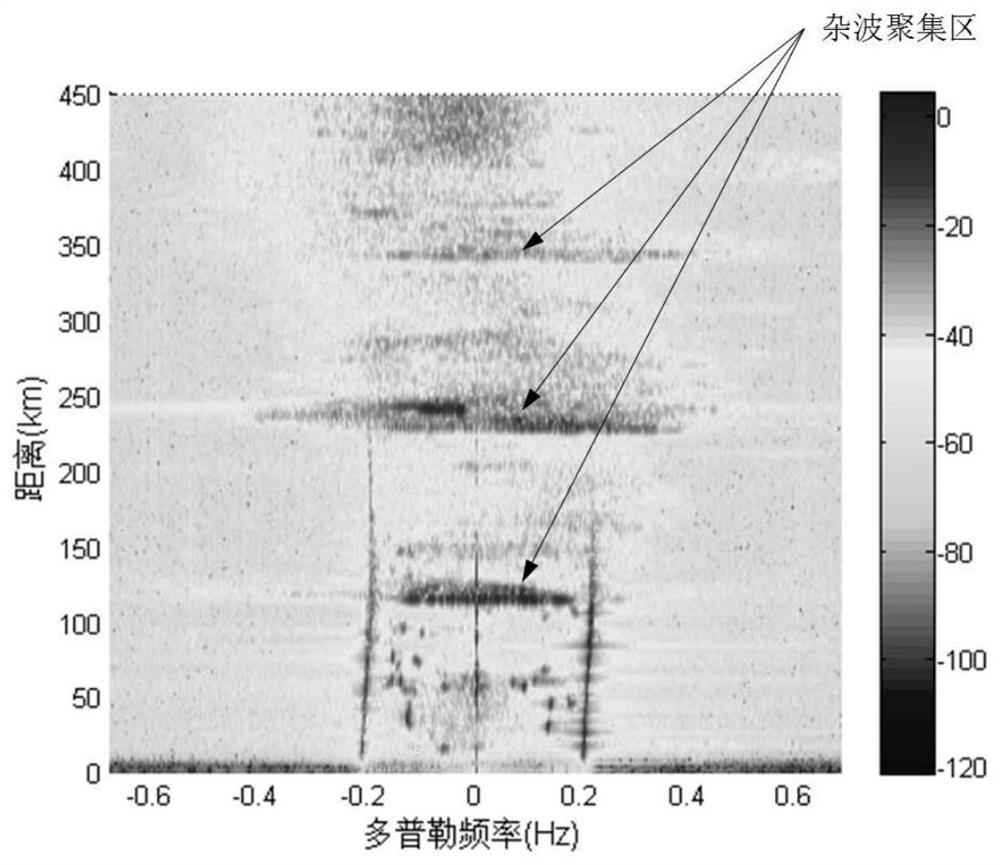
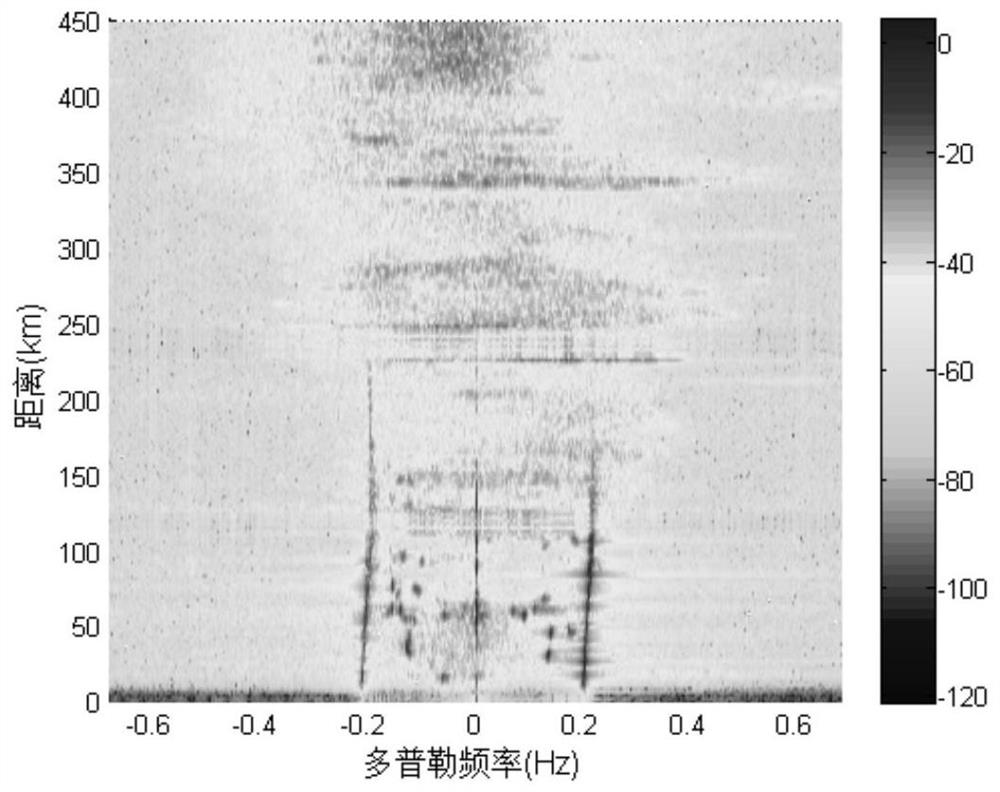
[0036] Step 1: From the radar range-Doppler spectrum (R-D spectrum), according to the ionospheric clutter distribution characteristics, determine the distance element k of the clutter center corresponding to each ionospheric clutter accumulation area according to the distance from near to far i ,i=0,1,...,p, corresponding to Es layer clutter and its one-hop echo, two-hop echo, etc., p is the number of clutter center distance elements;
[0037] Step 2: According to the clutter center distance element k determined in step 1 i , to calculate the ionospheric clutter distance element k in the clutter center i and the distance element k adjacent to the clutter center distance element i +1 on the distance correlation coefficient
[0038] Step 3: Research shows that the distance correlation coefficient of normal ocean echo signals is 0...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0050] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the ionospheric clutter is calculated in the step two in the clutter center distance element k i and the distance element k adjacent to the clutter center distance element i +1 on the distance correlation coefficient The specific process is:
[0051]
[0052] where X(k i ) is the k-th radar i Echo data on distance elements, Cov[X(k i ), X(k i +1)] is the kth i distance element and the kth i Covariance of echo data on +1 range element, Var[X(k i )] for X(k i )Variance; The larger the ionospheric clutter is at two adjacent distance elements k i with k i The stronger the correlation on +1.
[0053] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0054] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the clutter center distance element d of calculating the clutter center of the ionospheric accumulation area in the described step 4 0 The distance element d from the clutter center of the j-th jump echo gathering area j The correlation coefficient of The specific process is:
[0055]
[0056] where X(d 0 ) is the distance element d of the clutter center of the radar in the accumulation area of the Es layer 0 The echo data on X(d j ) is the clutter center distance element d j The echo data on , Cov[X(d 0 ), X(d j )] is the covariance of the ionospheric Es-layer clutter and its j-th jump echo data, Var[X(d j )] for X(d j )Variance; The larger is, the stronger the cross-correlation between the ionospheric Es layer clutter and its j-th jump echo.
[0057] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com