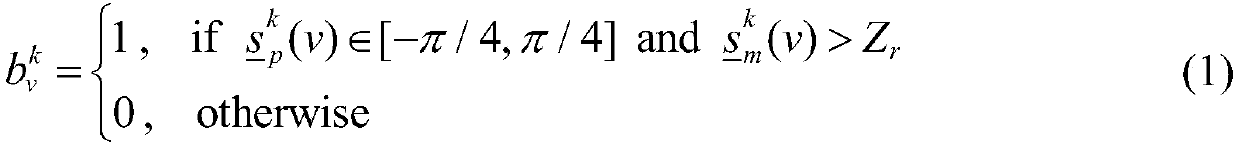Method for recognizing spatial difference by utilizing complex number fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) space source phase
A phase recognition and spatial difference technology, applied in the field of biomedical signal processing, to achieve high sensitivity and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] A specific embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the technical scheme and accompanying drawings.
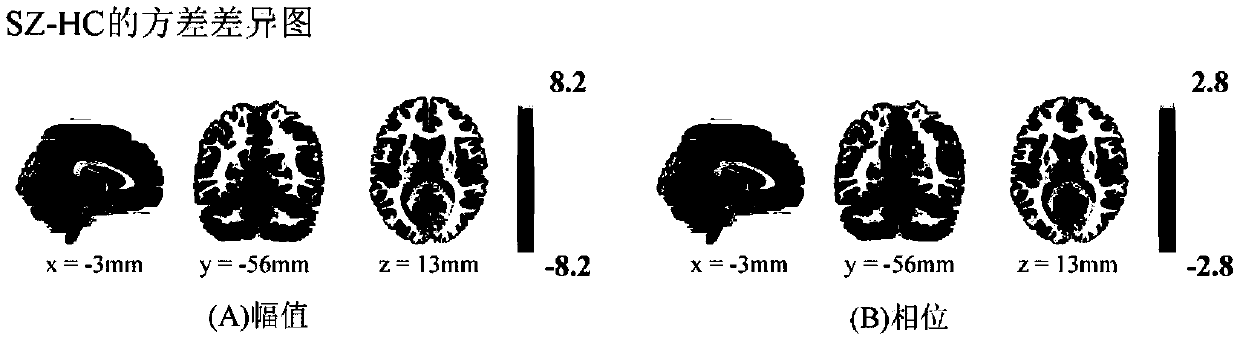
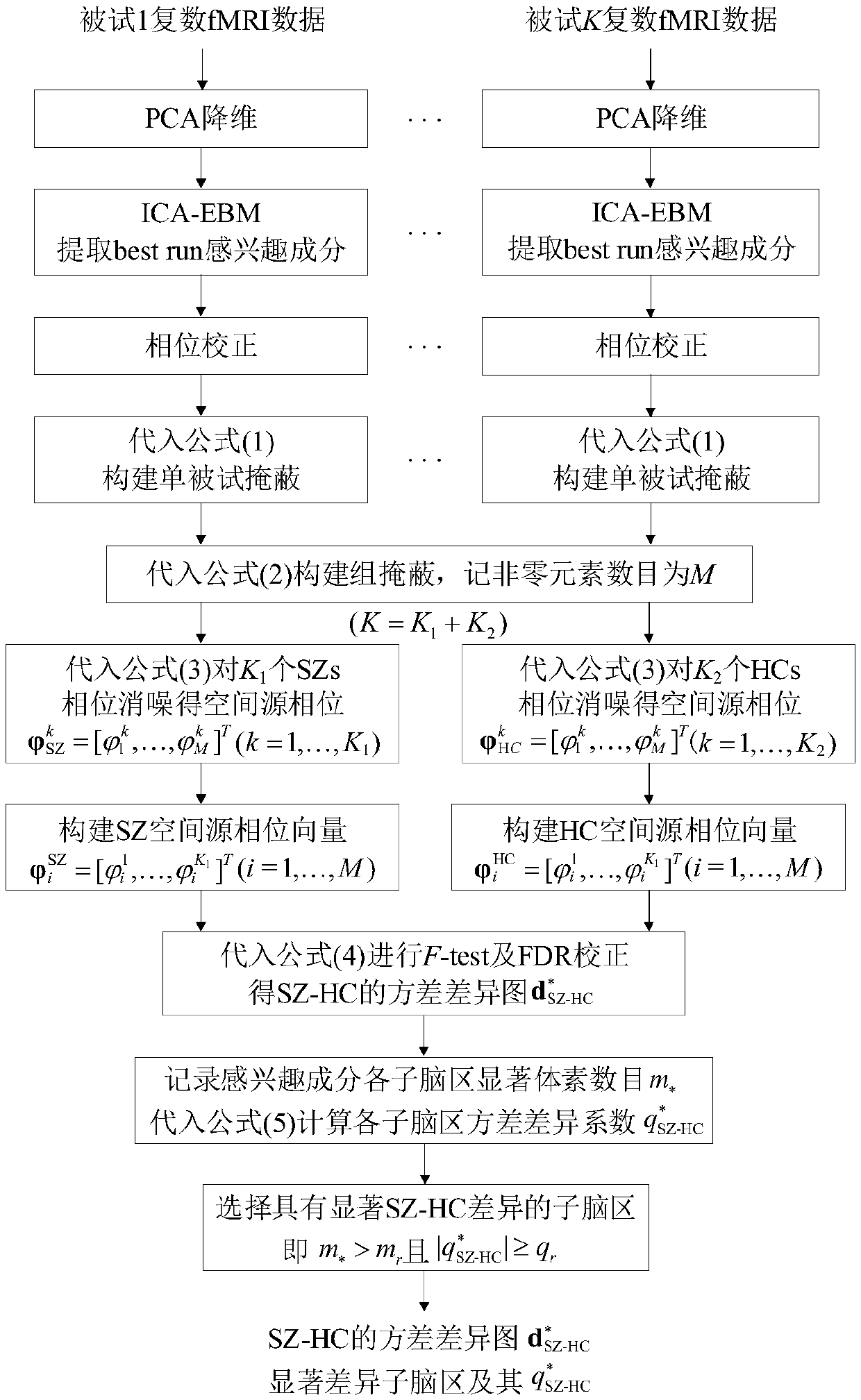
[0034] Existing K 1 = 42 SZs and K 2= Complex fMRI data acquired in the resting state of 40 HCs (K=82). In the time dimension, T=146 scans were performed, each scan obtained 53×63×46 whole brain data, and the number of voxels in the brain was V=62336. The steps of using the present invention to analyze the spatial source phase to identify the spatial difference between SZs and HCs are as attached figure 2 shown.
[0035] Step 1: Input multi-subject complex fMRI data
[0036] Step 2: For all single subjects X k Carry out PCA dimensionality reduction, take N=120, and obtain dimensionality reduction data
[0037] Step 3: Use the complex EBM algorithm for all single subjects Perform R=10 times of complex ICA separation in sequence, extract the component of interest DMN from 120 estimated components, use the best ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com