Conductive polymer dispersion liquid, conductive substrate and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of conductive polymers and conductive substrates, which is applied in the direction of conductive coatings, coatings, fireproof coatings, etc., and can solve problems such as poor display, adverse effects of detection of electrostatic capacitance changes on touch panels, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
manufacture example 1
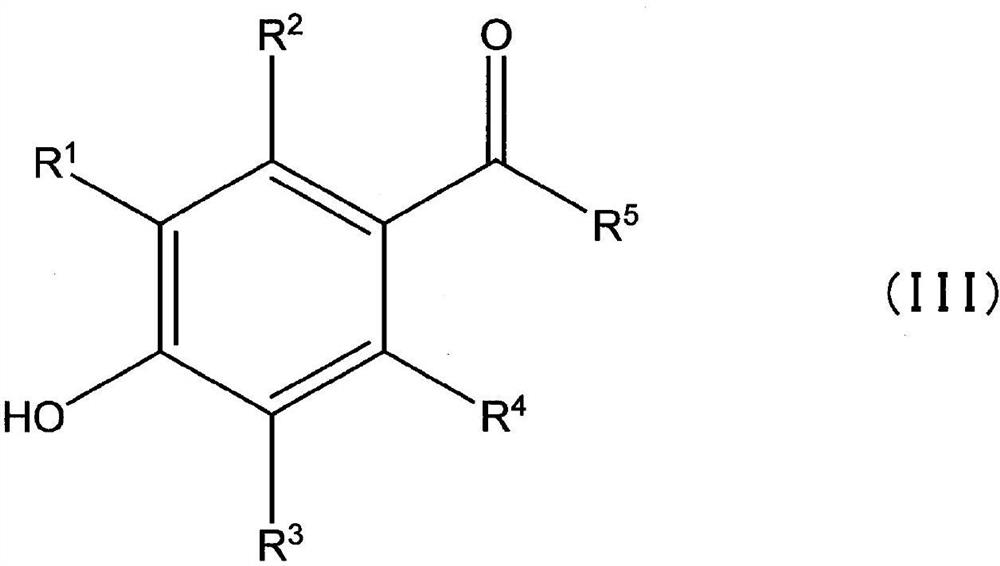
[0156] 206 g of sodium styrene sulfonate was dissolved in 1000 ml of ion-exchanged water, and while stirring at 80° C., 1.14 g of ammonium persulfate oxidizing agent solution previously dissolved in 10 ml of water was added dropwise over 20 minutes, and the solution was stirred for 12 hours.
[0157] 1,000 ml of sulfuric acid diluted to 10% by mass was added to the obtained solution containing sodium styrene sulfonate, and 1,000 ml of the solution containing polystyrene sulfonic acid was removed by ultrafiltration, and 2,000 ml of ion-exchanged water was added to the raffinate. About 2000ml of the solution was removed by filtration. The above-mentioned ultrafiltration operation was repeated 3 times. About 2000 ml of ion-exchanged water was added to the obtained polystyrenesulfonic acid solution, and about 2000 ml of the solution was removed by ultrafiltration. This ultrafiltration operation was repeated 3 times.
[0158] Water in the resulting solution was removed under redu...
manufacture example 2
[0160] 14.2 g of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene and a solution obtained by dissolving 36.7 g of polystyrenesulfonic acid obtained in Production Example 1 in 2000 ml of ion-exchanged water were mixed at 20°C. While stirring the thus obtained mixed solution at 20°C, an oxidation catalyst solution of 29.64 g of ammonium persulfate and 8.0 g of iron sulfate dissolved in 200 ml of ion-exchanged water was slowly added, stirred for 3 hours, and allowed to react .
[0161] 2000 ml of ion-exchanged water was added to the obtained reaction liquid, and about 2000 ml of the solution was removed by ultrafiltration. This operation was repeated 3 times. Next, 200 ml of sulfuric acid diluted to 10% by mass and 2000 ml of ion-exchanged water were added to the obtained solution, about 2000 ml of the solution was removed by ultrafiltration, 2000 ml of ion-exchanged water was added thereto, and about 2000 ml was removed by ultrafiltration The solution. This operation was repeated 3 times.
[0162...
Embodiment 1
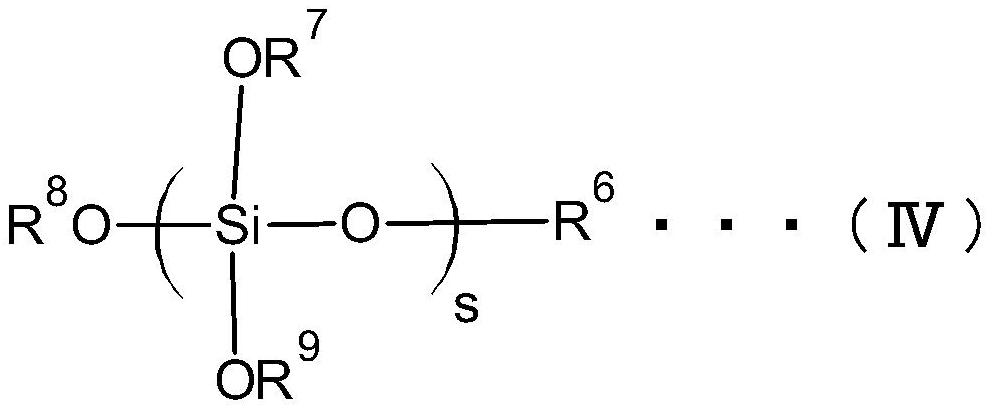
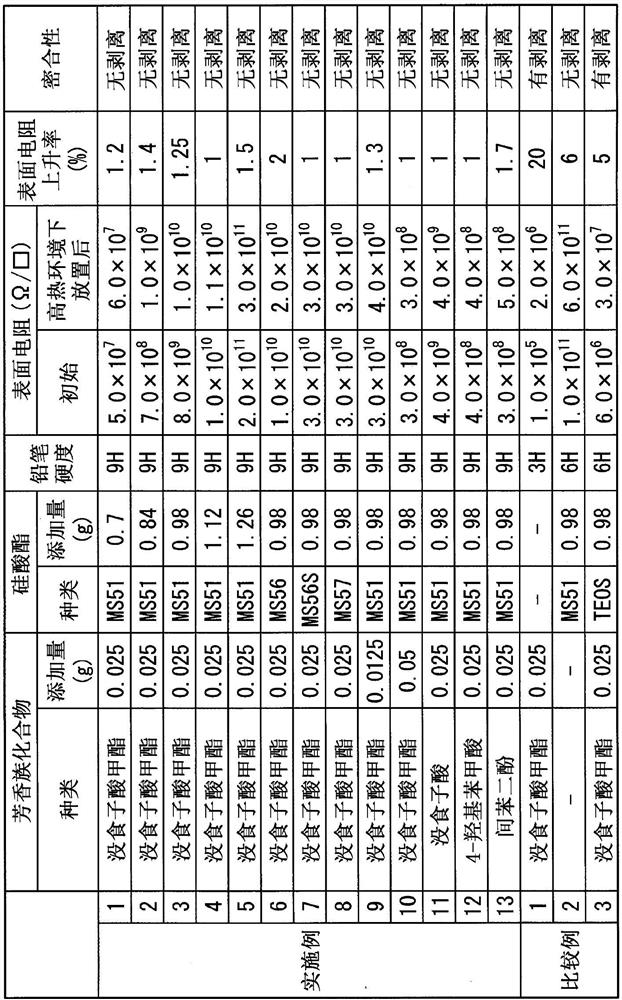
[0164] In 2.54 g of the PEDOT-PSS aqueous dispersion obtained in Production Example 2 (the amount of PEDOT-PSS is 0.03048 g), 2.54 g of water, 22.1 g of methanol, 2.73 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, 0.025 g of methyl gallate and Silicate (manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, MKC Silicate MS51, the silicate represented by the above chemical formula (I), a mixture of 4 to 6 silicon atoms, SiO 2 The content of the unit is 52 ± 1%, labeled "MS51" in the table. ) 0.7 g to obtain a conductive polymer dispersion.
[0165] The obtained conductive polymer dispersion was applied to an alkali-free glass substrate using a No. 8 bar coater to form a coating film. This coating film was heated and dried at a drying temperature of 110° C. and a drying time of 10 minutes to form a conductive layer and obtain a conductive substrate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com