Sudden capacity failure fault identifying and predetermining method for lithium iron phosphate power battery
A power battery, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as identification, and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of sudden capacity failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
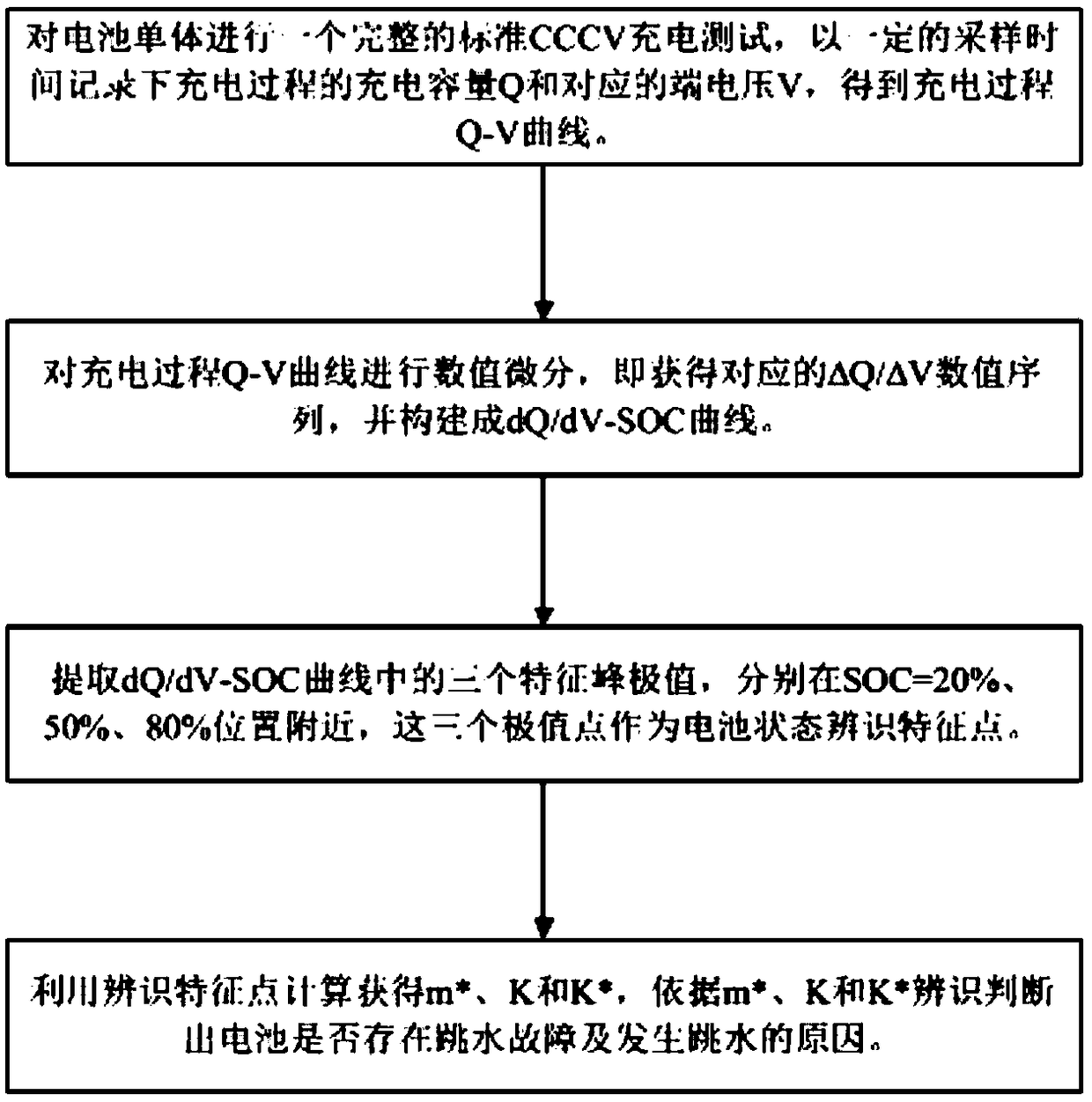
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for identifying and predicting the "diving" fault of a lithium iron phosphate power battery provided by the present invention includes the following steps:
[0027] Step S1: Carry out a complete standard constant current and constant voltage charging test (CCCV ), constant current charging to 3.65V, constant voltage charging until the end of current 0.02C, and record the charging capacity Q and the corresponding charging terminal voltage V data during the charging process, and get the Q-V curve of the charging process, the sampling and recording period used is 19s.
[0028] In principle, there is a certain difference between constant current and constant voltage charging and constant current charging. Constant current and constant voltage is to switch to constant voltage charging after constant current charging reaches the upper limit of the cut-off voltage until the current drops to approximately 0A. The two methods do not affect th...
Embodiment 2
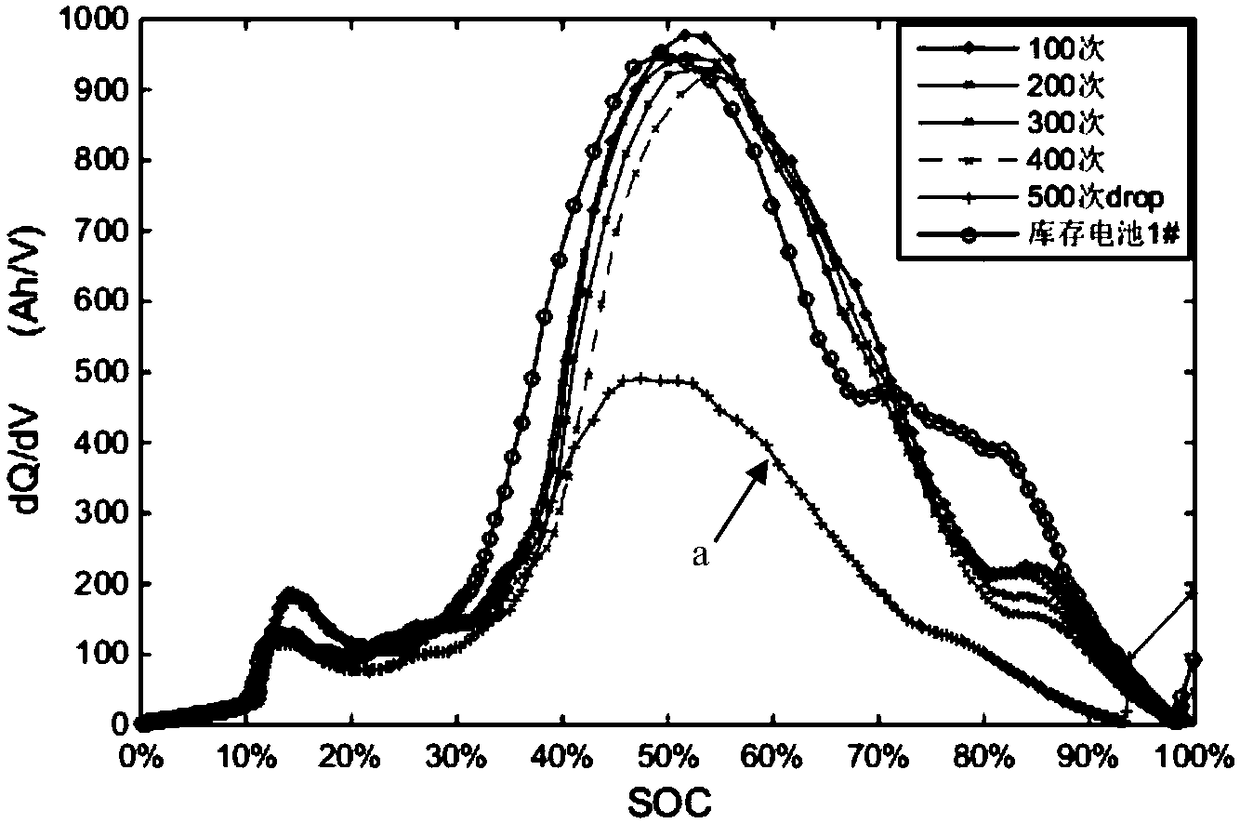
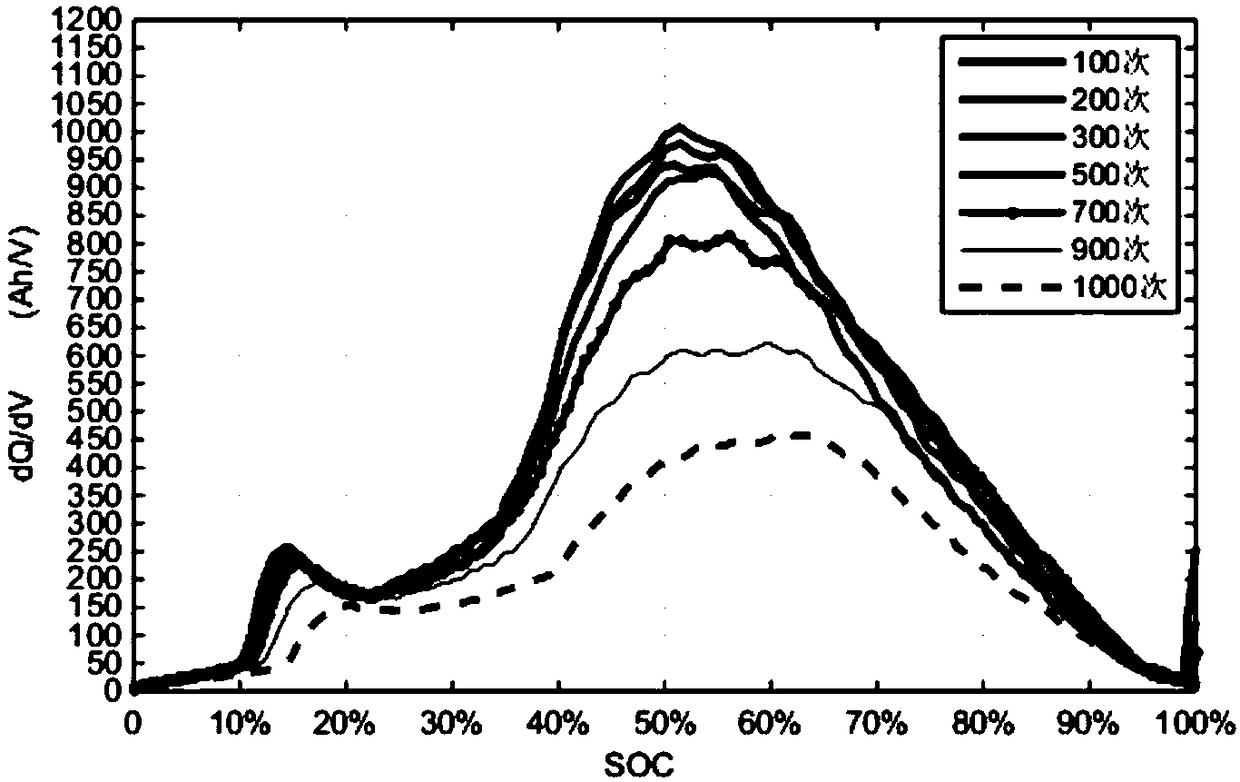
[0033] Embodiment 2 is a special case of Embodiment 1. The three characteristic peak extreme values in the dQ / dV-SOC curve described in step S3 may appear in some cases in the range of SOC=50% and SOC=80%. The coincidence of characteristic peaks (such as image 3 shown), the model of the battery under test is CA100FI, so the ordinate value corresponding to the dQ / dV curve at SOC=80% in the dQ / dV-SOC curve of the constant capacity charging process after the 700th cycle is approximately taken, as shown in image 3 , namely m*=355Ah / V, K=0.44, but K*=0.227 Figure 4 In the 59# cycle curve shown, the battery dives after the 1000th cycle, which is caused by the loss of active materials and eventually the loss of available active lithium ions. For example, the characteristic peaks corresponding to SOC=80% will disappear after hundreds of cycle decays for batteries with a capacity greater than 100Ah, and the characteristic peaks corresponding to SOC=50% and SOC=80% will be combined ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com