Method and device for temperature compensation of MEMS sensor
A temperature compensation and sensor technology, applied in the field of temperature compensation, can solve the problems of increasing hardware cost of MEMS sensors, obstacles to miniaturization and cost reduction of equipment, and insufficiency of sensors, so as to reduce CPU burden, reduce waiting time, Effect of Consistency Guarantee
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
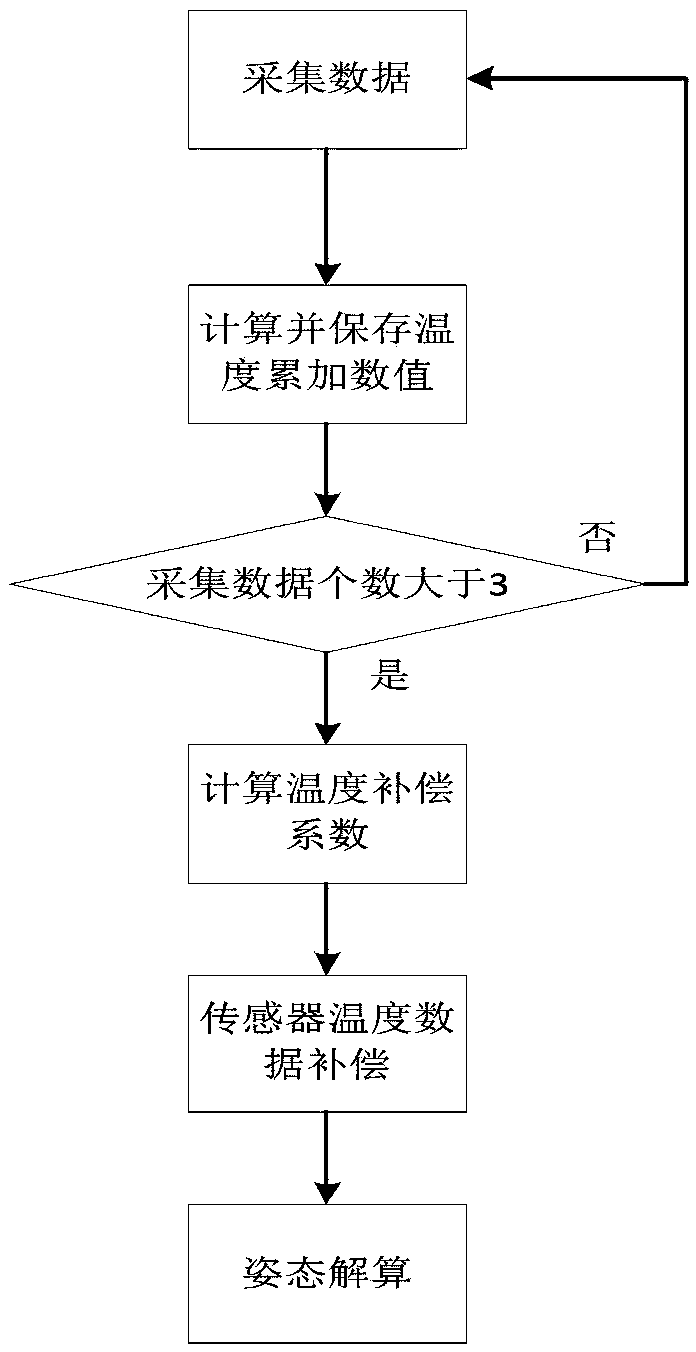
[0032] The flow process of the method of this embodiment is as follows figure 1 shown. Before describing the process, the theoretical basis of the method is introduced below.
[0033] (1) The specific implementation method of the fast temperature compensation algorithm.
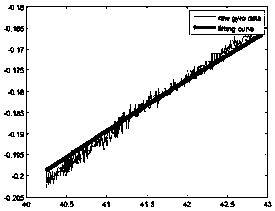
[0034] Assuming that the current sensor is in a static state, the ideal output should be the ideal initial value (this embodiment takes the gyroscope value, accelerometer, etc. as an example, and the ideal initial value is 0), but because of the influence of the ambient temperature change, its output It is not an ideal initial value (for example, a stationary gyroscope and accelerometer does not output a value of 0), but a biased value that has a certain relationship with temperature. This deviation is a static deviation, and compensating for this deviation is the main task of this embodiment.
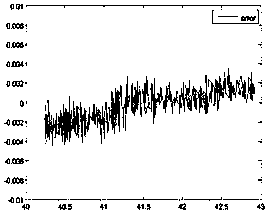
[0035] After a lot of experiments, we found that the static bias output data of the sensor can be fitted into a ...
Embodiment 2
[0087] In this embodiment, on the basis of the above-mentioned first embodiment, the assurance of considering the applicable conditions of the fast temperature compensation algorithm in the first embodiment is added.
[0088] If the carrier is static during the entire use time, then the temperature compensation can always be in operation and the temperature compensation coefficient can be calculated in real time, but this is obviously an ideal state. In actual use, the entire MEMS sensor is required to move, and the accuracy of this method is greatly reduced during movement. Therefore, how to distinguish the movement state and continue to perform temperature compensation after the movement stops is the key to improving the feasibility and accuracy of the entire algorithm.
[0089] When in motion, the noise output by the sensor is very large, which is almost an order of magnitude difference compared with that at rest. Therefore, it is only necessary to calculate the variance of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com