A low-power scheduling method for periodic tasks with proportional idle time allocation
A periodic task and idle time technology, applied in resource allocation, program control design, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of extended task execution time and increased static power consumption, so as to reduce energy consumption, reduce the number of processor shutdowns, and ensure The effect of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0039] Before the periodic task set is scheduled, calculate the optimal running speed of the periodic task in the offline state.
[0040] According to the earliest deadline first (EDF) principle, the periodic task set is sorted and inserted into the ready queue, and the first task in the ready queue is selected for scheduling.
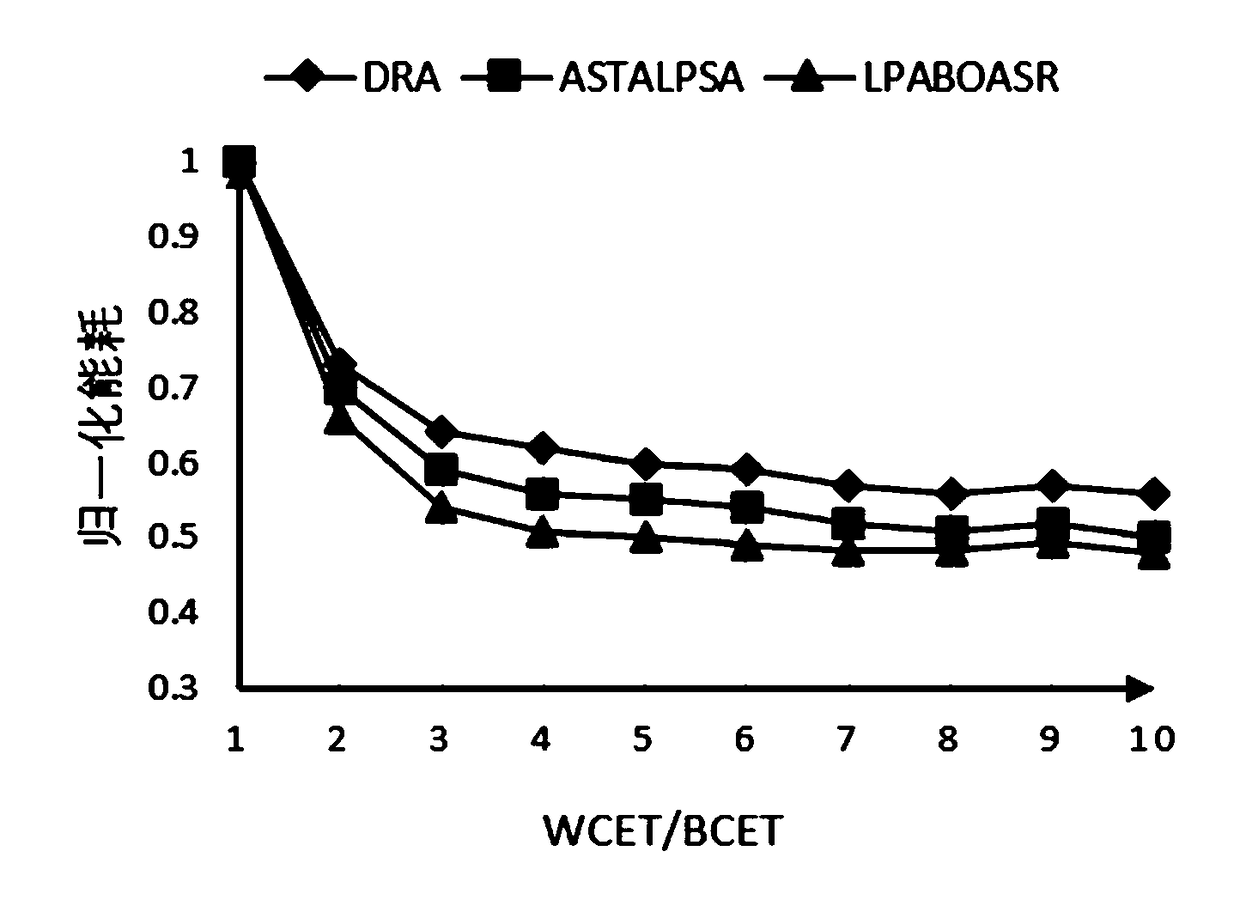
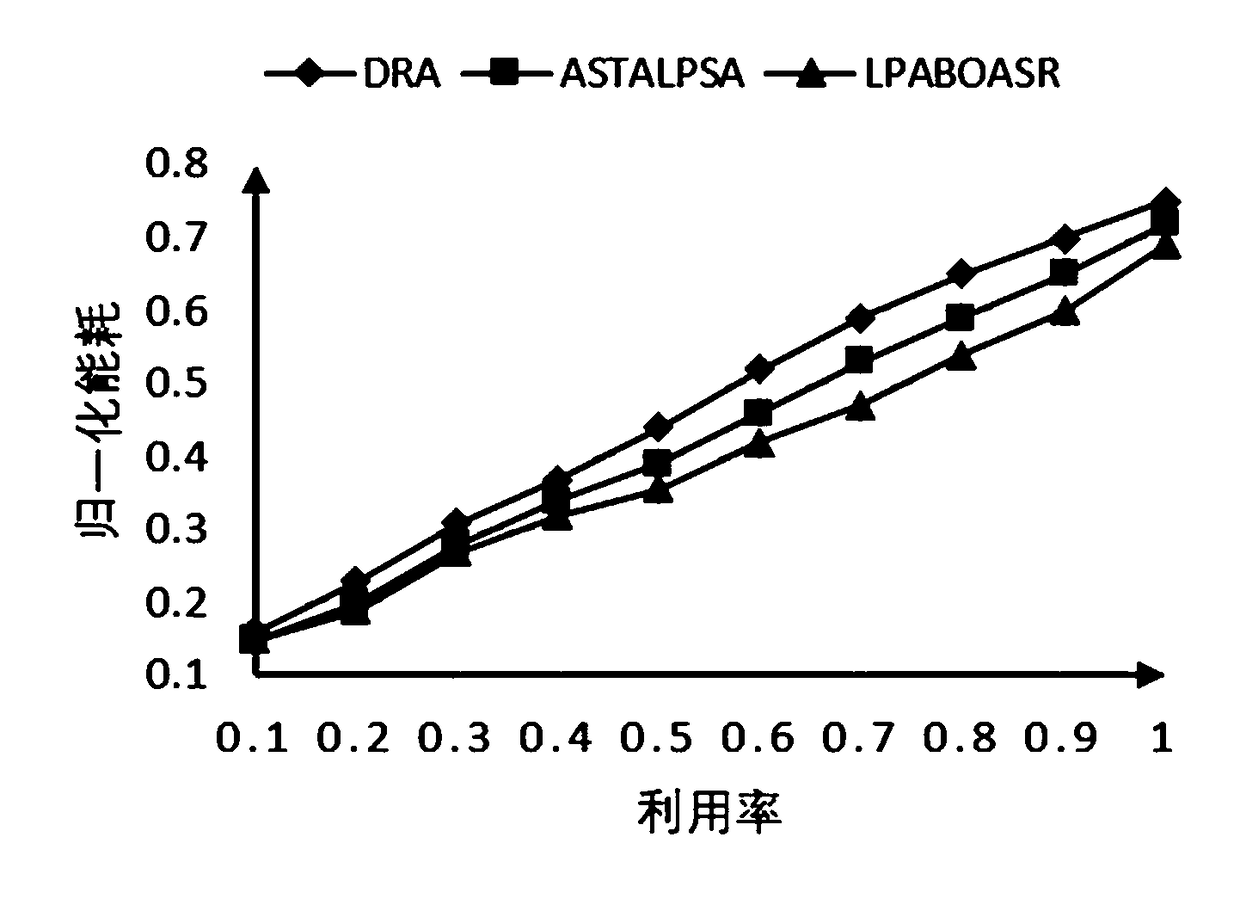
[0041] When a task completes, the task's idle time is reclaimed. If the ready queue is not empty, allocate the idle time to each task in the ready queue in proportion to WCET. Recalculate the running speed of each task in the ready queue. If the running speed is less than the critical speed, set the speed to the critical speed.
[0042] If the ready queue is empty and the idle time is greater than the overhead of shutting down the processor, shut down the processor until a new task arrives.
[0043] Specific steps a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com