Dynamic-accidental-task low-power-consumption scheduling method based on balance factor
A technology of balancing factor and scheduling method, applied in the direction of resource allocation, program control design, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing system energy consumption, reducing energy consumption, and increasing calorific value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
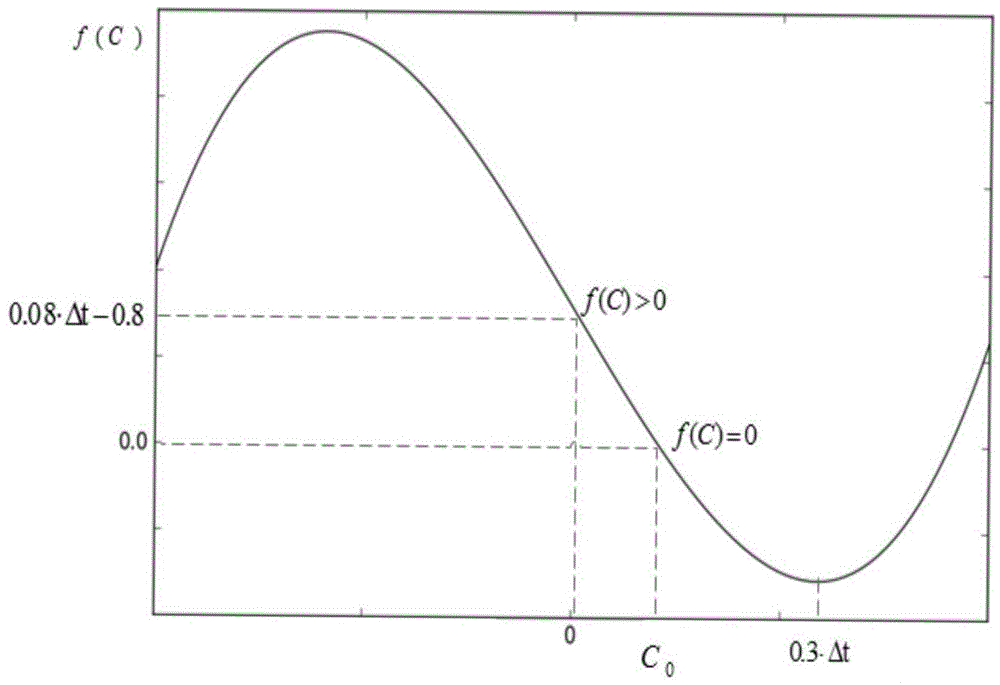
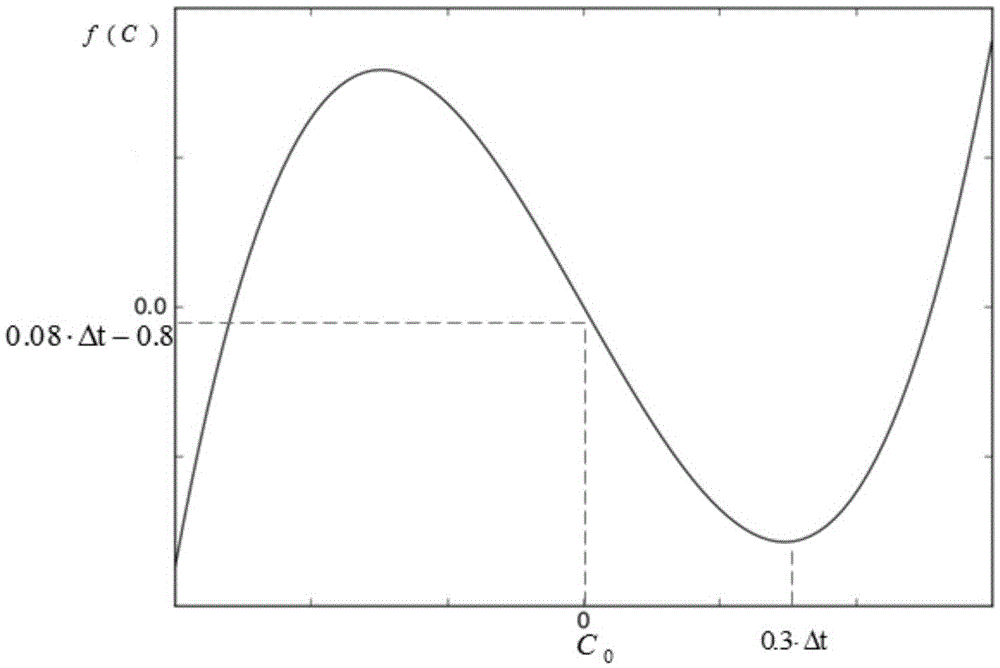
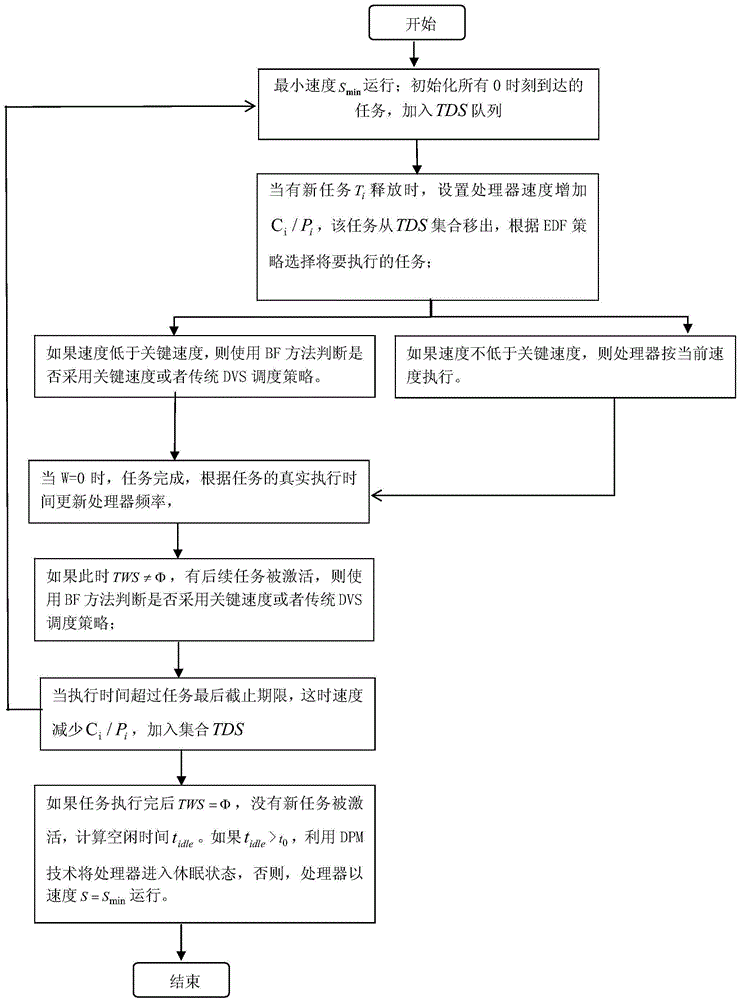
[0043] As shown in Fig. 1, DVS and critical speed strategy are commonly used technologies in low-power scheduling methods, and have been widely used. The invention in this paper combines these two low-power technologies. Considering the shortcomings of the traditional critical speed scheduling strategy, a sporadic low-power scheduling method based on balance factors is proposed. The present invention adjusts the speed of the processor in the offline phase according to the load of the released task, and fully utilizes the resources of the processor; in the online phase, the processor speed is dynamically updated by completing the remaining idle time in advance of the high-priority task, and when the processor has no task execution, Combined with the proposed balance factor critical speed scheduling strategy, it is judged whether to use DPM tech...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com