Dynamic identifier representation method, device and system for sequence learning
A dynamic identification and identifier technology, applied in the direction of text database query, unstructured text data retrieval, etc., to achieve the effect of stable convergence and small vocabulary
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
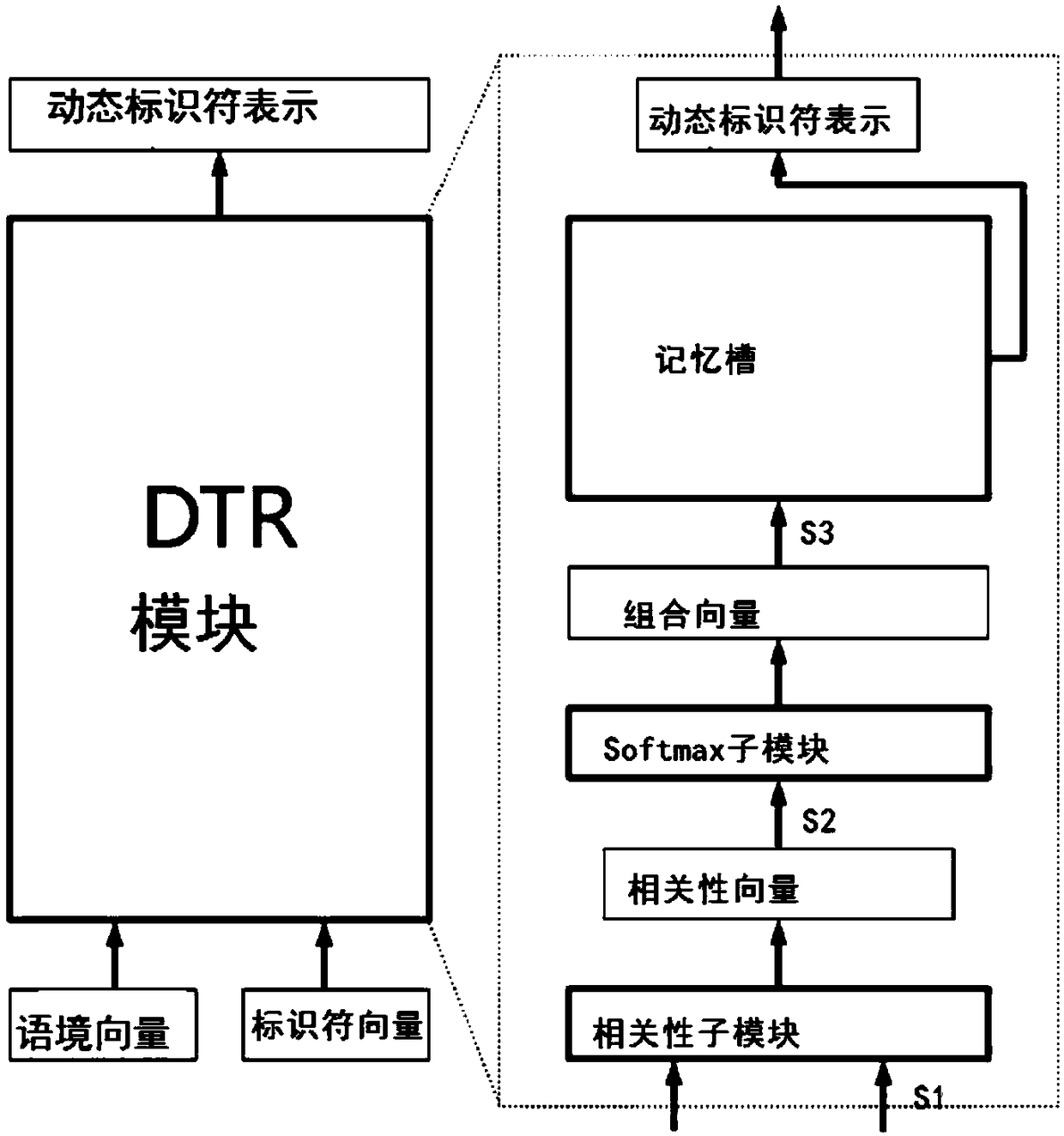
[0033] figure 1 Flowchart of the dynamic identifier representation method for sequence learning of the present invention. Including the following steps:
[0034] S1. The context vector and the identifier vector are used as input into the correlation sub-module, and a correlation operation is performed to obtain a correlation vector. The correlation operation can use many correlation functions, and the simplest correlation function is a splicing function. Assuming that the dimension of the context vector is n and the dimension of the identifier vector is m, then the dimension of the splicing function is n+m. Another correlation function that can be employed is the concatenation function of the fully connected variant. A well-designed correlation function can achieve better performance.
[0035] S2. Input the correlation vector into the Softmax sub-module, and perform a normalization operation (softmax) to obtain a combination vector. The combination vector is a probability...
Embodiment 2
[0038] According to another aspect of the present invention, the present invention also provides a dynamic identifier representation module for sequence learning. Including the following structures connected in the following order:
[0039] The correlation sub-module uses the context vector and the identifier vector as the input of the correlation sub-module to perform a correlation operation to obtain a correlation vector. The correlation operation can use many correlation functions, and the simplest correlation function is a splicing function. Assuming that the dimension of the context vector is n and the dimension of the identifier vector is m, then the dimension of the splicing function is n+m. Another correlation function that can be employed is the concatenation function of the fully connected variant. A well-designed correlation function can achieve better performance.
[0040] The Softmax sub-module inputs the correlation vector into the Softmax sub-module, performs...
Embodiment 3
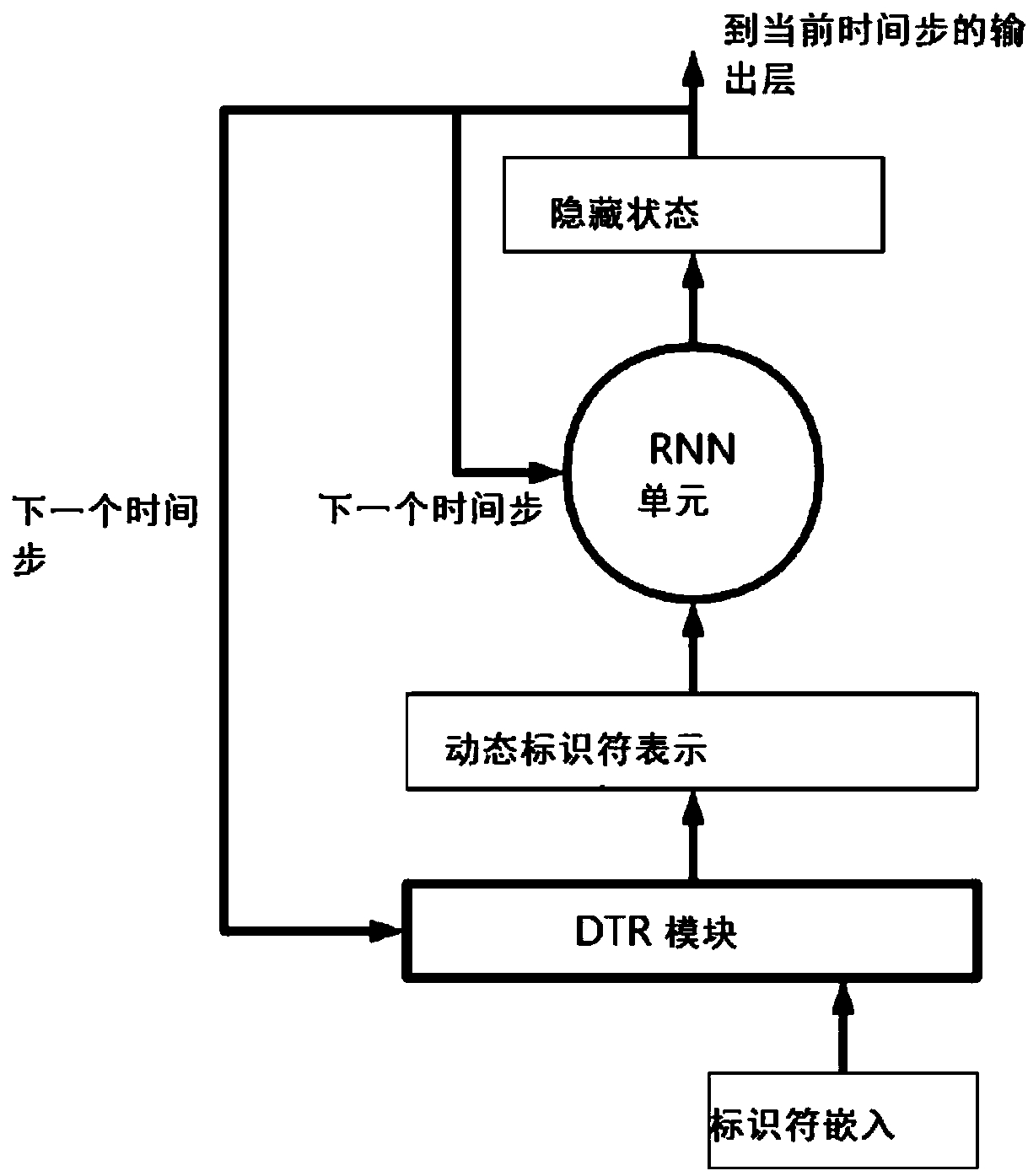
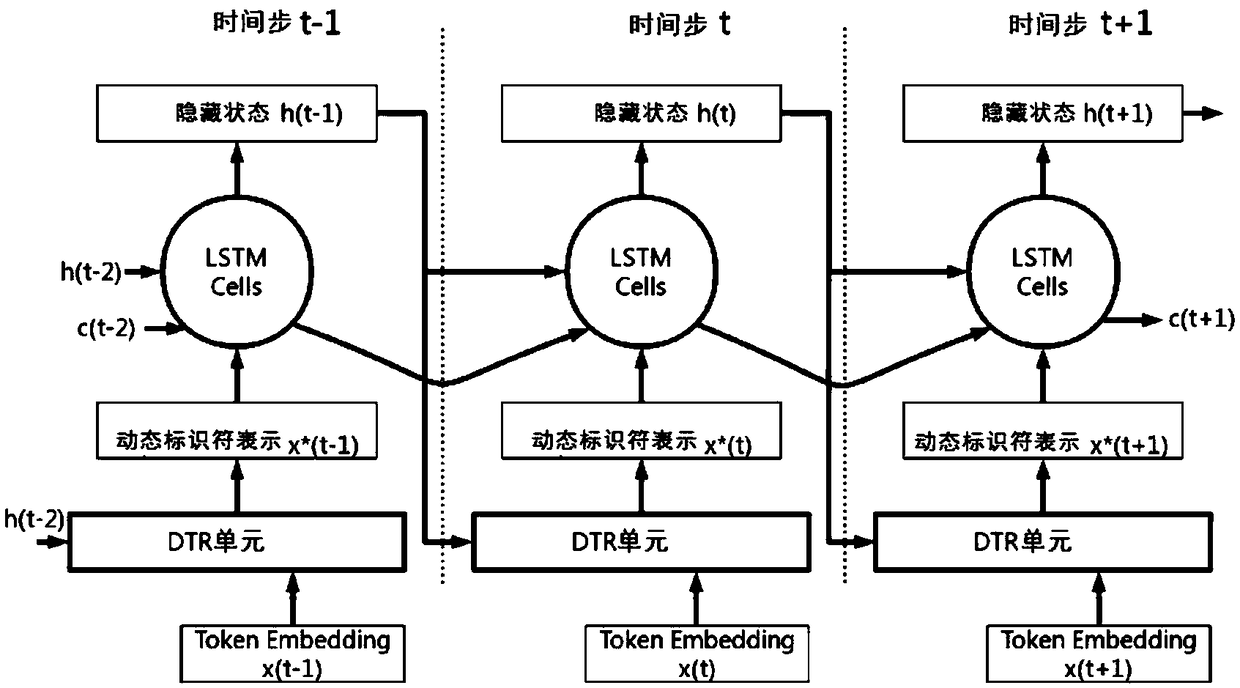
[0043] Such as figure 2As shown, according to another aspect of the present invention, the present invention also provides a DTR-RNN model. The DTR-RNN model is a group of RNN variants with DTR modules. The structure and function of the DTR module here are exactly the same as those in the above-mentioned embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here. Ordinary RNN uses the identifier embedding generated by the lookup table as unit input, while the DTR-RNN model of the present invention generates dynamic identifier representation as the input of RNN unit. In this way, the current context information is encoded into the RNN unit, so that the DTR module uses the hidden state as the context vector. Then the output of the DTR module is used as the input of the RNN unit. For each time step, the DTR module takes as input the identifier of the current time step (as an identifier vector) and the hidden state of the previous time step (as a context vector), and outputs a dynamic identi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com