A task scheduling method based on prospective prediction
A task scheduling and task technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve the problem of the sharp increase of satellite storage capacity, and achieve the effect of improving utilization and reducing storage capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
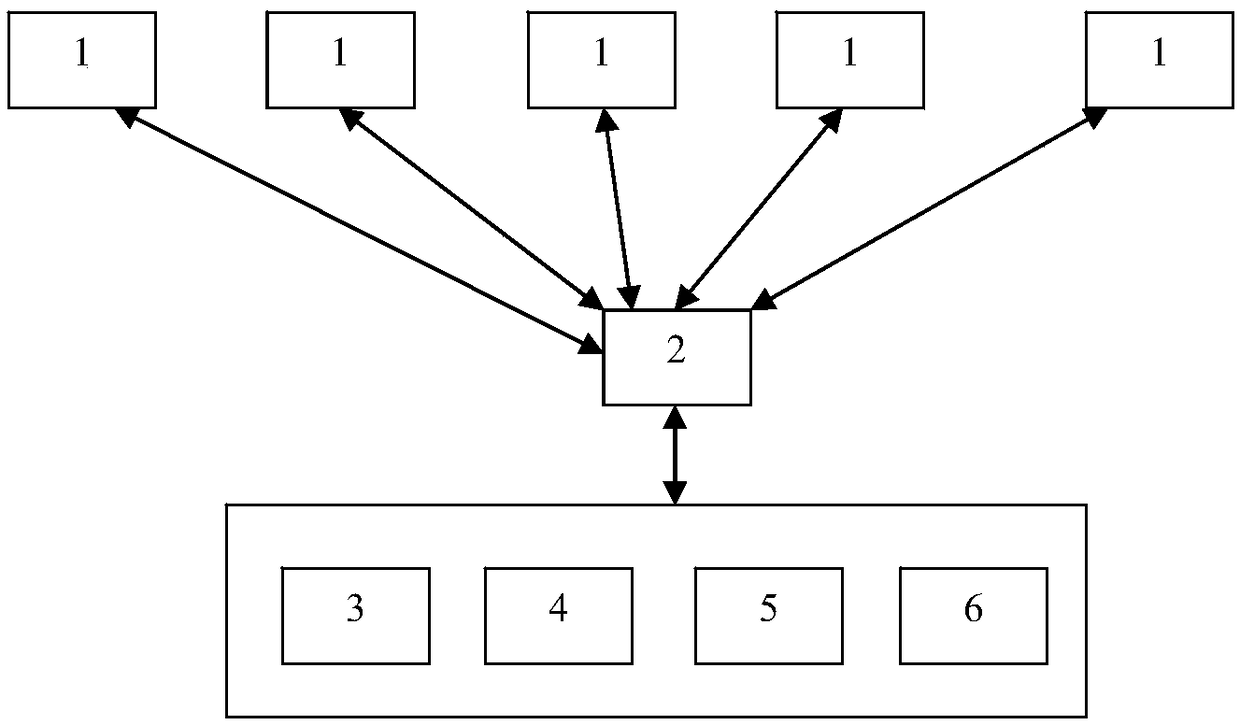
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a task scheduling system and method based on forward-looking prediction, which at least includes a remote sensing satellite 1 and a ground station 2 communicating with each other. Remote sensing satellites can be several satellites distributed in different orbits to perform image acquisition tasks. The ground station is used to establish data communication with the remote sensing satellite, so that the control command of the ground station can be transmitted to the remote sensing satellite when the remote sensing satellite enters the communication coverage area of the ground station, and at the same time, the image data collected by the remote sensing satellite can also be downloaded at this time to the ground station. The number of ground stations can be flexibly set according to actual usage requirements. For example, when the number of remote sensing satellites is increased in order to obtain more compreh...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This embodiment is a further improvement on Embodiment 1, and repeated content will not be repeated here.
[0045] Preferably, the task scheduling module completes the scheduling of remote sensing satellites by at least following the steps below to establish scheduling instructions:
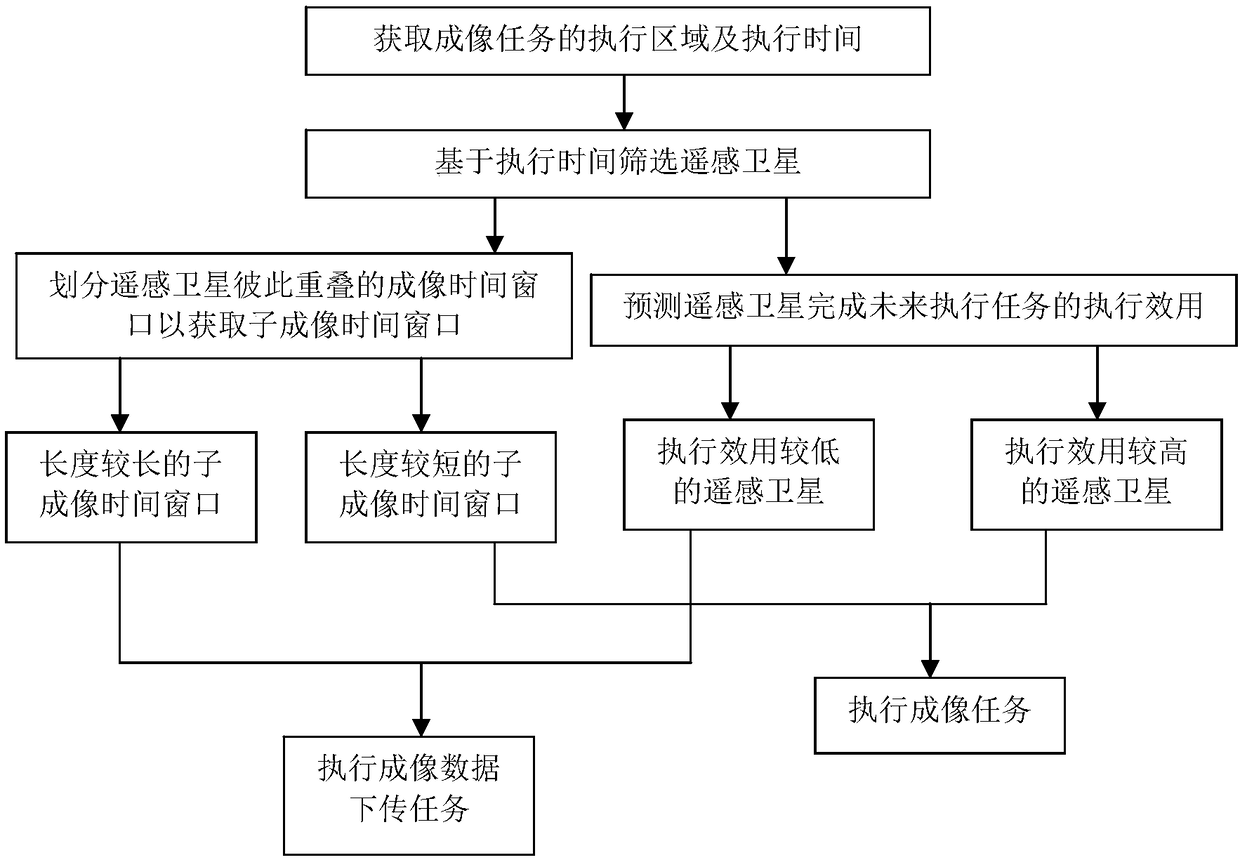
[0046] S1: Preliminarily classify imaging tasks based on the associated execution area information, imaging satellites, and imaging window time to establish an imaging task set that requires at least two remote sensing satellites 1 to complete cooperatively.
[0047] Preferably, the central processing module 6 is further configured to initially classify the corresponding imaging tasks based on the real-time task demand data of a third party. Imaging tasks can be classified into the first type, the second type, and the third type, wherein the imaging tasks belonging to the first type are imaging tasks that cannot be completed without suitable satellite resources or based on other constraint...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This embodiment is a further improvement on the foregoing embodiments, and repeated content will not be repeated here.
[0060] Preferably, the task scheduling module completes the scheduling of remote sensing satellites by at least following the steps below to establish scheduling instructions:
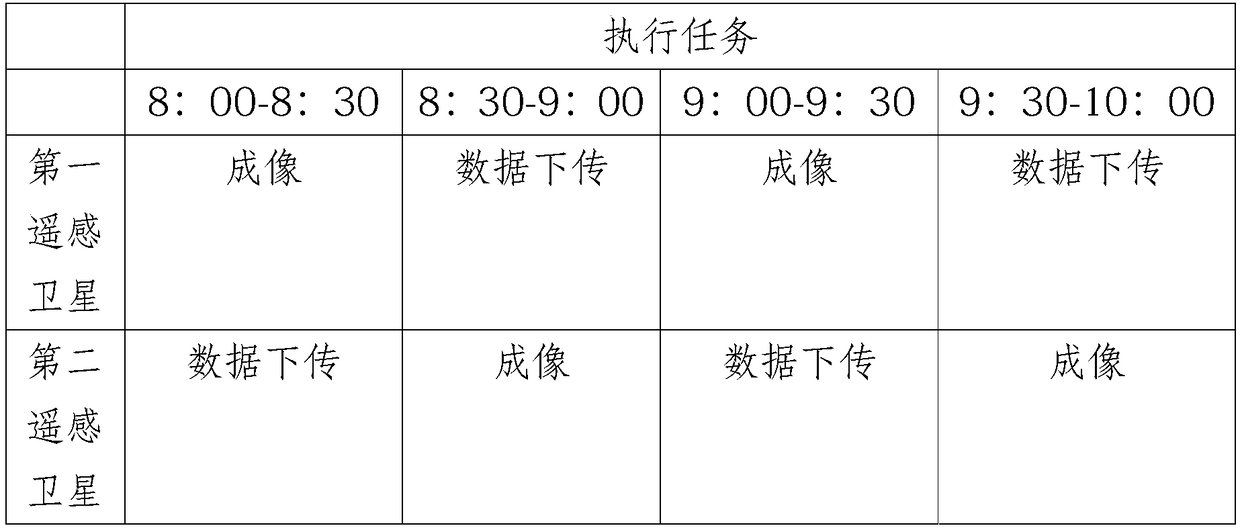
[0061] S1: Obtain the start execution time and end execution time of an imaging task that requires at least two remote sensing satellites 1 to cooperate to complete, and filter out at least one first remote sensing satellite and at least one first remote sensing satellite that include the start execution time and end execution time respectively in the imaging time window The second remote sensing satellite selects at least one third remote sensing satellite when the combination of the imaging time windows of the first remote sensing satellite and the second remote sensing satellite cannot fully cover the execution time of the imaging task.
[0062] Preferably, the task schedul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com