Synchronous positioning and map-constructing method for mobile robot facing indoor dynamic environment
A mobile robot, synchronous positioning technology, applied in the fields of instruments, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of low real-time performance of algorithms and inability to take into account accuracy and real-time performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0115] In view of the fact that the existing SLAM algorithm cannot effectively solve the problem of solving the camera pose in a dynamic scene, the present invention improves the real-time performance of the SLAM algorithm, and adds the image motion detection result to provide a semi-direct RGB- D SLAM algorithm (that is, the method of synchronous positioning and composition of mobile robots for indoor dynamic environments). The invention can effectively solve the positioning and mapping problems in SLAM, and provides an effective solution for the positioning and navigation problems of robots in dynamically changing indoor scenes.
[0116] On the one hand, after the camera pose is preliminarily solved by using the semi-direct method visual odometry, the outliers caused by moving objects in the local sparse map are eliminated with the help of the results of image motion detection, thereby effectively improving the positioning accuracy of the entire system .
[0117] On the oth...
Embodiment 2
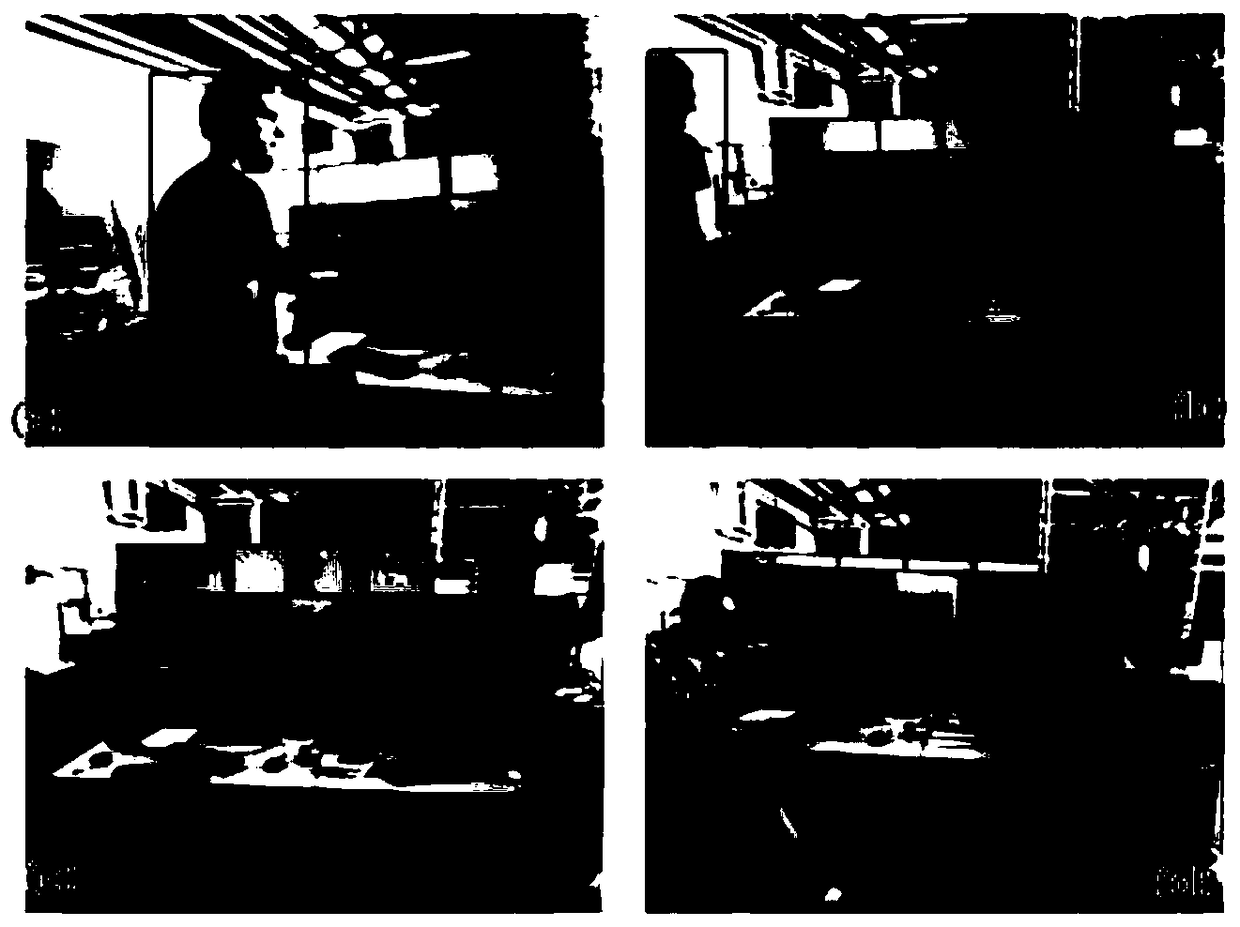
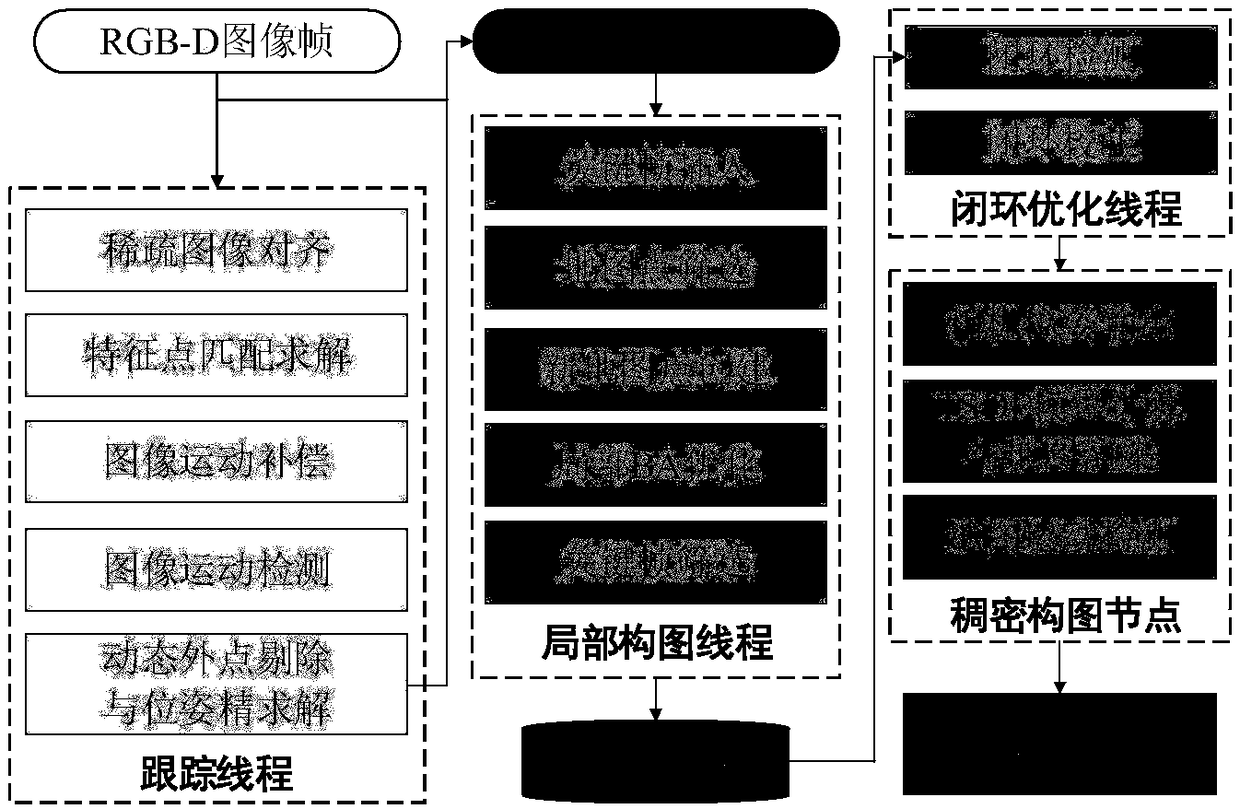
[0206] In the method of this embodiment, the hardware configuration is Intel E3-1230CPU, the main frequency is 3.30GHz, the memory is 12G, GPU acceleration is not used, and the tested system is Ubuntu14.04. The camera used is a first-generation Kinect. The structural diagram of the present invention is as figure 1 Shown:
[0207] Step 1: Collect an image I with a resolution of 640*480RGB from the Kinect camera, and extract 200 FAST corner points on I. The process of extracting corner points can be simply described as: first divide the image into 8*8 image blocks, and then extract FAST corner points in each image block separately, and only select the corner points with the highest response value. If the texture in some areas of the image is not rich enough, and the corner points may not be extracted, just skip it directly. Finally, among all the selected corner points, select the corner point whose response value is in the top 200 as the corner point to be tracked by the sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com