A control method for residual thermal stress and induced deformation in additive manufacturing
A technology of residual thermal stress and control method, which is applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the degree of deformation, the effect of macroscopic residual stress is small, the size of formed parts, and the structural accuracy are difficult to guarantee, so as to achieve the relief of mutual constraints and designability Strong, low-cost implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] In order to make the above-mentioned features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, the following specific embodiments are described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
[0029] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 11
[0030] 1) Obtain the residual stress distribution and stress value of the formed part by experiment or numerical simulation method;
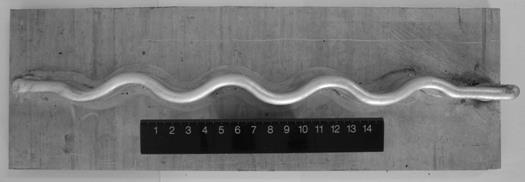
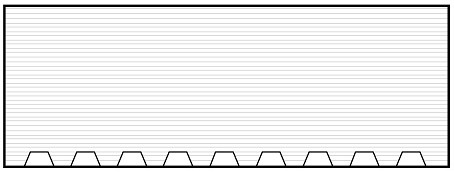
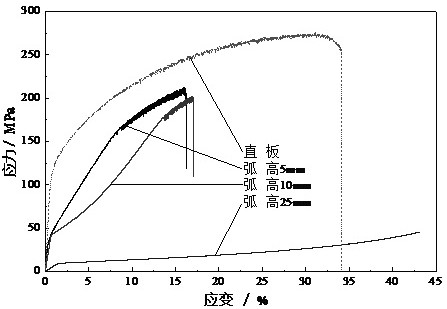
[0031] 2) According to the specific structural form of the formed part, design a continuous or discontinuous flexible base structure. The typical structure is shown in the attached figure 1 , 2 As shown, the equivalent strain of the designed flexible structure is lower than the allowable deformation range, and the equivalent elastic modulus is lower than that of the bulk material, such as Figure 3-Figure 10 , that is, after the residual stress is generated, the flexible structure deforms before the body material to suppress the yield of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com