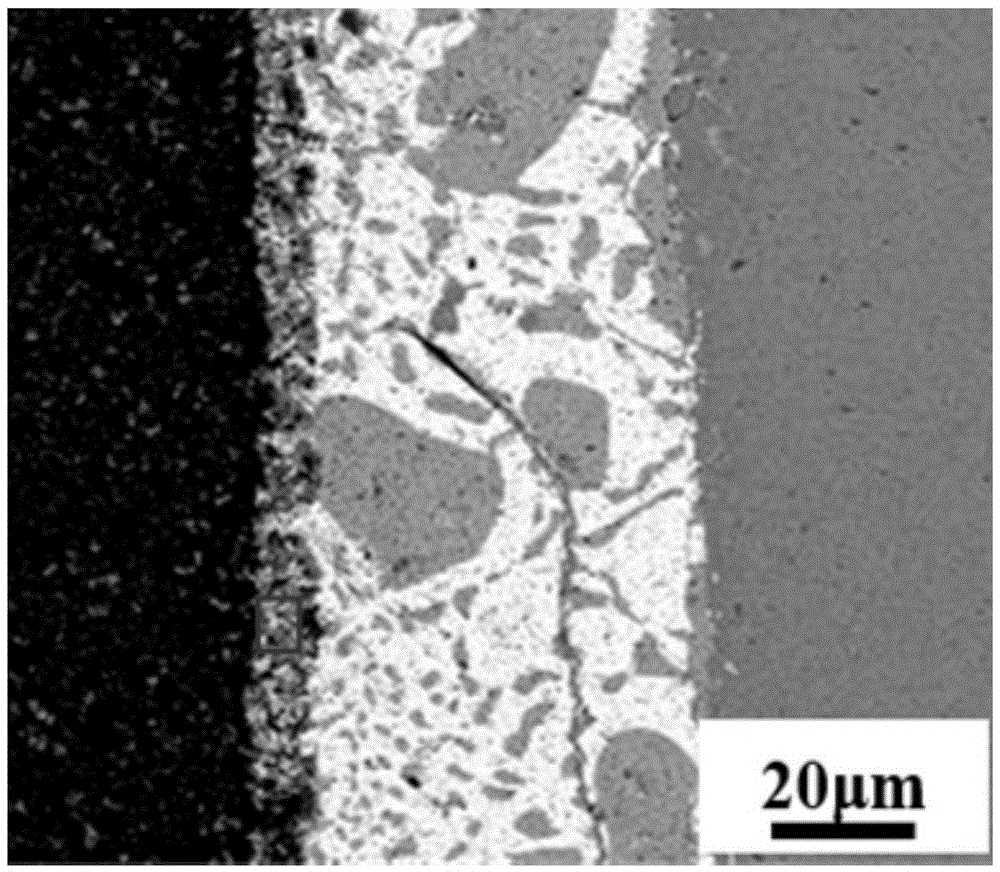
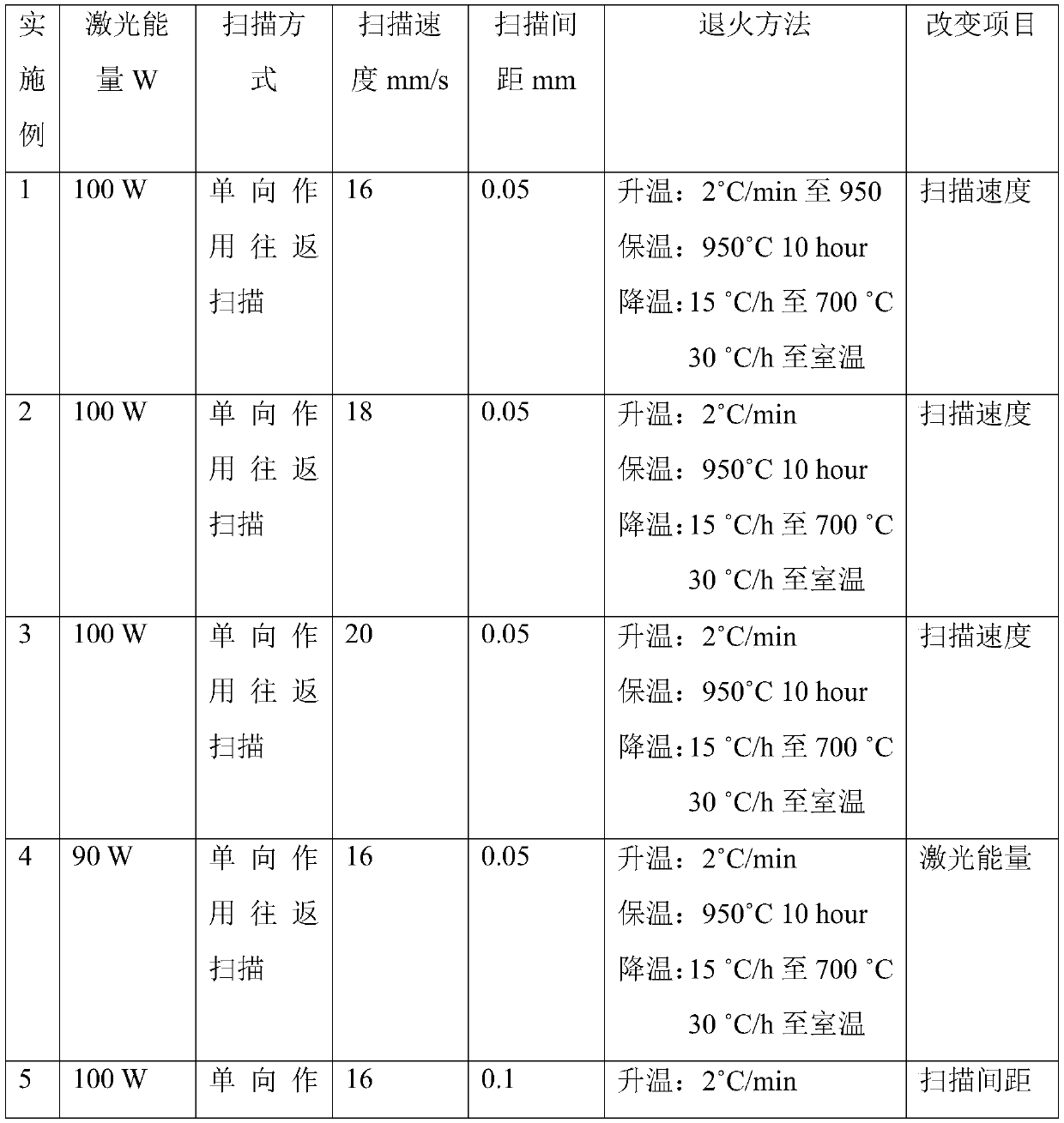
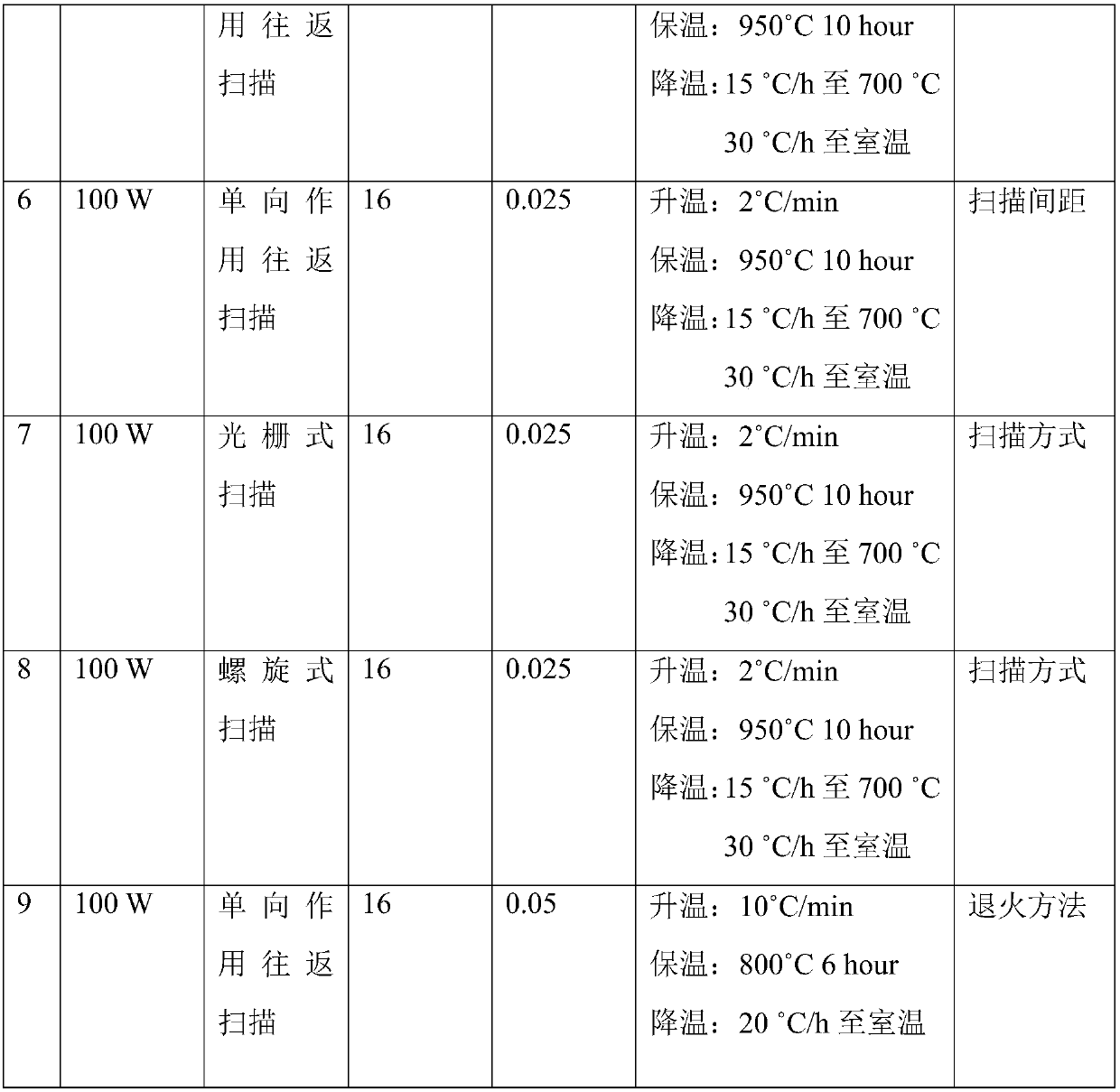
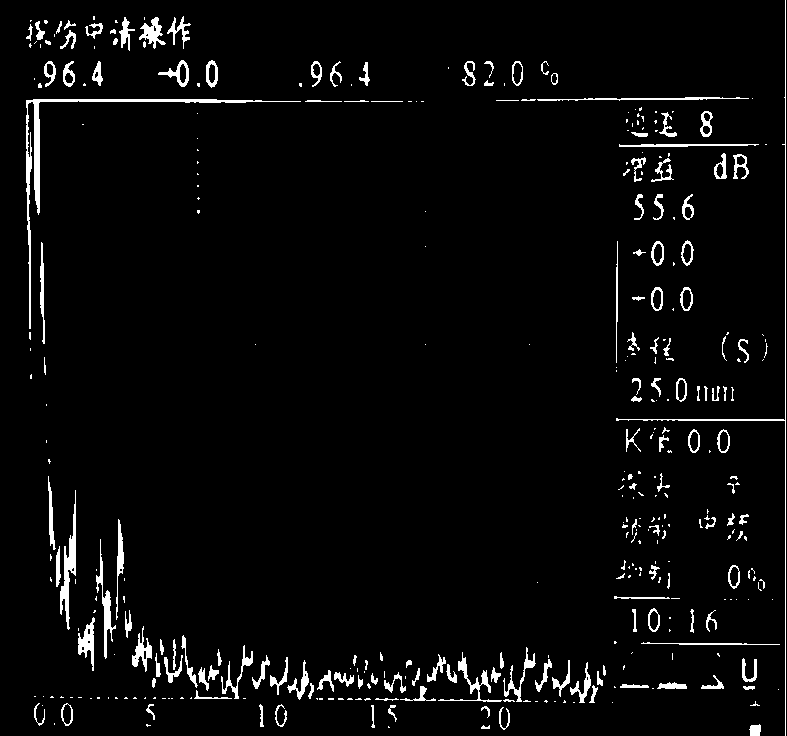
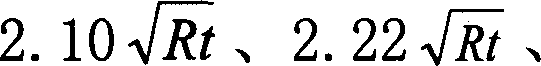Patents
Literature
102 results about "Residual thermal stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermally stable diamond brazing
A cutting element and a method for forming a cutting element is described and shown. The cutting element includes a substrate, a TSP diamond layer, a metal interlayer between the substrate and the diamond layer, and a braze joint securing the diamond layer to the substrate. The thickness of the metal interlayer is determined according to a formula. The formula takes into account the thickness and modulus of elasticity of the metal interlayer and the thickness of the TSP diamond. This prevents the use of a too thin or too thick metal interlayer. A metal interlayer that is too thin is not capable of absorbing enough energy to prevent the TSP diamond from fracturing. A metal interlayer that is too thick may allow the TSP diamond to fracture by reason of bending stress. A coating may be provided between the TSP diamond layer and the metal interlayer. This coating serves as a thermal barrier and to control residual thermal stress.
Owner:RADTKE ROBERT P
Ceramic/ceramic connection method for regulating and controlling middle solder layer through multi-physical-field coupling
Provided is a ceramic / ceramic connection method for regulating and controlling a middle solder layer through multi-physical-field coupling. According to the ceramic / ceramic connection method, a heat source is adopted to fuse solder or solder and a part of base metal, meanwhile physical fields are additionally applied, the solder is a non-crystalline material or a mixed material of the non-crystalline material and a reinforcement phase, an outer heating source is acetylene flame or oxyhydrogen flame, electric arcs, laser, electron beams or a resistance heating method for melting metal through heat conduction and heat radiation is adopted, and the additionally-applied physical fields are one or more than two of ultrasonic waves, magnetic fields and electric fields which are simultaneously applied. The ceramic / ceramic connection method has the advantages of effectively controlling interface reaction, strengthening liquid metal flowing, regulating and controlling weld joint substance distribution, regulating the metallurgical welding process, controlling a weld joint organization structure, eliminating weld joint defects, reducing residual waste heat stress, improving weld joint toughness, promoting interface bonding, improving the mechanical property of welded joints, decreasing the material using amount and reducing environmental pollution through the additionally-applied physical fields and being widely applied to the fields of aviation, aerospace, electronic devices, fuel cells and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Porous ceramic connecting method
The invention relates to a porous ceramic connecting method, relates to a ceramic connecting method, and aims to solve the problem that the process is complex when wettability is improved and thermal stress is relieved simultaneously when conventional porous ceramic is connected with metals. The porous ceramic connecting method comprises the following steps: I, preparing an organic phenolic resin solution; II, performing thermal treatment on porous ceramic; and III, connecting the porous ceramic. Due to a surface layer pore structure of the porous structure, a brazing filler metal can permeate into a base body to form a connecting structure with mechanical occlusion and chemical bond combination, not only is residual thermal stress of a connector effectively relieved, but also a boundary reaction combination area is increased, and the strength of the connector can be improved. The porous ceramic connecting method is applied to the field of connection of ceramic and metal materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Silicon nitride based nano complex gradient function ceramic tool material and preparation thereof
The invention provides a silicon nitride-based nano composite functionally gradient ceramic cutter material and a preparation method thereof. The ceramic cutter material is provided with a five-layer symmetrical gradient level structure; the component contents of the symmetrical layers relative to a central layer are the same and the thickness of each layer is consistent; the components of each layer are all micron Si3N4, nano Si3N4, nano TiC, nano TiN, Al2O3 and Y2O3. The preparation method thereof is as follows: (1) preparing materials according to the content of each component in each layer; (2) dispersing the nano materials in each layer; (3) mixing the other materials in each layer with the dispersed nano materials to obtain the powder material of a composite ceramic material which disperses excellently; and (4) employing a powder layering paving method and a hot pressing sintering technique to carry out loading and sintering. The invention improves the anti-bending intensity and the fracture toughness property of the materials, and improves the fracture toughness property of the materials; while the gradients of the nano TiC and the nano TiN are arranged in layers, thus leading the mechanical property of the cutter material to be changed in stagewise gradient, and being capable of effectively easing the residual heat stress.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
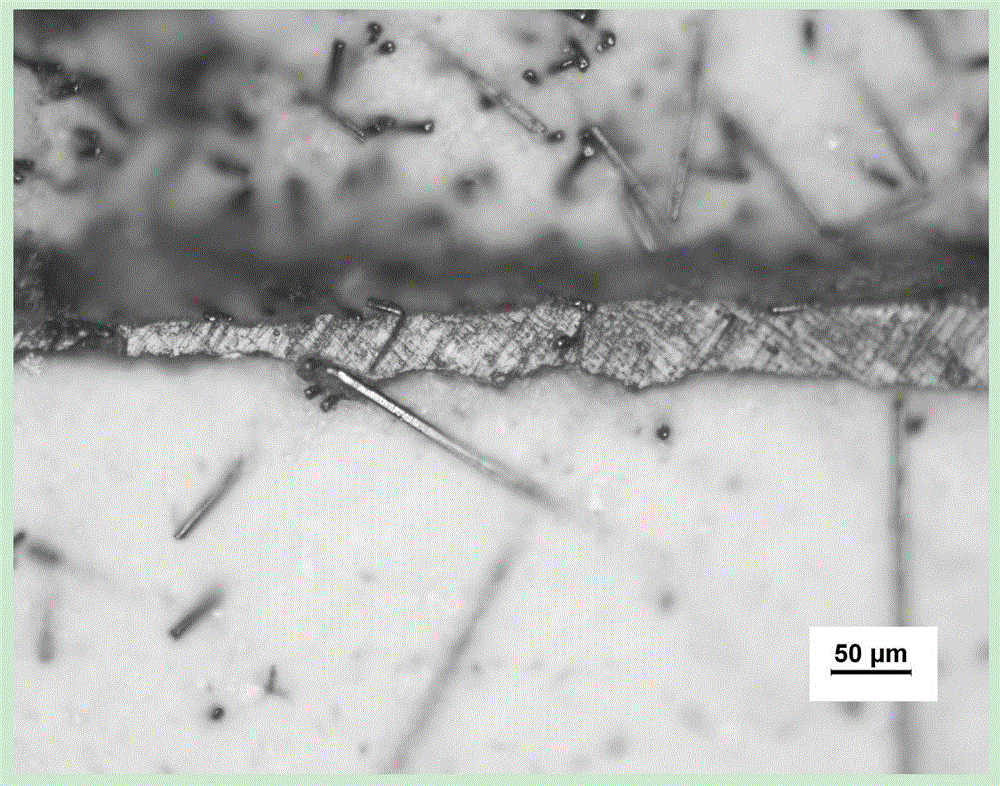
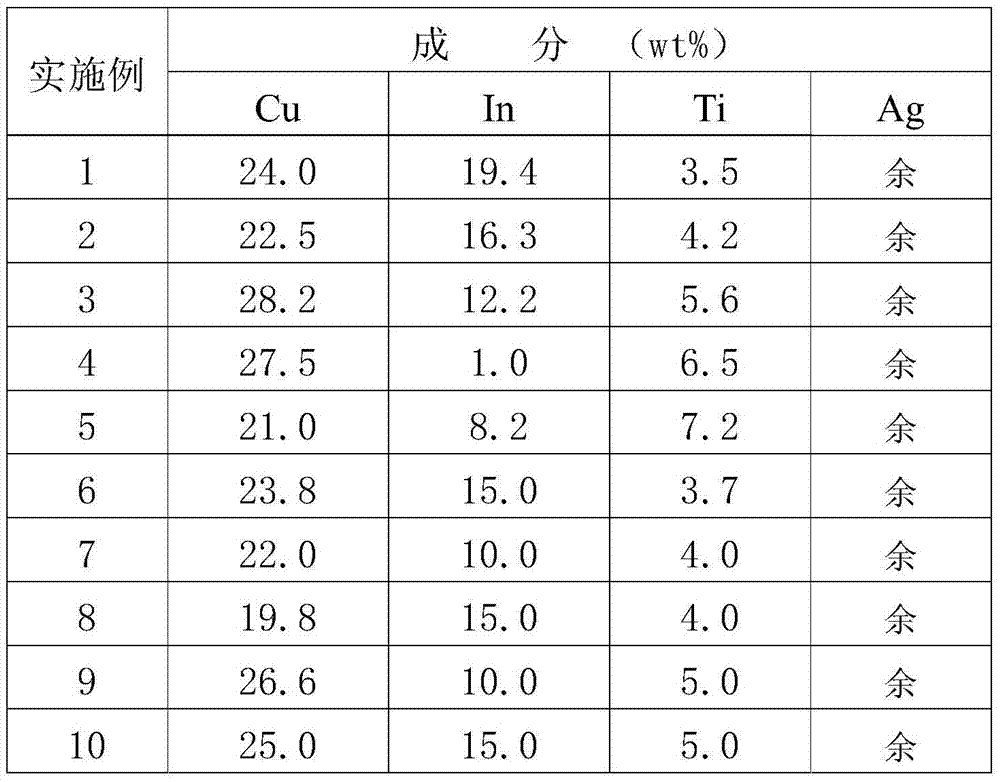
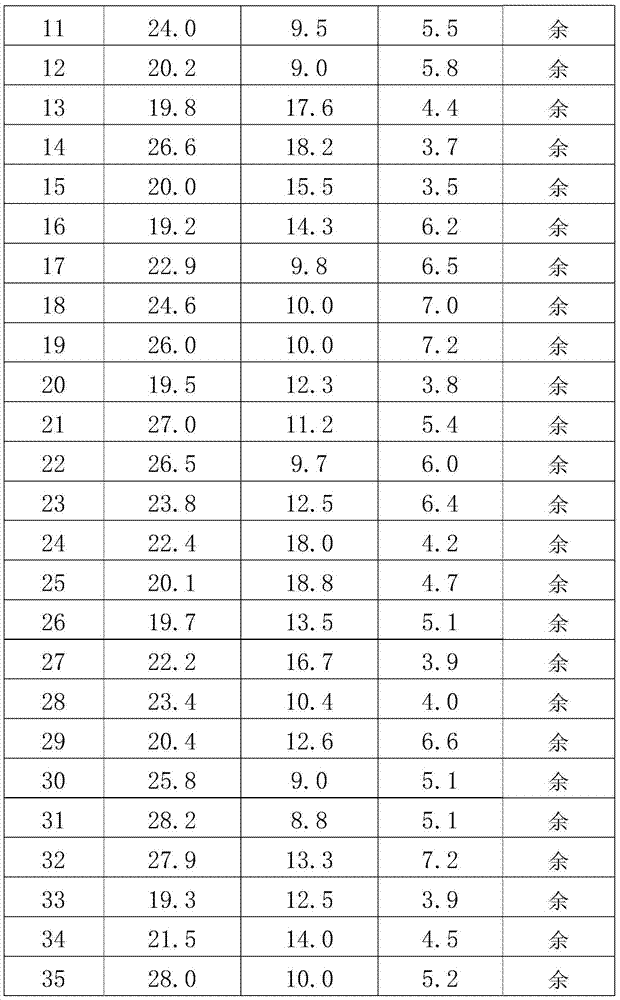
Silver-copper-indium-titanium middle-temperature brazing filler metal
InactiveCN105436741AHigh activityPromote wetting and spreadingWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesIndiumNiobium
The invention belongs to the technical field of welding, and relates to a silver-copper-indium-titanium brazing filler metal used for connecting SiO2f / SiO2 composite ceramics and metals (such as tungsten, molybdenum, tungsten-molybdenum alloy, niobium, niobium-molybdenum alloy, invar alloy and kovar alloy). The silver-copper-indium-titanium brazing filler metal is characterized by comprising, by weight percentage, 19.2-28.2% of Cu, 8.2-19.4% of In, 3.5-7.2% of Ti, and the balance Ag. The brazing filler metal is good in machinability, and can be machined into strips, and required brazing temperature is lower than that of a traditional Ag-Cu-Ti brazing filler metal by about 100 DEG C, so that the silver-copper-indium-titanium brazing filler metal has a great significance in the field of ceramic and metal brazing connection in the aspect of reducing post-welding residual thermal stress of joints. The brazing filler metal not only is suitable for connecting the SiO2f / SiO2 composite ceramics and metals, and is also suitable for connecting ceramics, or connecting ceramics and metals, or connecting metals owing to excellent activity of the brazing filler metal.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
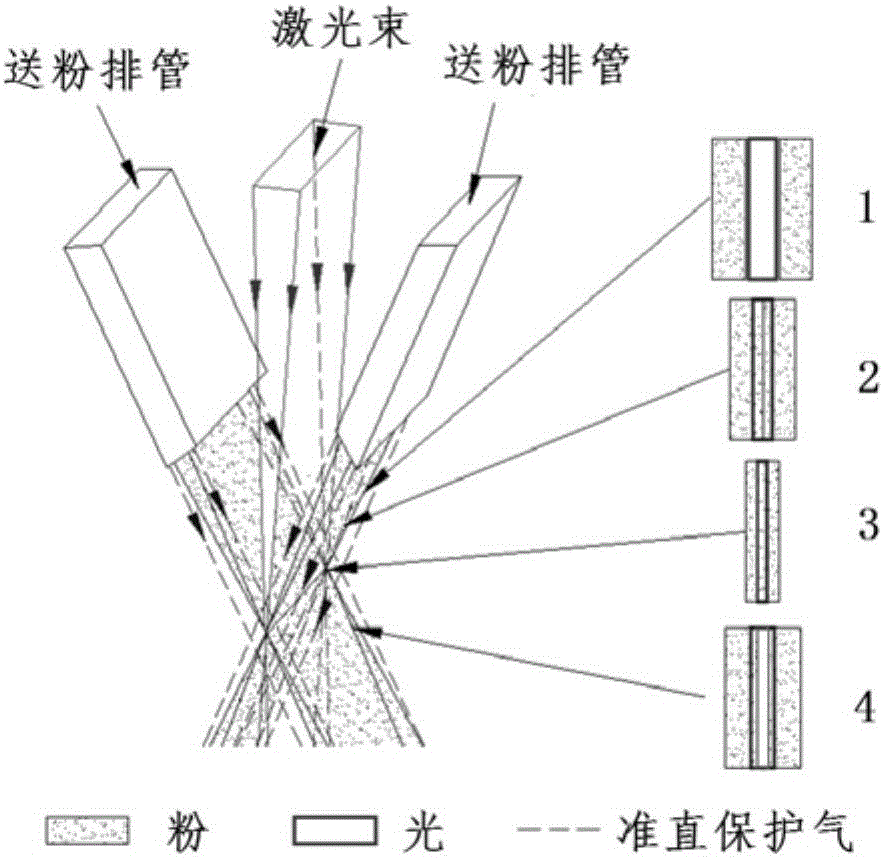
Laser broadband fusion covering device
ActiveCN106444049AMeet process heat treatment needsReduce the thermal stress of the molten layerAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyLight spotOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a laser broadband fusion covering device, and belongs to the field of 3D (three dimensional) formation. A laser beam sent by a laser can be converted and projected on a processing surface for broadband laser fusion covering processing by the laser broadband fusion covering device; the laser broadband fusion covering device comprises a reflecting mirror and a dual-molded- surface reflecting component; the laser beam is reflected to the dual-molded-surface reflecting component by the reflecting mirror; the dual-molded-surface reflecting component comprises an upper reflecting surface and a lower reflecting surface positioned under the upper reflecting surface; the upper reflecting surface is a parabolic focusing molded surface; the lower reflecting surface is a plane; after the upper reflecting surface receives the laser beam, the laser beam is reflected, so that a broadband focusing line spot is formed on the processing surface; after the lower reflecting surface receives the laser beam, the laser beam is reflected, so that a rectangular light spot is formed on the processing surface; the rectangular light spot is positioned at the outer side of the broadband focusing line spot. The laser broadband fusion covering device has the advantages that the technology heat treatment requirements of different materials and structures can be met; the defect probability of fusion layer residual thermal stress, cracks and the like is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for brazing porous Si3N4 ceramic and Invar alloy
ActiveCN105643038AImprove residual stressSmooth connectionWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesInvar alloyBriquette
The invention provides a method for brazing porous Si3N4 ceramic and an Invar alloy, relates to a brazing method and aims to solve the technical problems that larger residual thermal stress can be formed on a ceramic and metal interface and reduces joint strength in a brazing cooling process of the Invar alloy. The method comprises the following steps: 1, Ag-Cu-Ti brazing filler metal and a binder are mixed and applied to the lower surface of the porous Si3N4 ceramic, Ag-Cu brazing filler metal and the binder are mixed and applied to the upper surface of the Invar alloy, then Cu foil is clamped between the Ag-Cu-Ti brazing filler metal and the Ag-Cu brazing filler metal, and a test piece is obtained; 2, a briquette is added to the upper surface of the test piece, and the test piece is arranged in a vacuum sintering furnace, subjected to heat preservation at 300 DEG C, subjected to heat preservation at 850-950 DEG C and then cooled. The joint strength can reach 73 MPa with adoption of the method. The invention belongs to the field of brazing.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
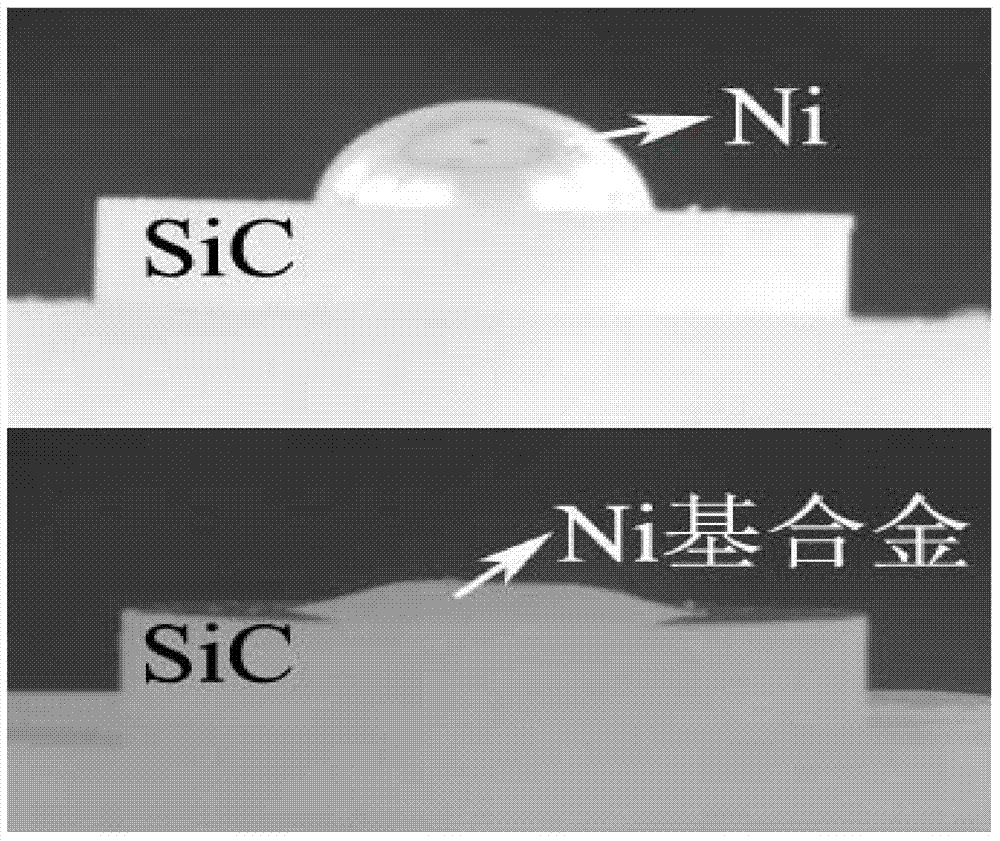
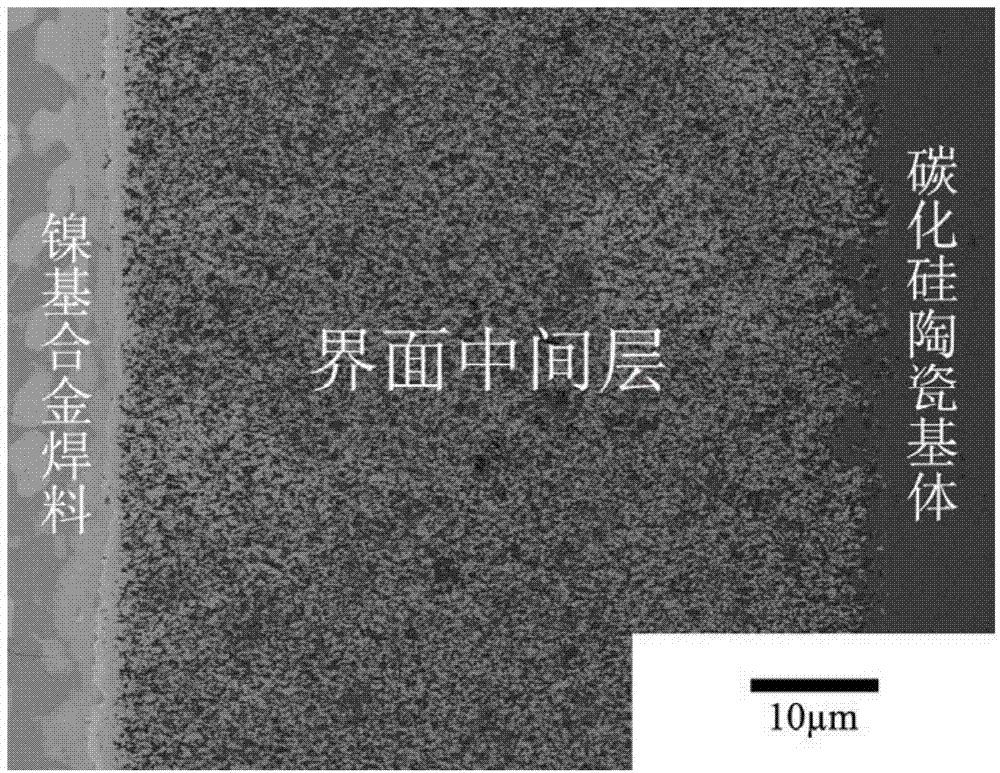
Solder for bonding C/SiC composite material with Ni-based alloy and bonding method
ActiveCN102219538AHigh strengthImprove room temperature flexural strengthRoom temperatureThermal expansion
The invention discloses a solder for bonding a C / SiC composite material with a Ni-based alloy and a bonding method. The solder is composed of 67-78% of Cu foil by mass, 8.5-15% of Ti foil by mass and 10-24.5% of Mo powder by mass. The thickness of the Cu foil is 30-70 mum. The thickness of the Ti foil is 80-120 mum. The granularity of the Mo powder is 3-15 mum. By pretreating the solder, the cleaned Cu foil, the cleaned Ti foil and the Mo powder paste can be obtained. A pre-bonded element is manufactured by using the solder. A bonding piece between a carbon / silicon carbide ceramic-based composite material and a nickel-based high-temperature alloy can be obtained through hot pressing. According to the solder disclosed by the invention, the mismatching property of thermal expansion coefficients between the solder and the C / SiC composite material is effectively reduced; the residual heat stress between the solder and the C / SiC composite material is reduced; and the room-temperature bending strength of the C / SiC composite material and an Ni-based high-temperature alloy joint are improved to 198 MPa.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
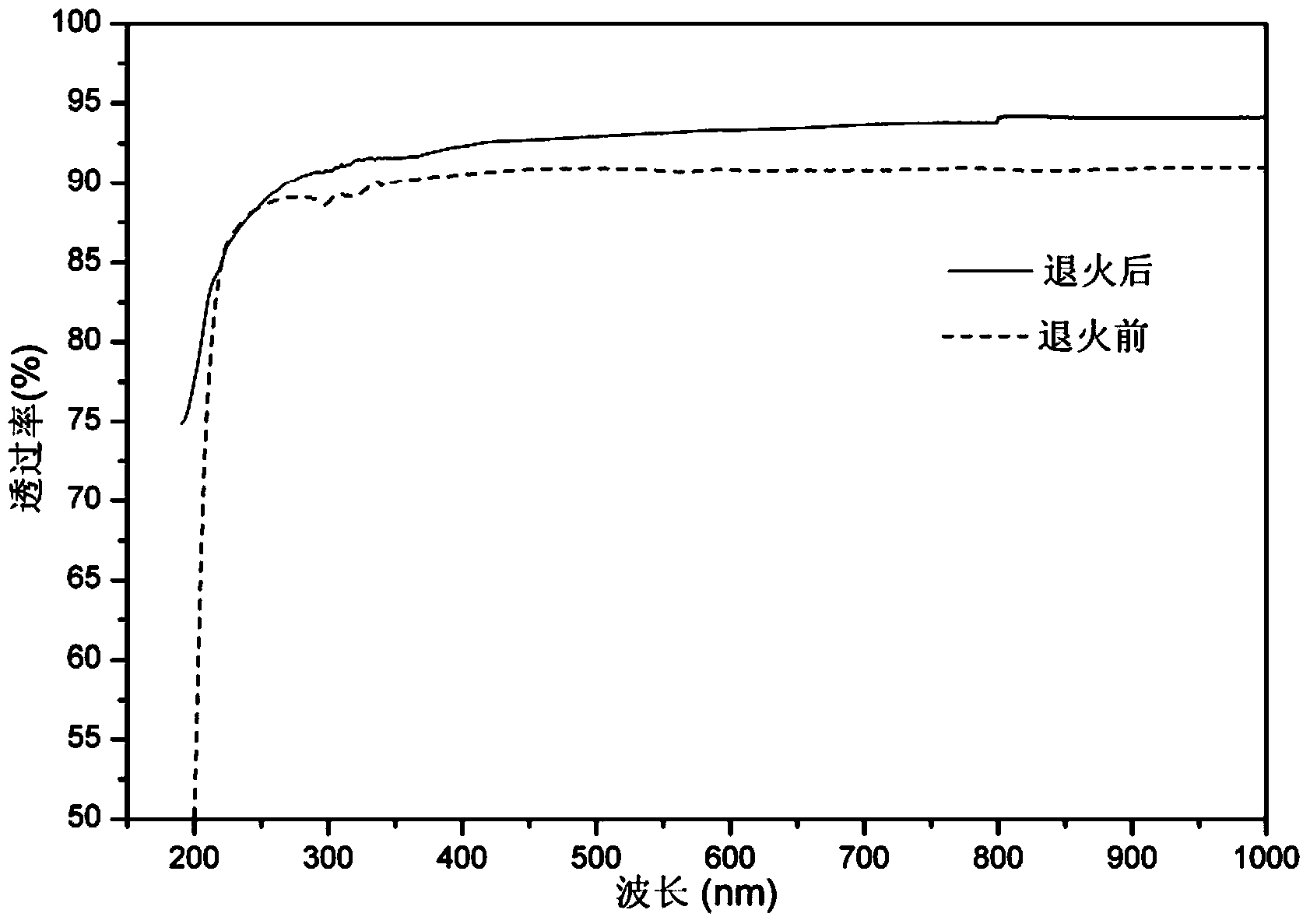
Laser beam polishing method of fused quartz optical glass
InactiveCN109590603ASolve the problem of expensive and inefficient polishingOvercoming the problem of uneven heat accumulationLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsTemperature monitoring
The invention provides a polishing method of fused quartz optical glass. According to the method, the fused quartz optical glass is polished by continuous CO2 laser beams, laser beam polishing of thefused quartz optical glass with the surface of which the roughness RMS is less than 0.2 nm is realized by combining a nonfocusing light source with a temperature monitoring and feedback system, and almost no microdefect and scratch exist on the surface of the polished fused quartz optical glass. The method comprises an annealing step, and can eliminate the thermal residual stress caused by laser beam polishing. The invention provides a novel method for processing fused quartz optical glass with a nondestructive super-smooth surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser cladding metal-ceramic coating material based on ZrO2 doping
ActiveCN108707893AReduce generationLow extensionMetallic material coating processesStress concentrationAlloy substrate
The invention discloses a laser cladding metal-ceramic coating material based on ZrO2 doping. The laser cladding metal-ceramic coating material based on ZrO2 doping is prepared by mixing 5-20 wt% of Ti powder, 70-92 wt% of TiBCN ceramic powder and 3-10 wt% of ZrO2 powder. The coating material is clad on the surface of a titanium alloy substrate by a laser cladding technology. The coating materialcan absorb strain energy of residual thermal stress of laser cladding, reduce crack generation and extension caused by stress concentration, improve fracture toughness of the cladding coating, and increase strength and corrosion resistance of the cladding coating to form a toughened metal-ceramic cladding coating.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
High temperature solder and application thereof
ActiveCN104711457AImprove wettabilityGood high temperature thermodynamicsWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaAlloyOxidation resistant
The invention discloses a high temperature solder and an application thereof. The high temperature solder is a nickel based alloy formed by nickel and at least one of molybdenum and chromium. The high temperature solder can be used for high temperature welding of silicon carbide ceramic materials. Experiments prove that the high temperature solder provided by the invention has good wetability, good high temperature thermodynamics, oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance, can reduce the influences of welded points on the integral performances of silicon carbide ceramic parts, can reduce the residual thermal stress in the welded points, improves the high temperature and corrosion resistance of welded silicon carbide ceramic connectors, and is in favor of popularizing the application of the silicon carbide ceramic materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Annealing treatment method and device for reducing internal stress of crystal
ActiveCN111074348AReduce radial stressAchieve Axial Temperature GradientPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsRadial stressCrucible
The invention provides an annealing treatment method for reducing the internal stress of a crystal. The annealing treatment method comprises the following steps: (1) a preparation stage: putting the crystal to be annealed into a crucible, vacuumizing the crucible, and introducing inert gas; and (2) a heating stage: heating the crucible by using a heating device, and in the heating process, respectively controlling the heating temperatures of a plurality of first heating rings concentrically arranged above the crucible in the heating device so that the crucible forms a radial temperature gradient. The heating temperature of a plurality of first heating rings of the heating device is controlled, the crucible forms the radial temperature gradient, the radial temperature gradient different from or opposite to the radial temperature gradient during crystal growth can be obtained and radial stress of the crystal can be remarkably reduced. The heating temperature of the first heating ring below the crucible and the heating temperature of the third heating ring on the side face of the crucible are controlled, the axial temperature gradient of the crucible is achieved, the axial temperaturegradient different from or opposite to the axial temperature gradient of the crystal in the growth process can be obtained and basic elimination of residual thermal stress can be achieved.
Owner:SICC CO LTD
Method for predicting interlayer thermal stress distribution in selective laser melting process based on COMSOL
ActiveCN113343521AThermal Stress PredictionResidual Thermal Stress PredictionAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingPowder bed
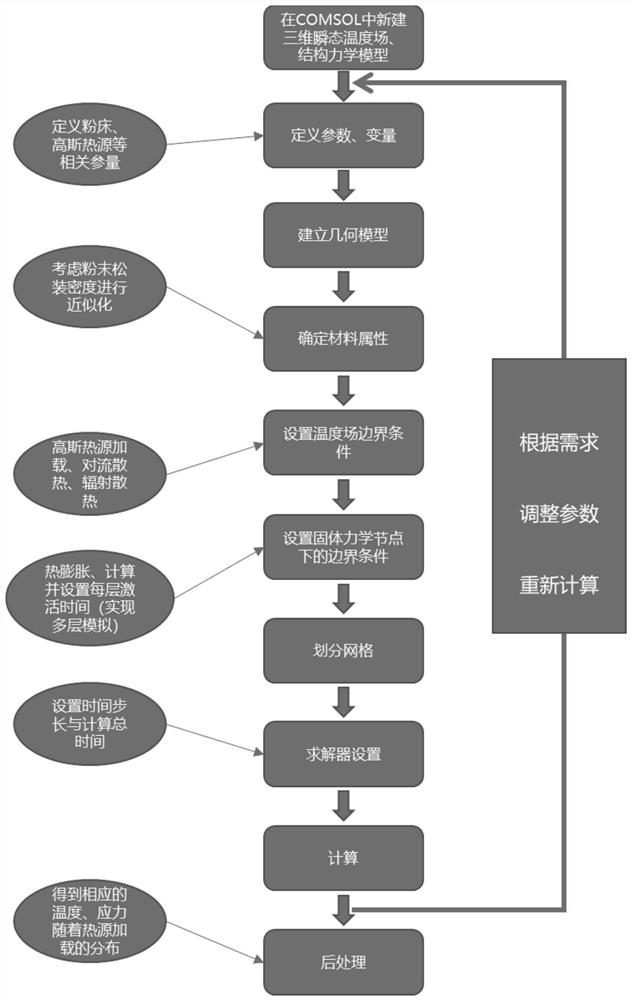
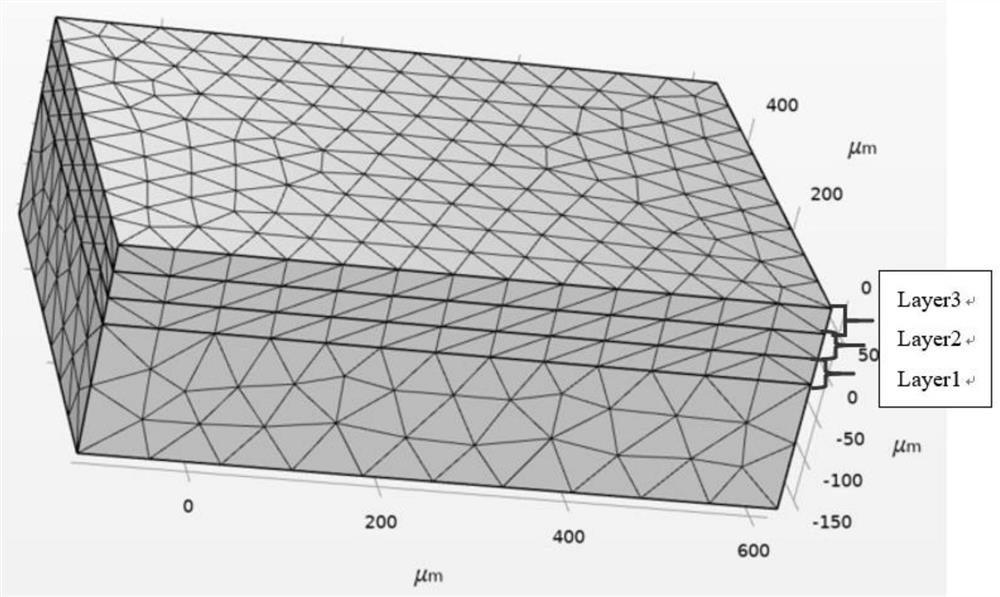
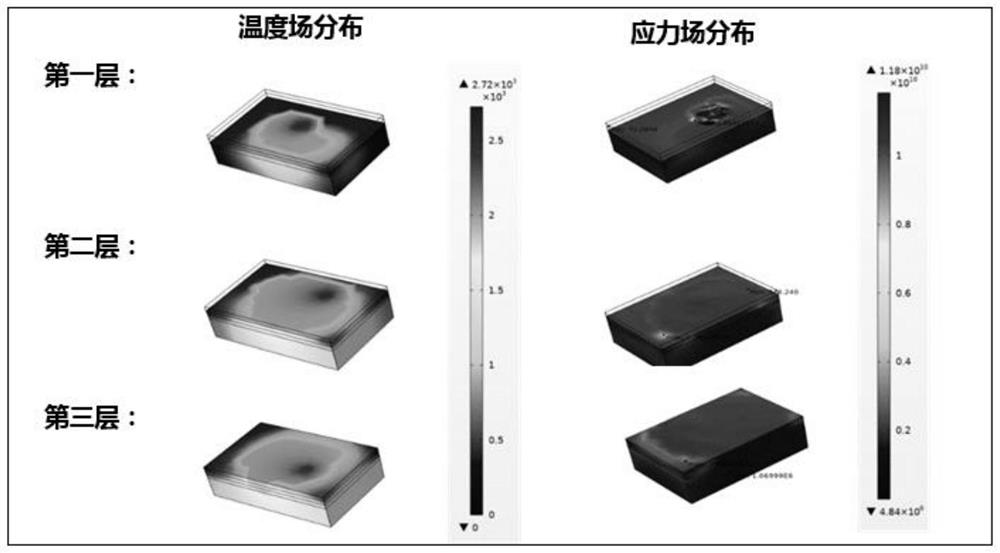
The invention provides a method for predicting interlayer thermal stress distribution in the selective laser melting process based on COMSOL. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a three-dimensional solid heat transfer and structural mechanics transient model based on COMSOL; s2, determining parameters in a simulation process; s3, determining the material attribute of the powder to be melted; s4, determining moving Gaussian heat source parameters; s5, constructing a geometric model of the powder bed; s6, achieving layer-by-layer manufacturing of selective laser melting; s7, carrying out grid division and calculating node temperature; and S8, predicting interlayer thermal stress distribution and residual thermal stress distribution according to a result of the step S7. According to the method, the laser heat source effect in the machining process is simulated through a moving Gaussian heat source mold, and a powder bed is replaced with a uniform material powder bed; in addition, the structural mechanics module is used for simulating the thermal stress generated by the layer and the deformation condition of a workpiece when the structural mechanics module moves along with a heat source, the layer-by-layer manufacturing process of the selective laser melting technology is simulated, and prediction of thermal stress among multiple layers and residual thermal stress is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Double-layer rotary tiller wear-resistant coating
InactiveCN109706445AExtended service lifeImprove work efficiencyTilling equipmentsWelding/cutting media/materialsWear resistantHeat stress
The invention provides a double-layer rotary tiller wear-resistant coating. The coating comprises an inner layer wear-resistant coating A and an outer layer wear-resistant coating B, wherein the innerlayer wear-resistant coating A comprises components by mass as following: 10%-25% of WC powder, and the balance BNi82CrSiBFe brazing filler metal; and the outer layer wear-resistant coating B comprises components by mass as following: 5%-9% of diamond micro-powder, and the balance BNi82CrSiBFe brazing filler metal. The preparation method of the coating includes steps of separately preparing pastyfluids of the inner layer wear-resistant coating A and the outer layer wear-resistant coating B, layered pre-setting the pasty fluid of the inner layer wear-resistant coating A and the pasty fluid ofthe outer layer wear-resistant coating B at the edge of a rotary tiller blade, drying the pasty fluids under the temperature of 110 DEG C to 150 DEG C for 30-60 minutes, using a vacuum brazing furnace with vacuum degree 1*10<-2> to braze the pasty fluids under the temperature of 1050 DEG C to 1080 DEG C for 30 minutes, furnace cooling to braze apply the wear-resistant coating on the surface of arotary tiller substrate, and applying vacuum heat treatment on the rotary tiller after being discharged from the furnace to eliminate residual heat stress on the blade and in the coating. By braze applying the composite wear-resistant coating on the surface of the rotary tiller, the problem of poor wear-resistance of a common rotary tiller is solved, and the service life of the rotary tiller is greatly prolonged.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Nonisocyanate-cured azide polyether binder system and propellant
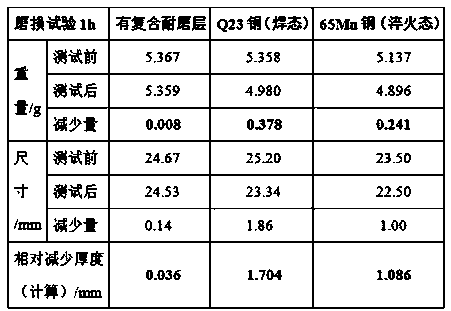
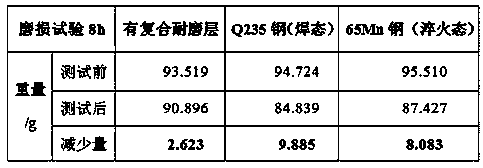
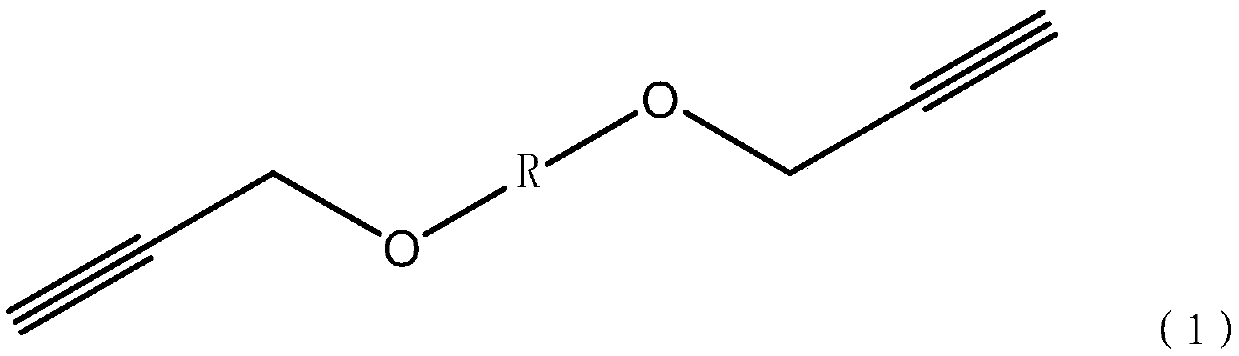
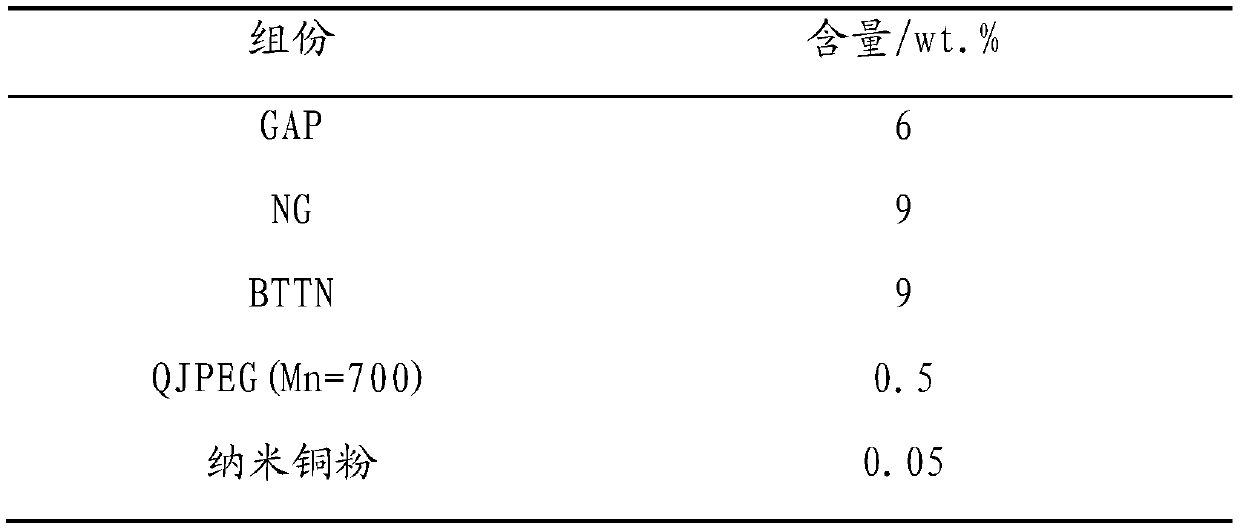
The invention relates to a nonisocyanate-cured azide polyether binder system and a propellant, and belongs to the technical field of solid propellants. The system includes the following components inparts by mass: 54% to 96.6% of a binder, 3.2% to 45.3% of a curing agent, and 0.2% to 1.5% of a curing catalyst, wherein the binder is glycidyl azide polymer (GAP), the curing agent is a bifunctionalor multifunctional alkynyl-terminated polyether, and the curing catalyst is at least one of nano copper powder and a cuprous salt. The propellant provided by the invention has higher curing reaction activity and a faster reaction speed, can be cured at normal temperature, and solves the problem of residual thermal stress of grain solidification; the reaction mechanism is not affected by moisture,and the affect of environmental humidity and the moisture of the raw materials on curing and mechanical properties can be eliminated; and the obtained propellant has excellent mechanical properties, especially has higher elongation, and the elongation can reach 100% or more and is much higher than a level of mechanical properties reported outside China.
Owner:HUBEI INST OF AEROSPACE CHEMOTECHNOLOGY
Method for annealing large-size calcium fluoride crystal
InactiveCN103643301AIncreased Laser Damage ThresholdImprove uniformityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsOptical propertyCrucible
The invention discloses a method for annealing a large-size calcium fluoride crystal. The method comprises the following steps: putting the calcium fluoride crystal to be annealed into a crucible, burying and covering by use of raw material crushed calcium fluoride crystal, and preventing the crystal from contacting with the crucible and air directly; putting into a vacuum annealing furnace for vacuum annealing or atmosphere annealing; for annealing process, firstly, heating up to 900-1100 DEG C at the heating rate of 20-50 DEG C per hour, then performing heat preservation for 20-60 hours, finally, cooling down to room temperature at the cooling rate less than 20 DEG C per hour. By adopting the method, residual thermal stress in the crystal can be completely eliminated, and the optical property of the large-size calcium fluoride crystal can be well improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
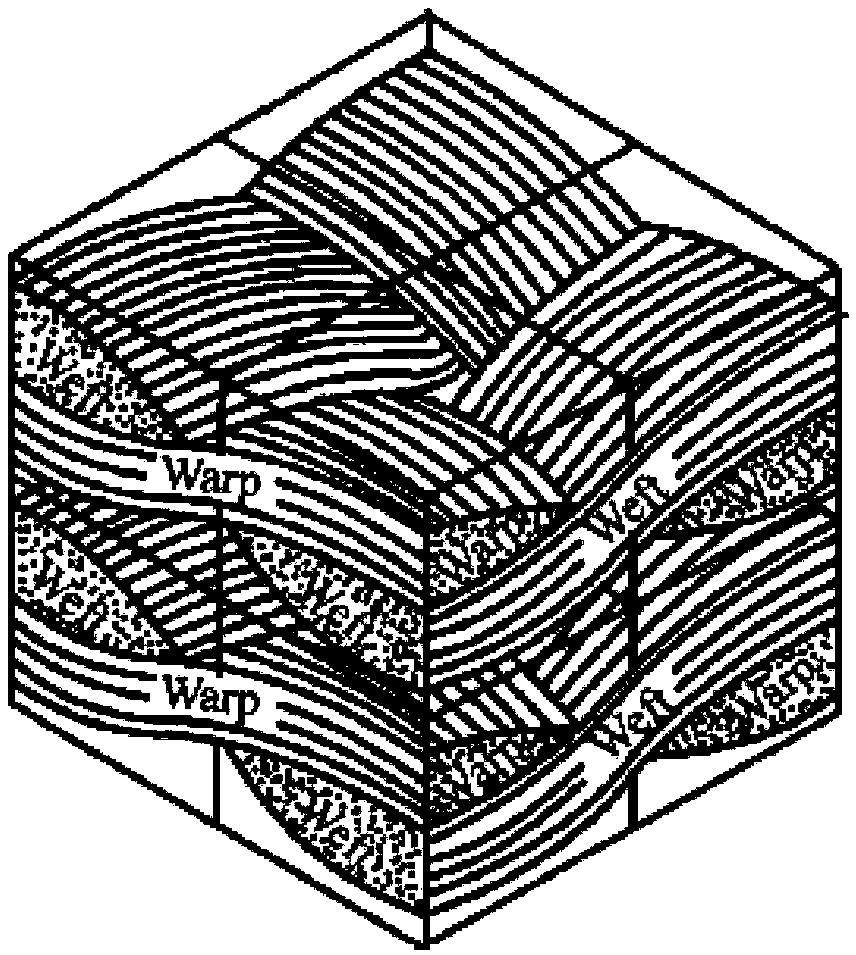
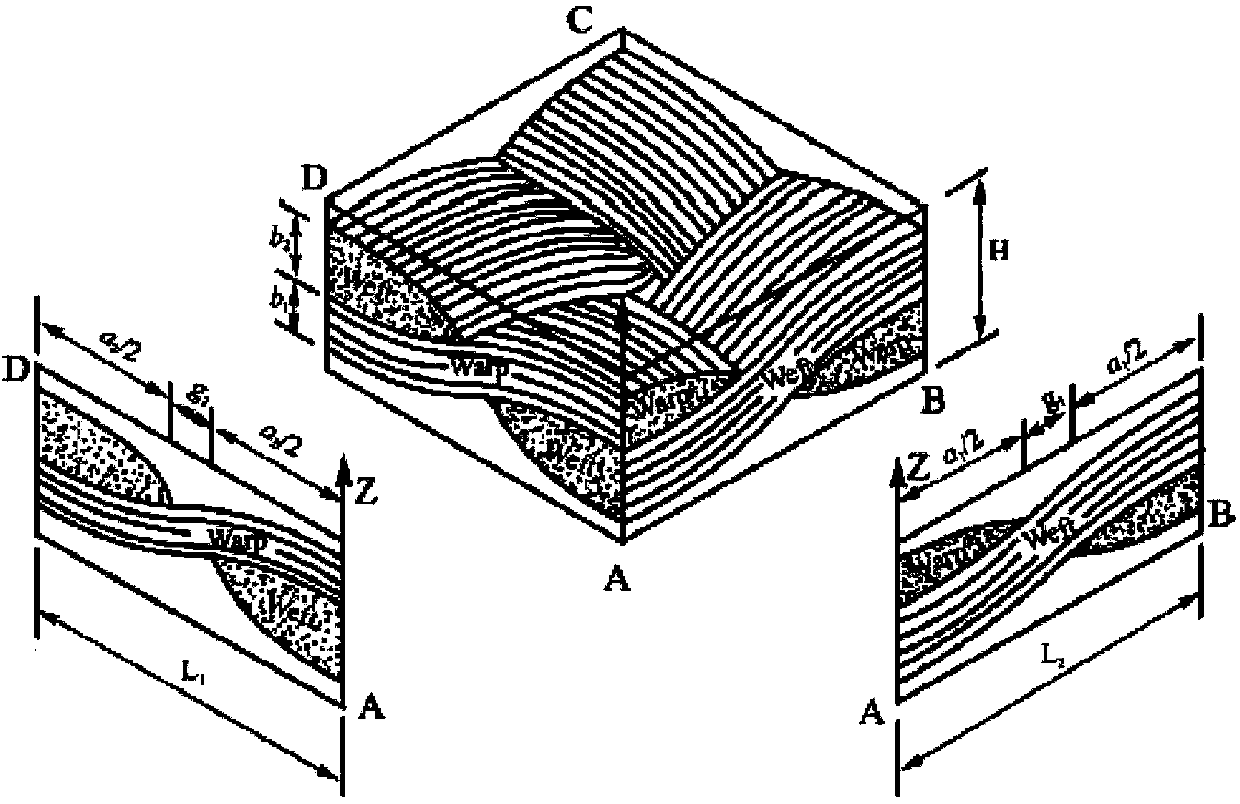
New method for predicting residual thermal stress of planar-knitted composite material
InactiveCN103473440APredict macroscopic residual thermal stressesSpecial data processing applicationsFlagellar basal bodyAnalytic model
The invention relates to a new method for predicting the residual thermal stress of a planar-knitted composite material, which comprises the following three steps of 1. selecting a minimum repetitive unit as a representative volume element according to the planar-knitting mode of a fiber bundle so as to determine the cell-body unit of the fiber bundle, and obtaining a simplified cell-body unit model according to the contraction deformation and stress conditions of component materials, i.e. a basal body and fibers, in the processes of cooling and solidification on the basis; 2. analyzing the stress of the basal body and the fibers in the cell-body unit according to the contraction-deformation compatibility conditions of the component materials i.e. the basal body and the fibers in the processes of cooling and solidification, and obtaining the constitutive relation between the thermal deformation of the component materials and the internal force of the cell-body unit so as to establish the thermal-stress analytic model of a planar-knitted composite-material single-layer plate; 3. establishing the thermal-stress equation of the planar-knitted composite-material single-layer plate according to the thermal-deformation compatibility conditions of the planar-knitted composite-material single-layer plate and a pure basal-body layer, and predicting the macroscopic residual thermal stress of a planar-knitted composite-material laminated plate through the performance of the component materials.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
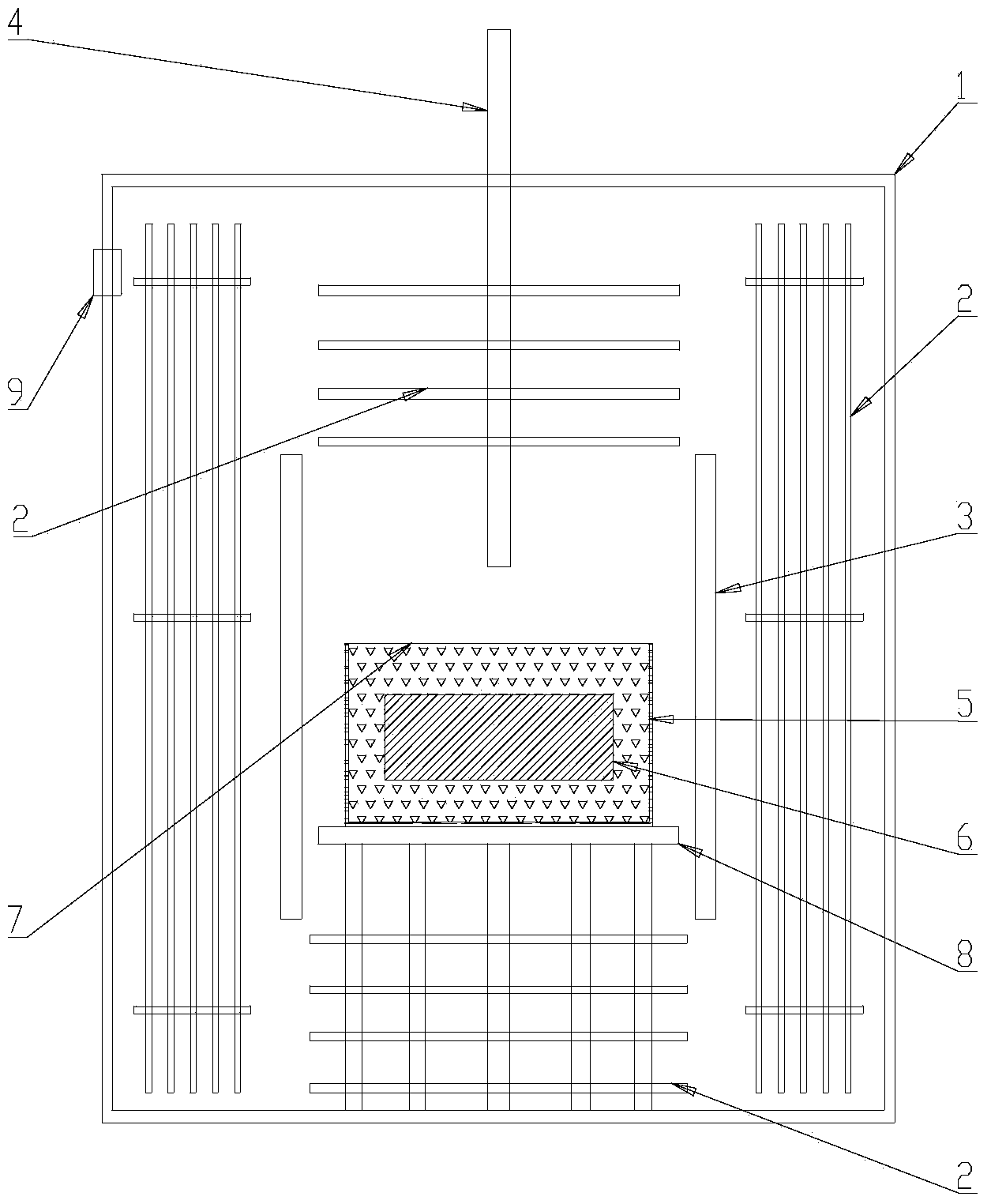
Local heat treatment residual heat stress control method of spherical vessel
ActiveCN1834268ASolve the problem of local heat treatment residual thermal stress controlImprove safety and reliability performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlStress corrosion crackingOperation safety
This invention discloses a method for controlling the residual thermal stress in spheric containers caused by local thermal treatment. The method comprises the steps of: (1) calculating the arc length or radius of the circular heating zone according to the volume, wall thickness and the area of the zone to be treated; (2) placing the heating device in the zone to be trated and heating; (3) performing single-sided or double-sided heating, and installing an insulating layer; (4) controlling the heating speed not higher than 150 deg.C / h until the predetermined constant temperature is reached; (5) keeping the temperature for a certain time; (6) cooling at a speed not high than 50% of the heating speed; and (7) removing the insulating layer. This invention can reduce the residual thermal stress in spheric containers caused by local thermal treatment by 60% to even 100%, thus can avoid such problems as stress corrosion cracking and brittle fracture, and can improve the operation safety of large scale equipment.
Owner:TIANJIN SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION INST
Hard alloy matrix for synthesis of polycrystalline diamond compact
InactiveCN103526095AQuality improvementImprove residual thermal stress distributionMetal layered productsStress concentrationPolycrystalline diamond
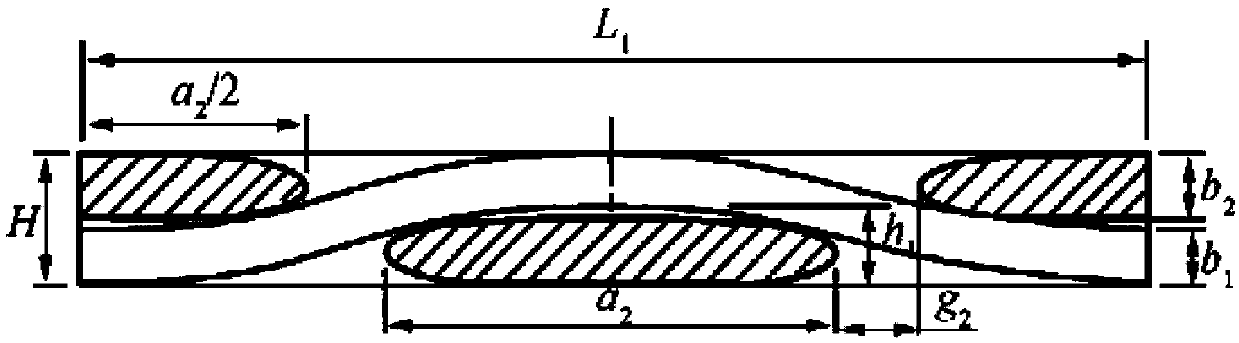
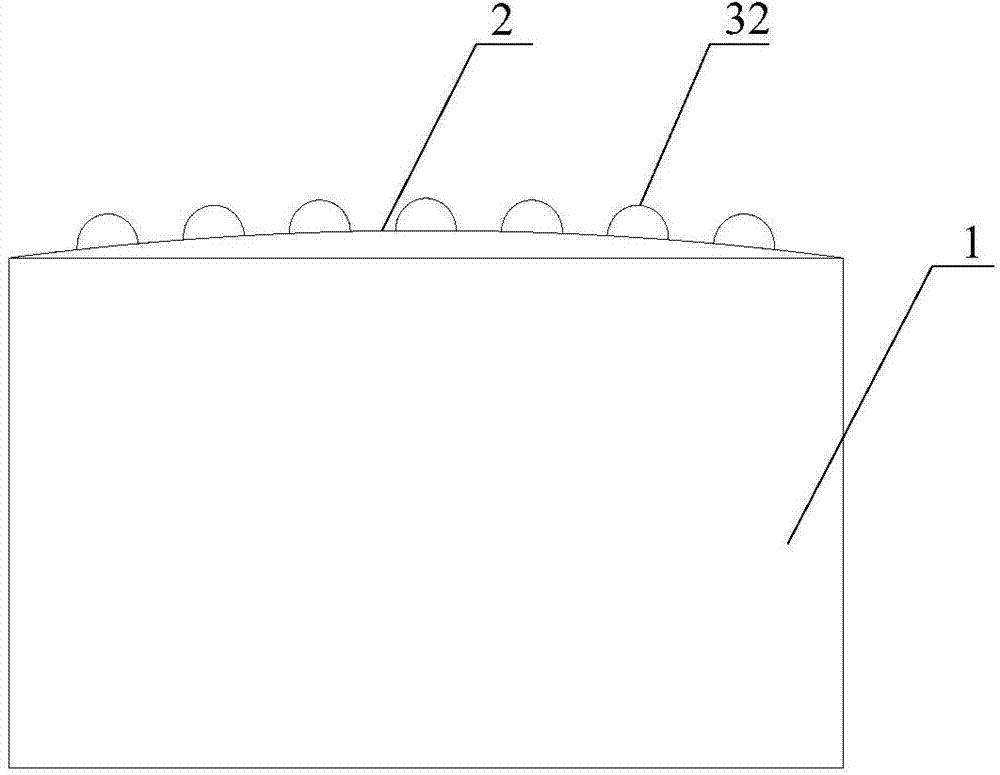
The invention provides a hard alloy matrix for synthesis of a polycrystalline diamond compact. The face, combined with a diamond, of the hard alloy matrix is an arc face and protrusions are evenly distributed on the arc face. Due to the fact that the face, combined with the diamond, of the hard alloy matrix is the arc face and the protrusions are arranged on the arc face, on one hand, the arranged arc face increases the contact area of a diamond layer and the hard alloy matrix so that the residual stress on the unit contact face can be reduced and the transverse pressure gradient in the process of polycrystalline diamond compact synthesis can be reduced, and therefore residual heat stress distribution in the diamond compact is improved. The protrusions arranged on the arc face can solve the problem of concentration of tensile stress. Thus, according to the arrangement, the residual stress on the unit contact face can be reduced and the reduction of stress concentration can be achieved, so that the binding force of the hard alloy matrix and the diamond is improved, and therefore the quality of the polycrystalline diamond is further improved.
Owner:HENAN JINGRUI SUPERHARD MATERIAL
Composite material reinforcing lead and production method thereof
InactiveCN101814338AGuaranteed mechanical propertiesGuaranteed service lifeNon-insulated conductorsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsGlass fiberManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a composite material lead and a production method thereof, in particular to a lead for overhead power transmission and a production method thereof. The lead comprises a composite material reinforcing rib encircled by a conducting material. The production method relates to a composite material pultrusion process. The lead comprises the reinforcing rib and a long-bar shaped conductive body distributed vertically along the reinforcing rib. The reinforcing rib comprises a continuous carbon fiber reinforced composite material carrier and a glass fiber mat reinforced composite material protective body. The reinforcing rib of the invention is produced by the pultrusion process including a die opening and closing technology and an induction heating technology. The reinforcing rib is wound with the conductive body outside to form the lead which can be used for overhead power transmission. The lead provided by the invention has the advantages of long service life, low cost, low sag and high transmission efficiency. The production method of the reinforcing rib has fast pultrusion speed and even internal and external heating of materials and can eliminate residual heat stress during solidification.
Owner:JIANGSU AOSHENG COMPOSITE MATERIALS HI TECH +1
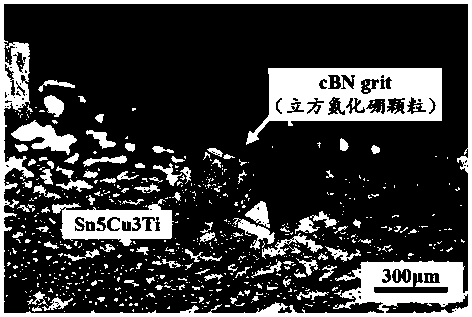
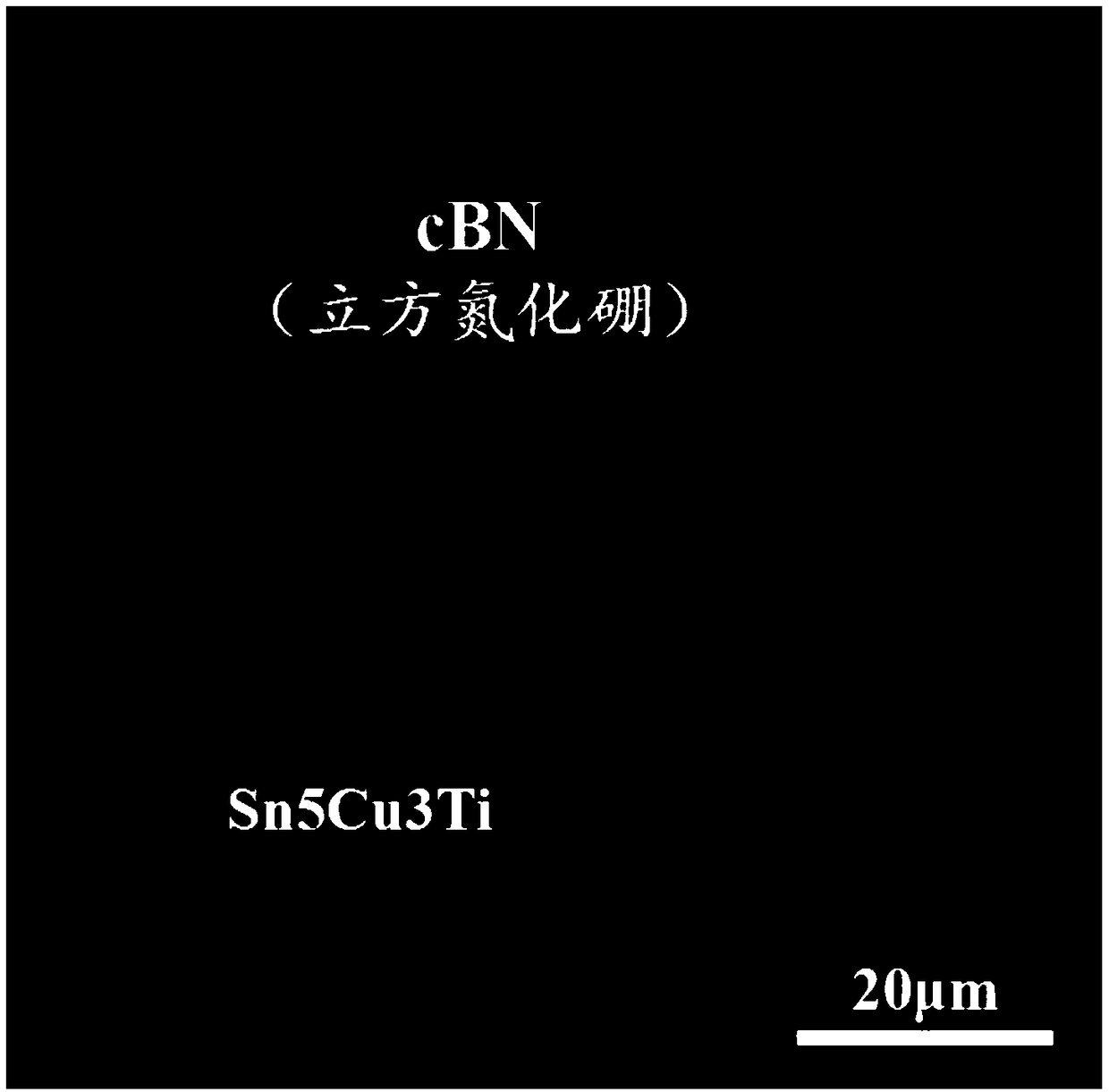
Method for brazing CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) abrasive particles at low temperature
ActiveCN108655524ASufficient binding strengthReduce residual stressWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMetallic materialsBoron nitride
The invention discloses a method for brazing CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) abrasive particles at a low temperature and belongs to the technical field of superhard abrasive material tool manufacture. The method comprises the following steps: adopting acetone to clean CBN abrasive particles ultrasonically and drying the CBN abrasive particles, sequentially paving and spraying Sn-Cu-Ti alloy powder and CBN abrasive particles on a polished tool substrate; placing the tool substrate in a quartz tube and vacuumizing; then, moving the tool substrate to a heating furnace and heating the tool substrate for5-60 minutes at 350-700 DEG C; and finally, cooling the tool substrate to the room temperature under the vacuumizing state. The method has the following technological advantages: on the premise thatbrazing filler metal and the CBN abrasive particles are ensured to generate chemical bonding and the abrasive particles have sufficient bonding strength, the brazing temperature is greatly reduced toreduce loss of the metal material performance, size and shape of the tool substrate and the residual thermal stress at the bonding interface of the CBN abrasive particles and brazing filler metal is reduced.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
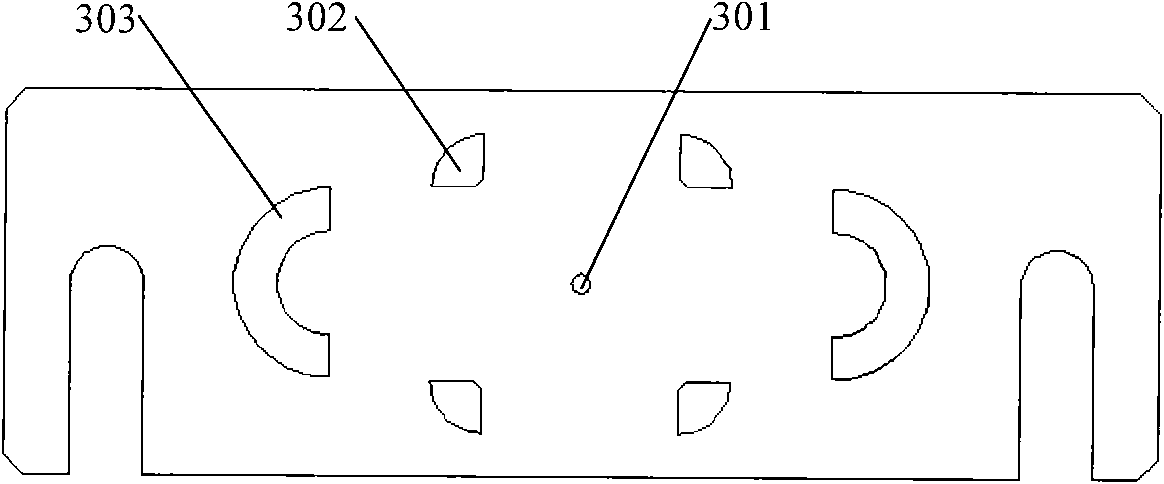
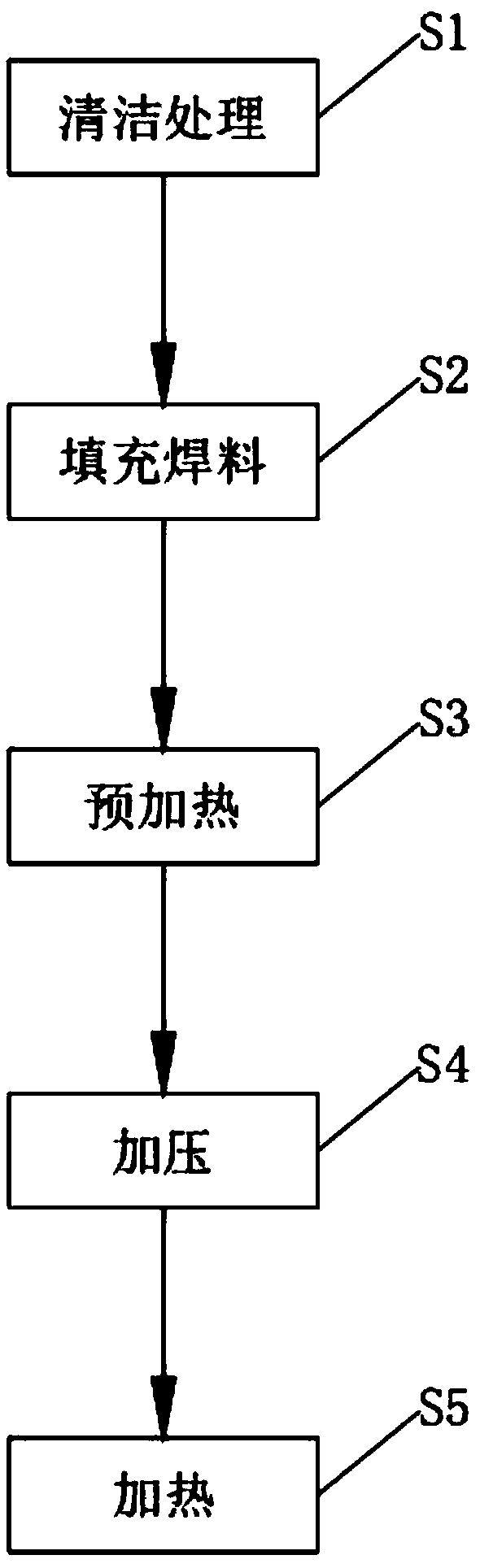
Kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method
The invention relates to a kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method. The kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method comprises the following steps of cleaning, filling welding flux, preheating, pressurizing and heating. The kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method has the advantages of simple process, time saving, low production cost and high production efficiency, and additionally, the thermal residual stress of a joint is small, so that the performance of the joint is good, the joint is reliable, and the application requirement of the kovar alloy andtungsten copper alloy connecting joint can be met.
Owner:SUZHOU SAITERUI PRECISION MACHINERY PARTS CO LTD
Method for forming reinforced-phase-strengthened composite welding seam structural material by regulating
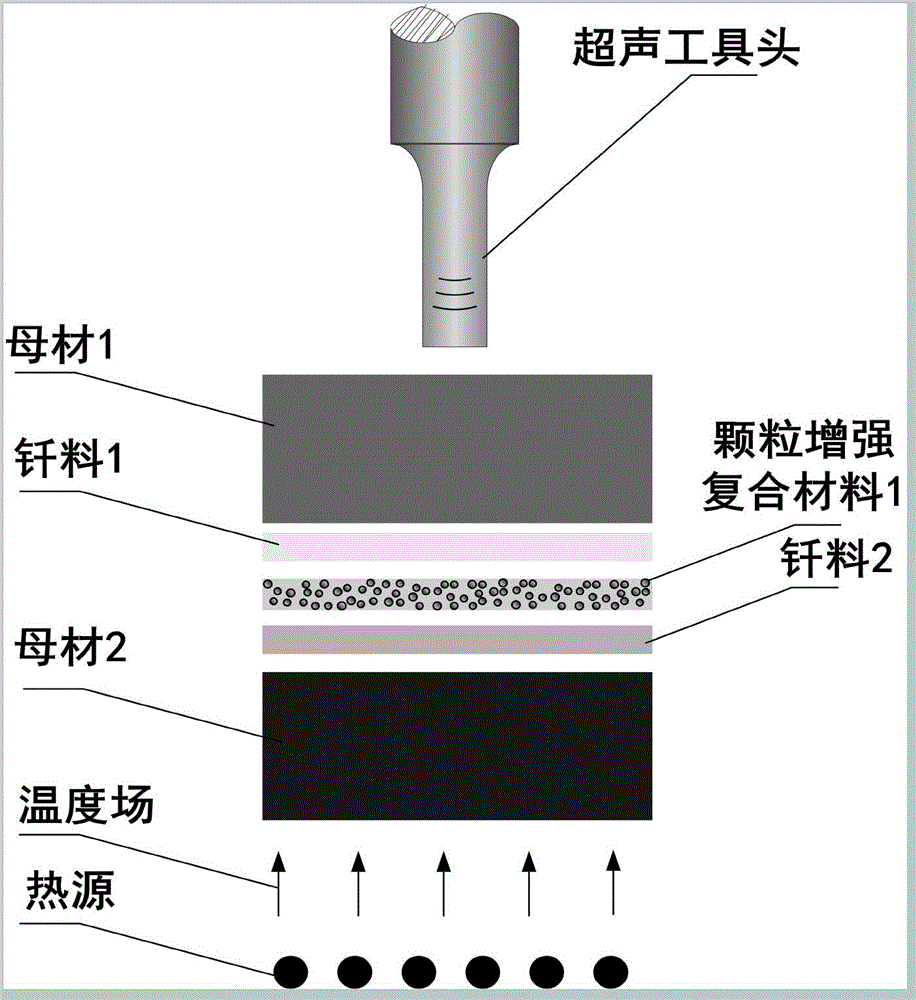
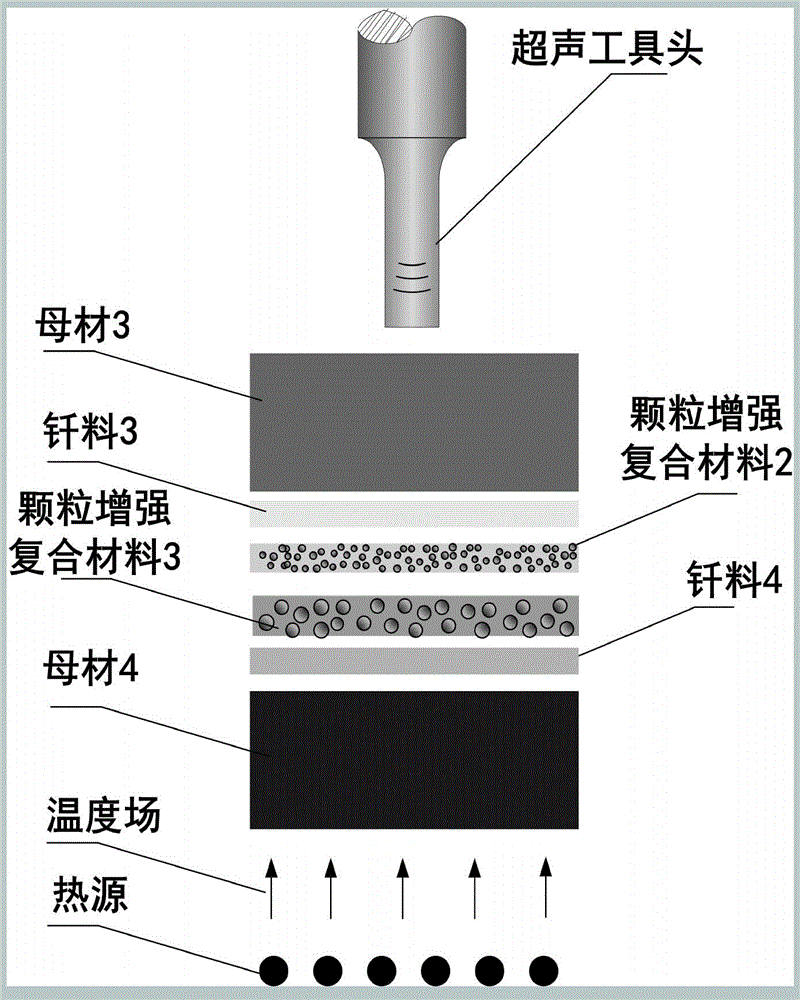
ActiveCN105618885AControllable binding interface reactionReduce residual thermal stressSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesUltrasonic assistedRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for forming reinforced-phase-strengthened composite welding seam structural material by regulating. The method comprises the following steps: separately cleaning the surfaces of a to-be-welded parent material, a composite material and brazing filler metal to remove an oxide film, stains and grease, and drying the to-be-welded parent material, the composite material and the brazing filler metal for later use; and then, assembling the materials according to a structure of parent material / brazing filler metal / composite material / brazing filler metal / parent material, putting the assembled materials into an ultrasonic auxiliary welding device, applying ultrasonic waves while heating and preserving the heat, starting a pressurizing device to carry out welding in case of reaching a predetermined temperature and ultrasonic fields, stopping ultrasonic action while the temperature is reduced to the room temperature after welding, and taking out a welded part, thereby obtaining the reinforced-phase-strengthened composite welding seam structural material. The method has the advantages and the positive effects that: the method is used for forming reinforced-phase-strengthened composite welding seam structural material by regulating, welding for metal and nonmetal can be carried out, bonding interface reaction is controllable, residual thermal stress is relatively small, and the bonding strength is relatively high.
Owner:浙江邦驰汽车零部件有限公司
Preparation method of silicon carbide composite film of reflector used in space
InactiveCN102242348AImprove uniformityEasy to manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingComposite filmMetallurgy
The invention provides a preparation method of a silicon carbide composite film of a reflector used in space, and the method is characterized in that the polished reaction sintering silicon carbide substrate is placed in a deposition chamber, a silicon carbide whisker film is deposited at first: one path of gas is mixed gas of methyl silicochloroform and hydrogen from a vaporization kettle, wherein the pressure in the vaporization kettle can be controlled at 0.2 - 0.3 MPa, the total flow of mixed gas can be controlled at 200 - 300 ml / minutes, methyltrichlorosilane is sent to the deposition chamber by hydrogen through a bubbling method, the other path of gas is argon with flow of 800 - 900ml / minutes, a process of low pressure chemical vapor deposition is employed, wherein the deposition pressure in the deposition chamber is 6 - 7 kPa, the deposition temperature is 1100 - 1150 DEG C; redepositing a silicon carbide particle film: the total flow of hydrogen and methyl silicochloroform can be modified to 300 - 400 ml / minutes, the air flow rate of argon is modified to 500 - 600 ml / minutes, the deposition pressure in the deposition chamber is 3 - 5 kPa; finally, a process of polishing is performed and the silicon carbide composite film can be obtained on the substrate. According to the invention, the residual thermal stress between the substrate and the silicon carbide composite film is small, and associativity is good, and the method of the invention is beneficial to preparation of large size silicon carbide reflectors.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for eliminating residual thermal stress of hard alloy cutter
The invention discloses a method for eliminating residual thermal stress of a hard alloy cutter. A hard alloy cutter sample is subjected to flatness treatment and then mounted in a cold-pressing mold; the cold-pressing mold containing the hard alloy cutter sample is charged into a press to be pre-pressed, after pressure maintaining, two times of pressing pressure increasing are conducted until the pressure reaches the maximum set value, and pressure is unloaded in two steps after pressure maintaining; and the pressure increasing speed and the pressure decreasing speed are controlled, and pressing is repeated for 8-12 times with same pressing parameters. The side face of the pressed hard alloy cutter sample is changed to a stressed face, the pressing load is changed according to the same pressure intensity, operation is repeated with the same pressing parameters, the sample is taken out after pressing is completed, and the low-internal-stress hard alloy cutter is obtained.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
Ceramic micro-crack repairing method
The invention discloses a ceramic micro-crack repairing method. The method comprises the following steps: discovering and extracting size characteristic parameters of micro-cracks on a ceramic part byutilizing a nondestructive testing process; processing the micro-crack area into micro-holes by using an optical fiber laser processing procedure; removing burrs on the surface of the optical fiber laser machining area and chipping residues in the micro holes through a polishing and cleaning procedure; removing residual thermal stress of the fiber laser processing area by using a thermal treatment process; filling the micro-holes after the chipping residues are removed with brazing filler metal by utilizing a brazing filler metal coating procedure, and compacting; tightly combining the brazing filler metal and the ceramic matrix combined through a brazing procedure; removing excess brazing filler metal reactants through a polishing post-treatment procedure to obtain a repaired smooth ceramic surface. After the microcracks on the ceramic are repaired through the method, the defective rate in the ceramic production and machining process can be greatly reduced, and the use limit of the repaired ceramic product is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
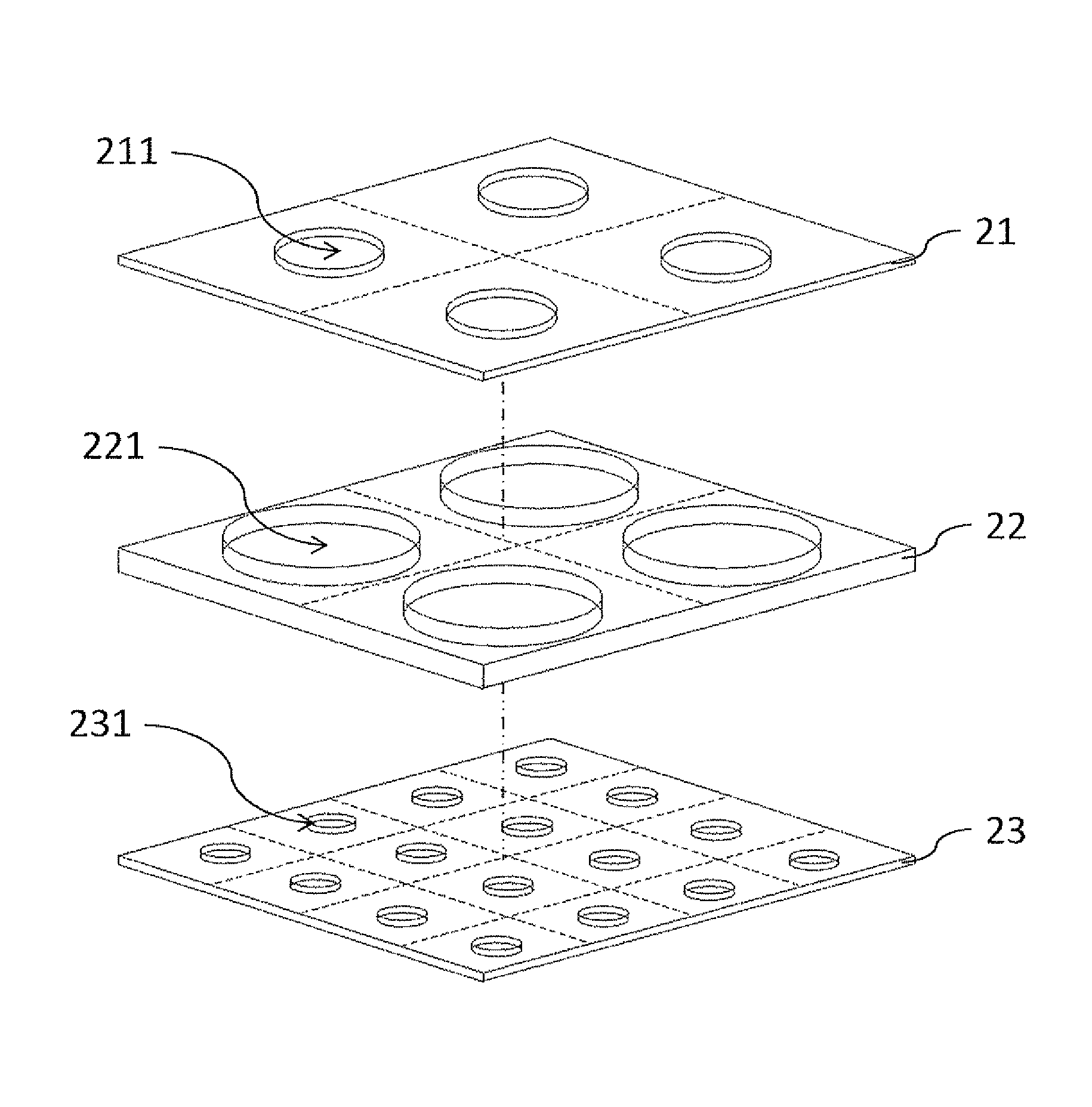
Miniature sieve apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
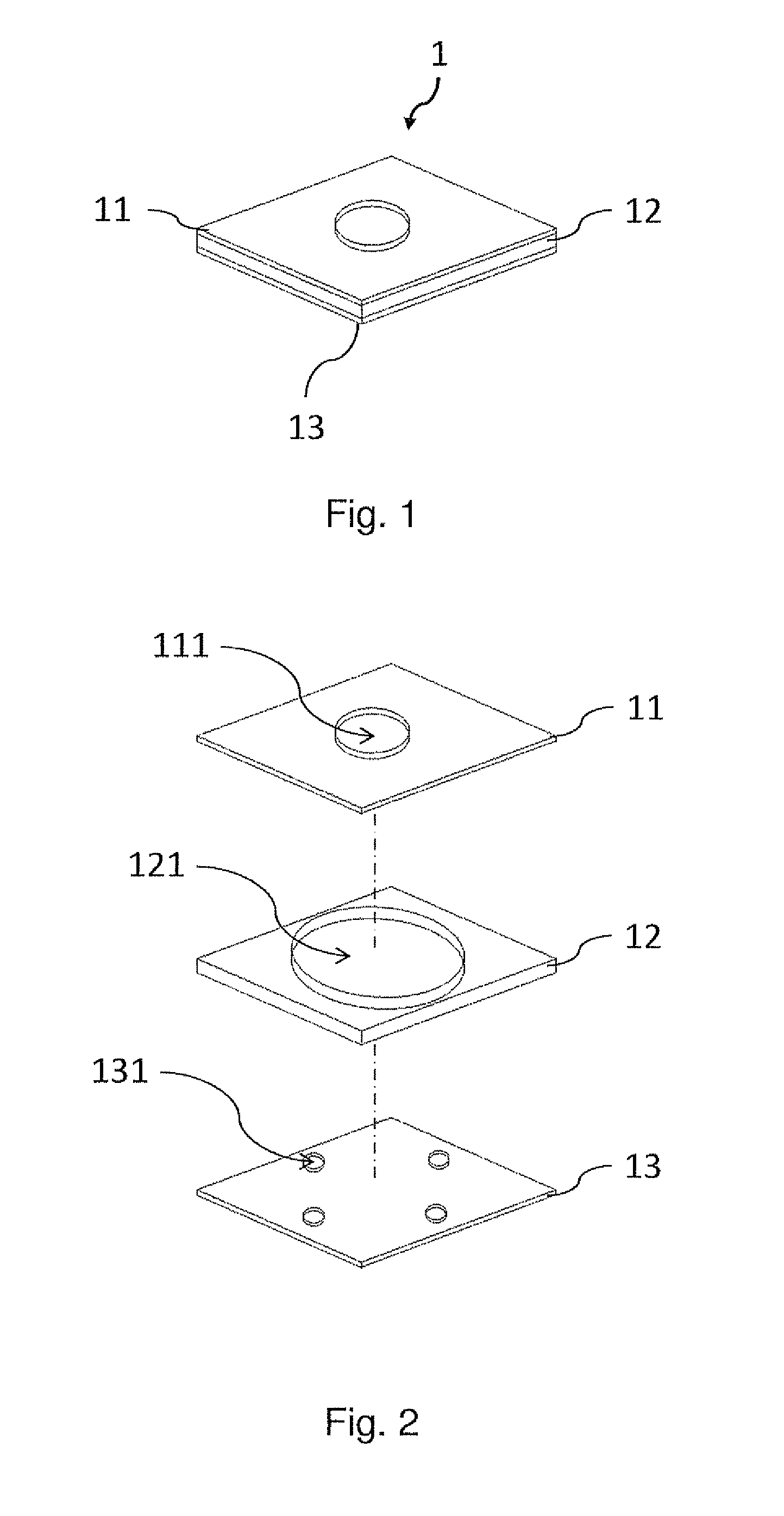
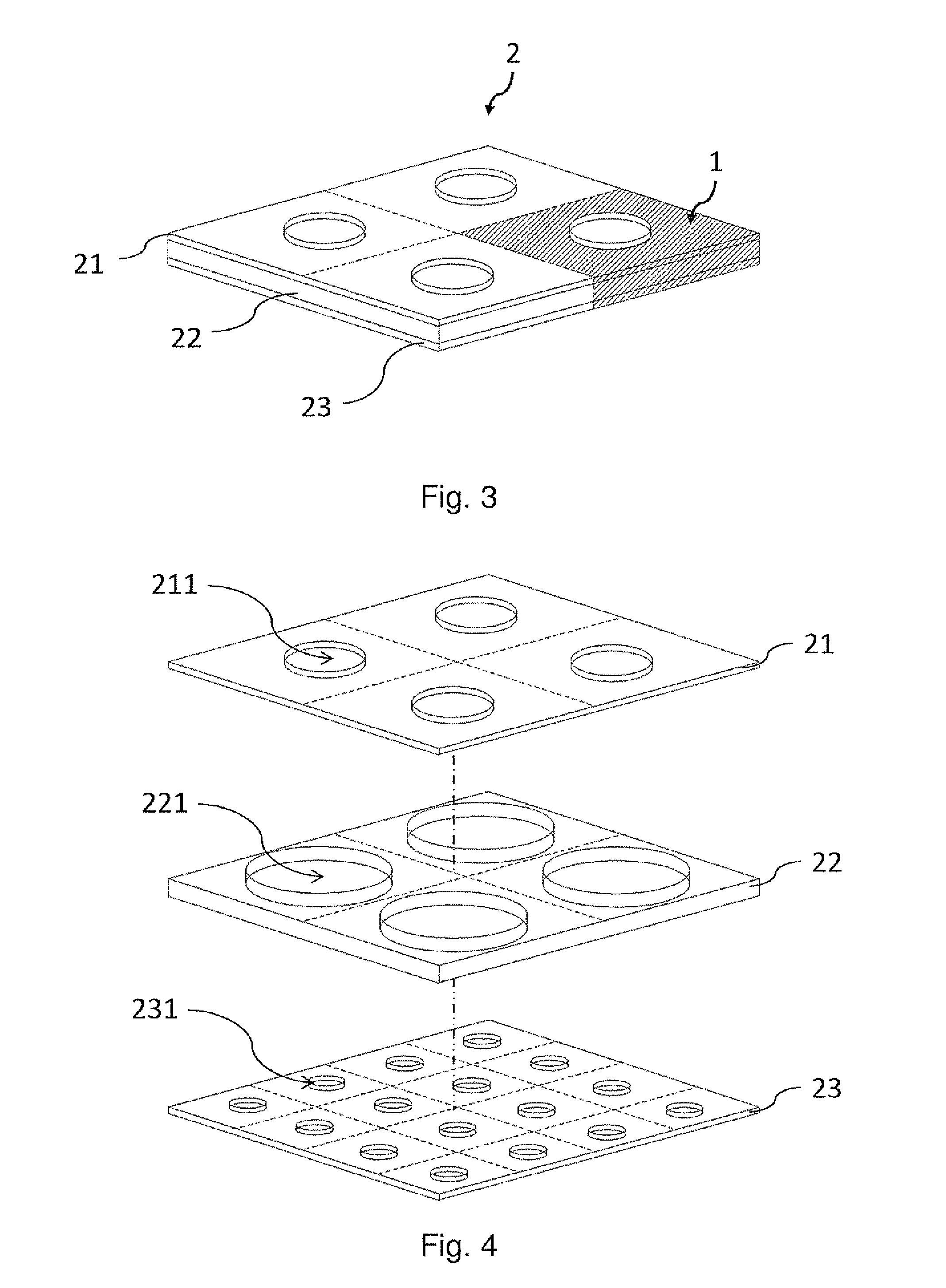
InactiveUS20130259772A1Improve structural stabilityImprove design flexibilityPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresMicroparticleResidual thermal stress
A miniature sieve apparatus is described and includes a first sieve, a separator and a second sieve from top to bottom. The first and second sieves are formed with at least one first mesh and a plurality of second meshes, respectively. The first and second meshes are misaligned with each other in a vertical direction of the first and second sieves. The miniature sieve apparatus is provided to separate or screen microparticles with different sizes, such as target cells, bio-medical particles, organic or inorganic microparticles. Additionally, the invention also provides a manufacturing method of the miniature sieve apparatus, and the same material is applied to manufacture the sieves and the separators. Thus, the problem caused by the residual thermal stress due to different material can be solved. Therefore, the cost of the miniature sieve apparatus can be lowered as the yield rate thereof is improved.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Laser cladding device for self-healing of cracks of cladding layer and processing method of laser cladding device
ActiveCN110453216AQuality improvementImprove performanceIncreasing energy efficiencyMetallic material coating processesHigh current densityPorosity
The invention relates to a laser cladding device for self-healing of cracks of a cladding layer and a processing method of the laser cladding device. The device comprises a laser cladding mechanism and a pulse current mechanism, wherein the laser cladding mechanism comprises a fixing seat and a laser head which are arranged above a workbench; and the pulse current mechanism comprises adjustable electrode assemblies which are respectively arranged at two ends of the laser cladding mechanism, and the adjustable electrode assemblies are connected with the fixing seat through adjustable connectingpieces. By arrangement of the pulse current mechanism, the cladding efficiency is improved, crystal grains of the cladding layer can be refined, the porosity of the cladding layer is reduced, the structure of the cladding layer is uniformized, meanwhile, the residual thermal stress and the cracking sensitivity of the cladding layer can be reduced, particularly, on-line self-healing of the cracksof the cladding layer can be realized due to a flow-around effect and a Joule thermal effect formed at the tips of the cracks of the cladding layer due to the pulse high current density, and a high-quality and high-performance laser cladding layer can be prepared.
Owner:TONGLING UNIV
Miniature sieve apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS8911687B2Improve structural stabilityImprove design flexibilitySemi-permeable membranesLaboratory glasswaresMicroparticleMechanical engineering
A miniature sieve apparatus is described and includes a first sieve, a separator and a second sieve from top to bottom. The first and second sieves are formed with at least one first mesh and a plurality of second meshes, respectively. The first and second meshes are misaligned with each other in a vertical direction of the first and second sieves. The miniature sieve apparatus is provided to separate or screen microparticles with different sizes, such as target cells, bio-medical particles, organic or inorganic microparticles. Additionally, the invention also provides a manufacturing method of the miniature sieve apparatus, and the same material is applied to manufacture the sieves and the separators. Thus, the problem caused by the residual thermal stress due to different material can be solved. Therefore, the cost of the miniature sieve apparatus can be lowered as the yield rate thereof is improved.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
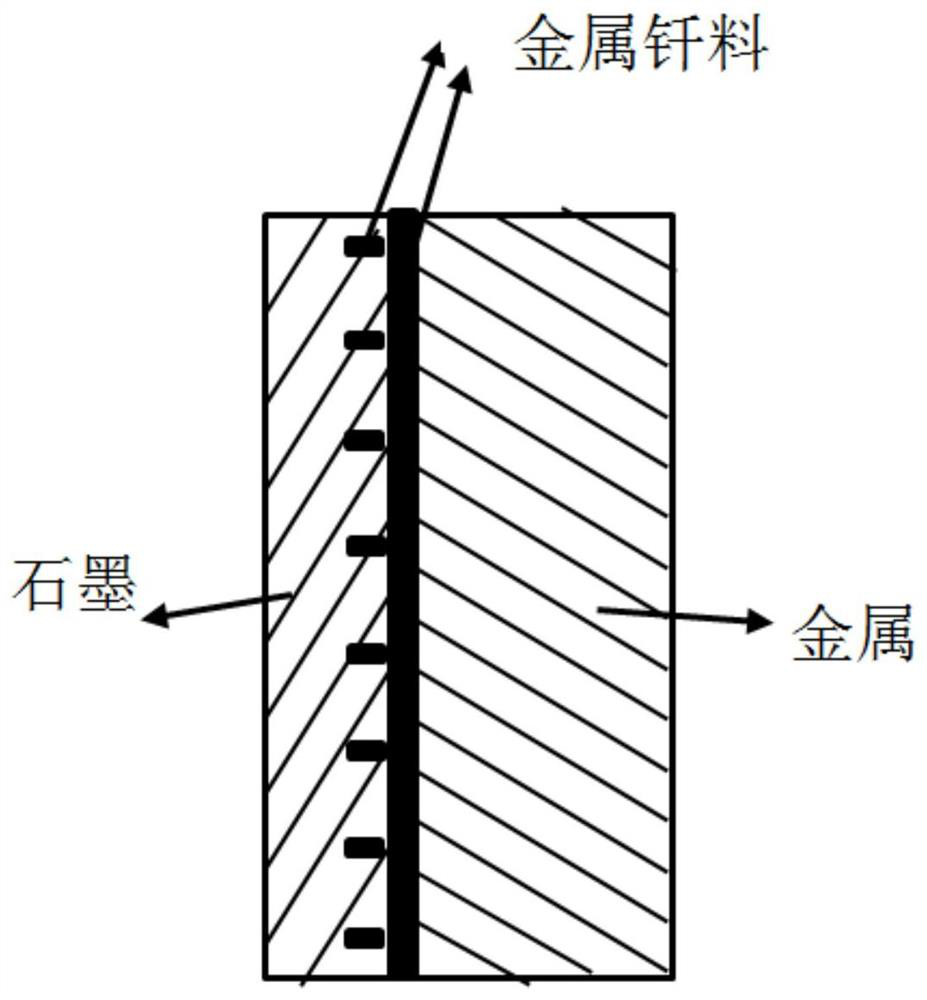
Heat shock resistant graphite and metal brazing method
The invention discloses a heat shock resistant graphite and metal brazing method, and belongs to the technical field of ceramic / metal dissimilar material connection. The method comprises the steps that a groove is machined in the welding surface of to-be-brazed graphite, the groove is filled with metal brazing filler metal, the welding surface of the graphite is covered with a foil strip made of the metal brazing filler metal, the foil strip is covered with the welding surface of to-be-brazed metal, a to-be-brazed module is formed, the to-be-brazed module is placed in a vacuum brazing furnace to be subjected to vacuum brazing, and the to-be-brazed graphite is obtained. The brazing temperature ranges from 780 DEG C to 900 DEG C, after heat preservation is conducted for 5 min to 20 min, the temperature is reduced to 450 DEG C at the cooling rate lower than 5 DEG C / min, and then the alloy is cooled to the room temperature along with a furnace. According to the invention, the residual thermal stress formed after graphite / electromagnetic pure iron heterogeneous brazing is reduced, the reliability of the joint is improved, and the joint can bear thermal shock of 450 DEG C to cold water (20 DEG C) for not less than 10 times.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com