New method for predicting residual thermal stress of planar-knitted composite material
A technology of residual thermal stress and planar weaving, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as reducing the strength of composite materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0078] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0079] See Figure 6 , the present invention is a new method for predicting the residual thermal stress of plane braided composite materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
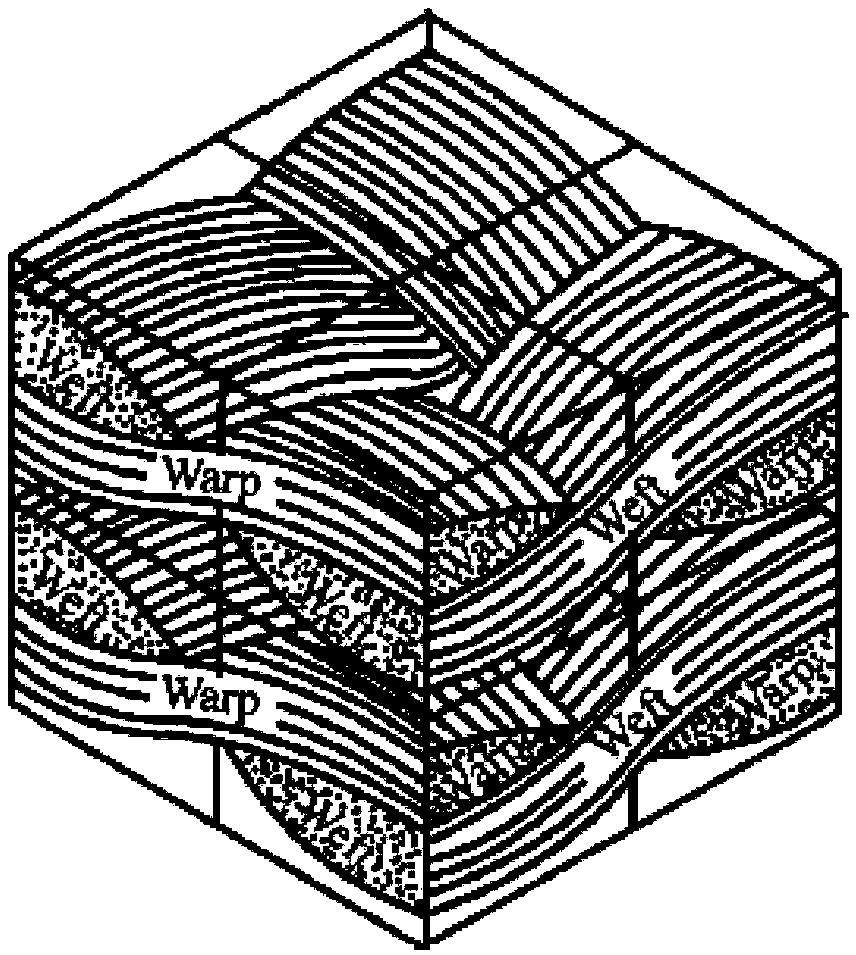
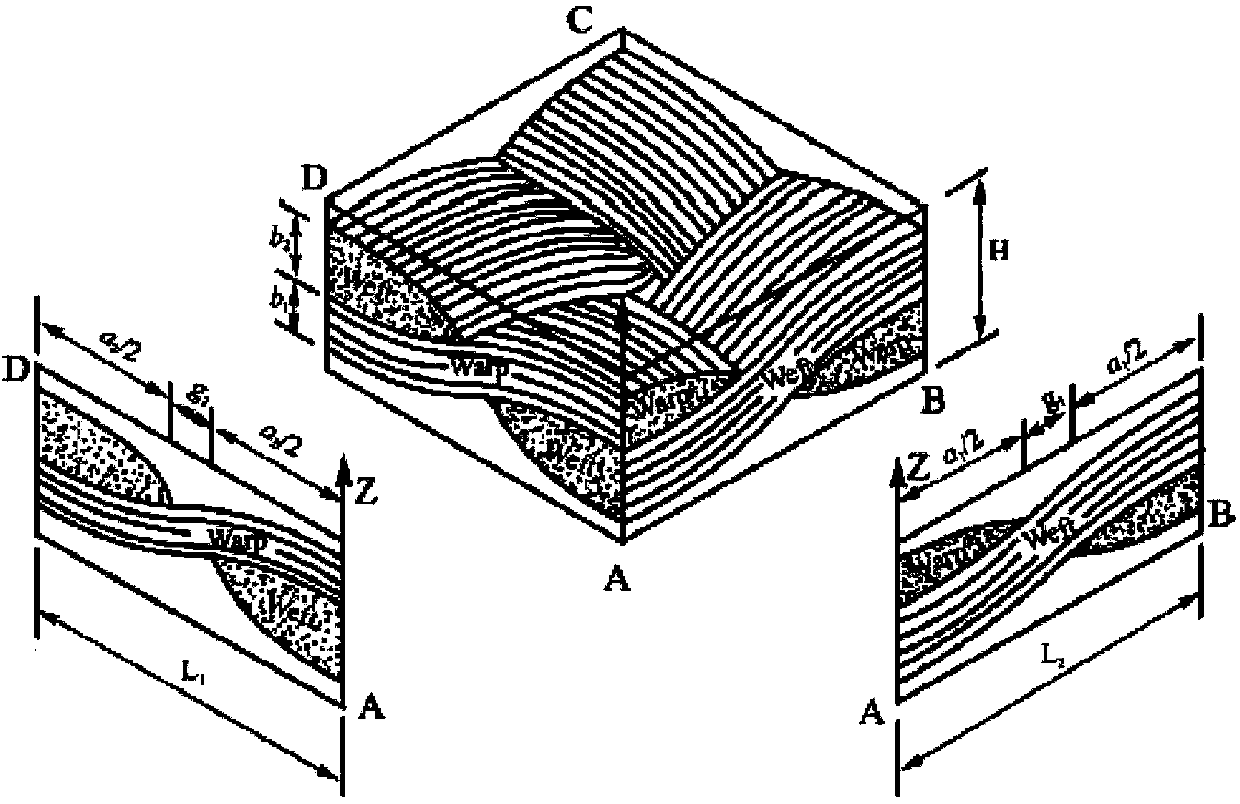
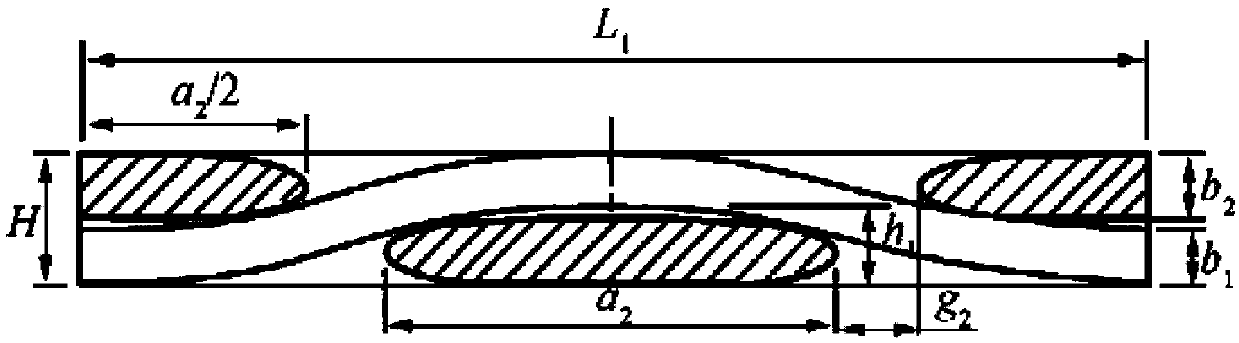
[0080] Step 1. Determination of cell body unit. according to figure 1 For the weaving method shown, consider the periodicity and repetition of weaving, select a representative volume element model, figure 2 is the selected representative volume element (cell body unit), which contains two orthogonal warp yarns and weft yarns (fiber bundles), where direction 1 is defined as the warp direction, and direction 2 is defined as the weft direction. according to figure 2 , the Z coordinate expressions of the centerlines of the warp and weft yarns can be obtained:
[0081] z ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com