Method for removing or inhibiting alga in eutrophic water
A technology of eutrophication and production methods, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, other chemical processes, etc., can solve problems such as uneconomical, secondary pollution of water, unscientific, etc., to avoid garbage and resource recycling. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
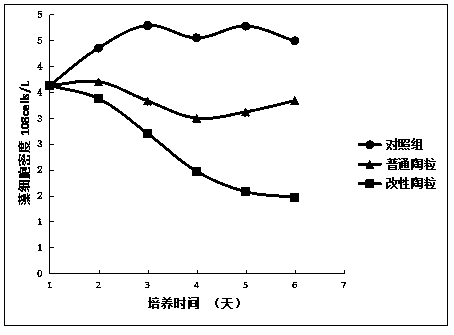
[0035] Example 1: Effects of common ceramsite and modified ceramsite on algae cells
[0036] figure 1 It is the change chart of algae cell density. Three experimental groups are set up. One group is the control group without adding anything, one group is added with ordinary ceramsite, and the last group is added with modified ceramsite. increased, indicating that there are excess nutrients in the culture medium to maintain algae proliferation; the density of algae cells added with ordinary ceramsite first decreased and then increased slightly, indicating that the porous structure of ordinary ceramsite can indeed absorb algae cells, making the algae cell density The removal rate of common ceramsite on algae cells reached 25.7%; the density of algae cells added with modified ceramsite decreased significantly, indicating that the algae cells were affected by the adsorption and phosphorus removal of the porous structure of ceramsite, making the algae cell density The rate of remo...
Embodiment 2
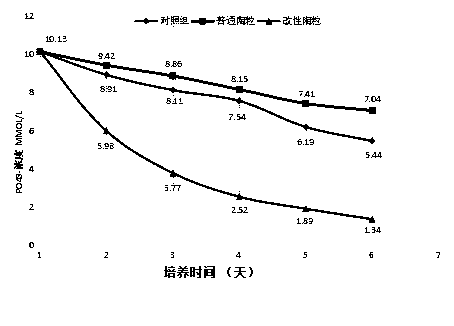
[0037] Example 2: Effect of ordinary ceramsite and modified ceramsite on phosphate
[0038] figure 2It is a diagram of the concentration change of phosphate in water. Set up three experimental groups, one group without adding anything is the control group, one group is added with ordinary ceramsite, and the last group is added with modified ceramsite. After 6 days of cultivation, the phosphate of 3 bottles Concentrations are gradually decreasing. Due to the adsorption of ceramsite, the density of algal cells and the consumption of phosphate in the flask with ordinary ceramsite were lower, so the phosphate concentration was generally higher than that of the control group; the phosphate concentration in the flask with modified ceramsite was significantly higher. , indicating that the modified ceramsite has a very significant effect on the removal of phosphate, and the growth of algae is inhibited by removing phosphorus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com