Thoracic and abdominal surface area respiratory signal cycle prediction method based on single-period and double-period hybrid judgment
A technology of breathing signal and surface area, which is applied in the fields of engineering technology and mathematics, tumor medicine, and precision instruments. It can solve problems such as judging cycle and difficulty, and achieve the effect of small amount of calculation, simple function, and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0074] This embodiment is an embodiment of a method for predicting the period of the respiratory signal in the chest and abdomen surface area based on mixed judgment of single and double periods.
[0075] The method for predicting the period of the respiratory signal in the thoracoabdominal surface area based on mixed judgment of single and double periods in this embodiment consists of the following steps:
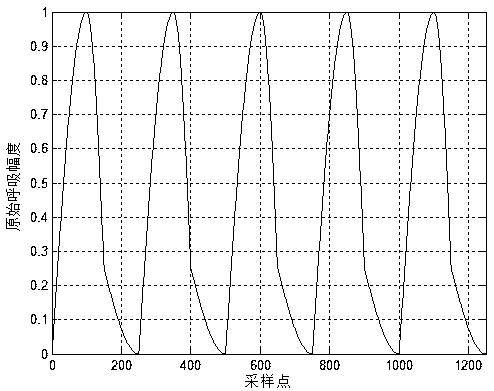
[0076] Step a, constructing an ideal single-period respiratory signal;
[0077] Step b, performing period extension on the ideal single-period respiratory signal obtained in step a, to obtain an ideal multi-period respiratory signal;
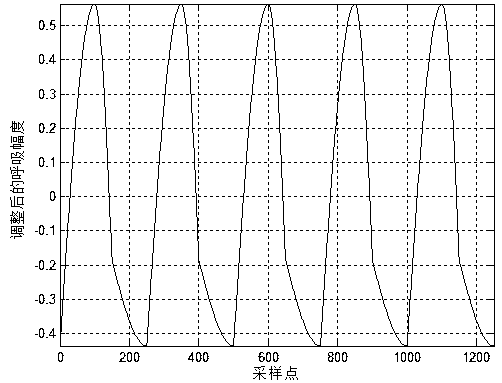
[0078] Step c, carry out periodic extraction to the ideal multi-period breathing signal obtained in step b, including:
[0079] Step c1, extracting the DC component of the ideal multi-period respiratory signal obtained in step b;
[0080] Step c2, subtracting the DC component obtained in step c1 from the ideal multi-cycle respiratory signa...
specific Embodiment 2
[0088] This embodiment is an embodiment of a method for predicting the period of the respiratory signal in the chest and abdomen surface area based on mixed judgment of single and double periods.
[0089] The method for predicting the respiratory signal period of the thoracoabdominal surface area based on the mixed judgment of single and double periods in this embodiment, on the basis of the specific embodiment 1, further limits the construction of an ideal single-period respiratory signal described in step a, including the following steps:
[0090] Step a1, according to the normal breathing process of human beings, the breathing movement is divided into three stages: inhalation process, exhalation process and quasi-pause process;
[0091] Step a2, respectively determine the duration T of the inhalation process 1 , the duration of the exhalation process T 2 and the duration T of the class suspension process 3 ;
[0092] Step a3, with a period of 4T 1 A sinusoidal function ...
specific Embodiment 3
[0095] This embodiment is an embodiment of a method for predicting the period of the respiratory signal in the chest and abdomen surface area based on mixed judgment of single and double periods.
[0096] The method for predicting the period of the respiratory signal in the thoracoabdominal surface area based on mixed judgment of single and double periods in this embodiment consists of the following steps:
[0097] Step a, constructing an ideal single-period respiratory signal;
[0098] Step a1, according to the normal breathing process of human beings, the breathing movement is divided into three stages: inhalation process, exhalation process and quasi-pause process;
[0099] Step a2, respectively determine the duration T of the inhalation process 1 , the duration of the exhalation process T 2 and the duration T of the class suspension process 3 ;
[0100] Step a3, with a period of 4T 1 A sinusoidal function with a phase of [0, π / 2] simulates the inhalation process to ob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com