Hepatocyte-like cells from humanized adipose-derived stem cells and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of hepatocyte-like cells and adipose stem cells, applied in the field of stem cells and biomedicine, can solve the problems of inconsistent and unknown liver differentiation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
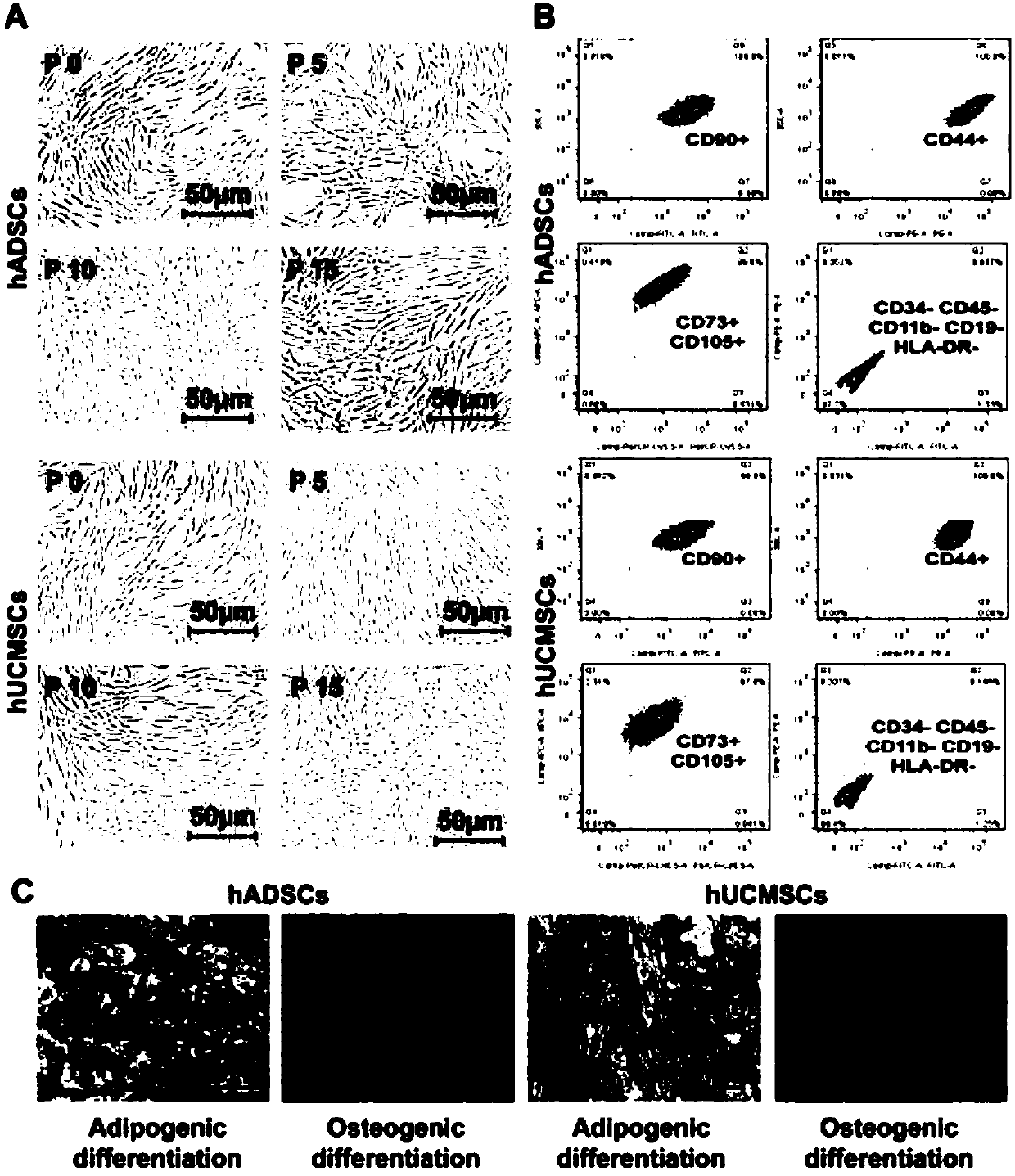
[0123] Example 1. Morphology and identification of hASCs and hUCMSCs
[0124] Morphological identification of hASCs and hUCMSCs was performed as described in "Materials and Methods".
[0125] The results were as follows: three days after the primary inoculation of hASC and hUCMSC, cell colonies were formed, and the cells in the colonies were long spindle-shaped, uniform in size, arranged closely and growing radially; the morphology and proliferation speed of P5, P10, and P15 generation cells had no obvious changes ( See figure 1 A). Flow cytometry detection of P3 generation hASC and hUCMSC: CD90, CD44, CD73, and CD105 were all positively expressed, while CD34, CD45, CD11b, CD19, and HLA-DR were negatively expressed (see figure 1 B). After two weeks of adipogenic induction of hASCs and hUCMSCs, oil red O staining showed that there were a large number of translucent red lipid droplets with good refraction in hASCs cytoplasm, while only a small amount of fine red stained parti...
Embodiment 2
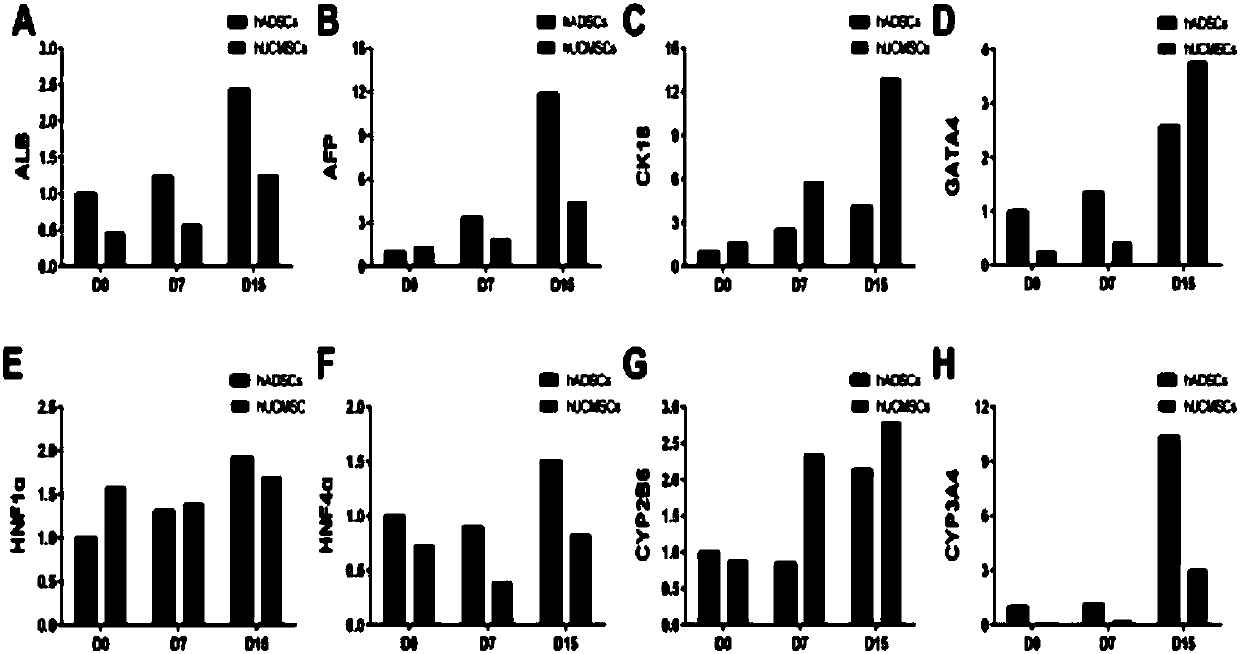
[0126] Example 2. Differentiation of hASC and hUCMSC to hepatocytes
[0127] Hepatic differentiation of hASCs and hUCMSCs was performed as described in "Materials and Methods".
[0128] The results were: the results of fluorescent quantitative PCR showed that compared with the hUCMSC induction group, the expression of ALB, AFP, HNF1α, HNF4α, and CYP3A4 mRNA were significantly enhanced in the hASC induction group, and the expression levels increased with the induction time (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
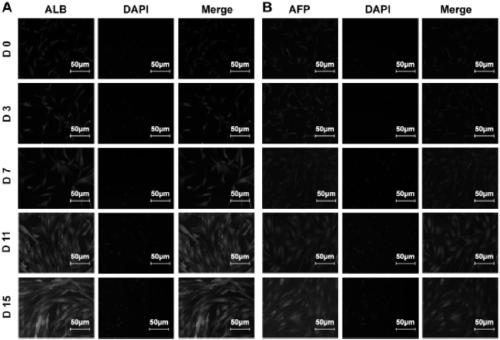
[0129] Example 3. Alb and AFP cell immunofluorescence observation
[0130] The expression levels of Alb and AFP in hASC-induced cells and hUCMSC-induced cells were detected according to "Materials and Methods".
[0131] The results were: in the hASCs induction group, the expression levels of Alb and AFP increased with the prolongation of the induction time, and the expression level of Alb increased significantly on the 11th day (such as image 3 shown). However, in the hUCMSC induction group, the expression of ALB and AFP was not significantly increased (such as Figure 4 shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com