A silicon carbide trench Schottky diode device and its preparation method
A Schottky diode, silicon carbide technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of inability to improve surge current resistance, achieve low specific on-resistance, reduce forward Effects of voltage drop, high surge current capability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
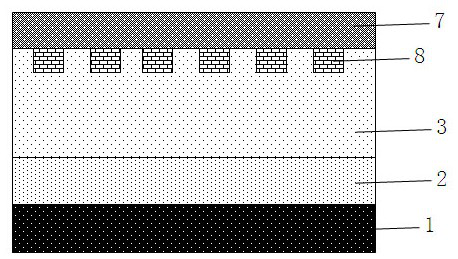
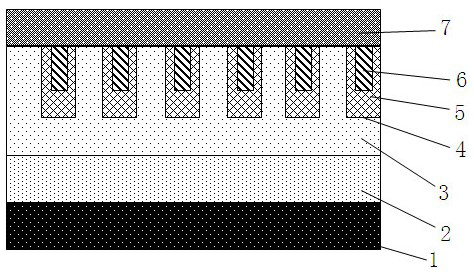
[0069] like image 3 As shown, a silicon carbide trench Schottky diode device includes from bottom to top: cathode electrode 1, substrate layer 2, N-type SiC epitaxial layer 3, trench 4, dielectric layer 5, conductive layer 6 and anode electrode 7 , a plurality of trenches 4 are located on the top of the N-type SiC epitaxial layer 3, the dielectric layer 5 and the conductive layer 6 are filled in the trenches 4 in sequence, and a P-type region 8 is also included, and the P-type region 8 is embedded in part of the trenches 4 between the N-type SiC epitaxial layer 3 and the junction of the anode electrode 7, the P-type region 8 is located in the N-type SiC epitaxial layer 3, and the upper boundary 81 of the P-type region 8 is connected to the anode electrode 7, and the P-type region 8 The side boundary 83 borders on the side wall 43 of the trench 4 , and the side boundary 83 is a boundary parallel to the side wall 43 of the trench 4 .
[0070] Present embodiment is prepared by ...
Embodiment 2
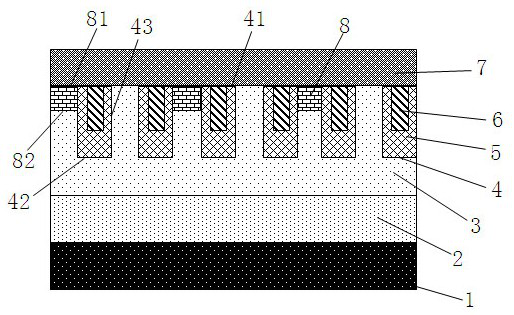
[0077] like Figure 4 As shown, the upper boundary 81 of the P-type region 8 protrudes above the trench 4 and is connected to the anode electrode 7 , and the lower boundary 82 is located on or above the top 41 of the trench 4 . This structure allows the P-type region 8 to be directly formed by epitaxial growth, avoiding material damage caused by ion implantation and activation processes, and also simplifies the process.
[0078] In another embodiment of the present invention, the dielectric layer 5 extends upward from the lower boundary 82 of the P-type region 8 to the side boundary of the P-type region, may extend to the upper boundary 81 of the P-type region 8, and may not extend to the P-type region. The upper boundary 81 of the area 8 is set according to actual needs. In this way, the connection between the anode electrode 7 and the N-type SiC epitaxial layer 3 can be avoided, and the short circuit between the P-type region 8 and the N-type SiC epitaxial layer 3 can preve...
Embodiment 3
[0087] like Figure 5 As shown, the difference from the first embodiment is that the side boundary 83 of the P-type region 8 does not border on the sidewall 43 of the trench 4 . And its preparation method is the same.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com