A ground source heat pump system performance prediction method
A system performance and prediction method technology, applied in the direction of prediction, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of only considering the impact of the future performance of the system, the unsatisfactory heat transfer performance of the GSHP system, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
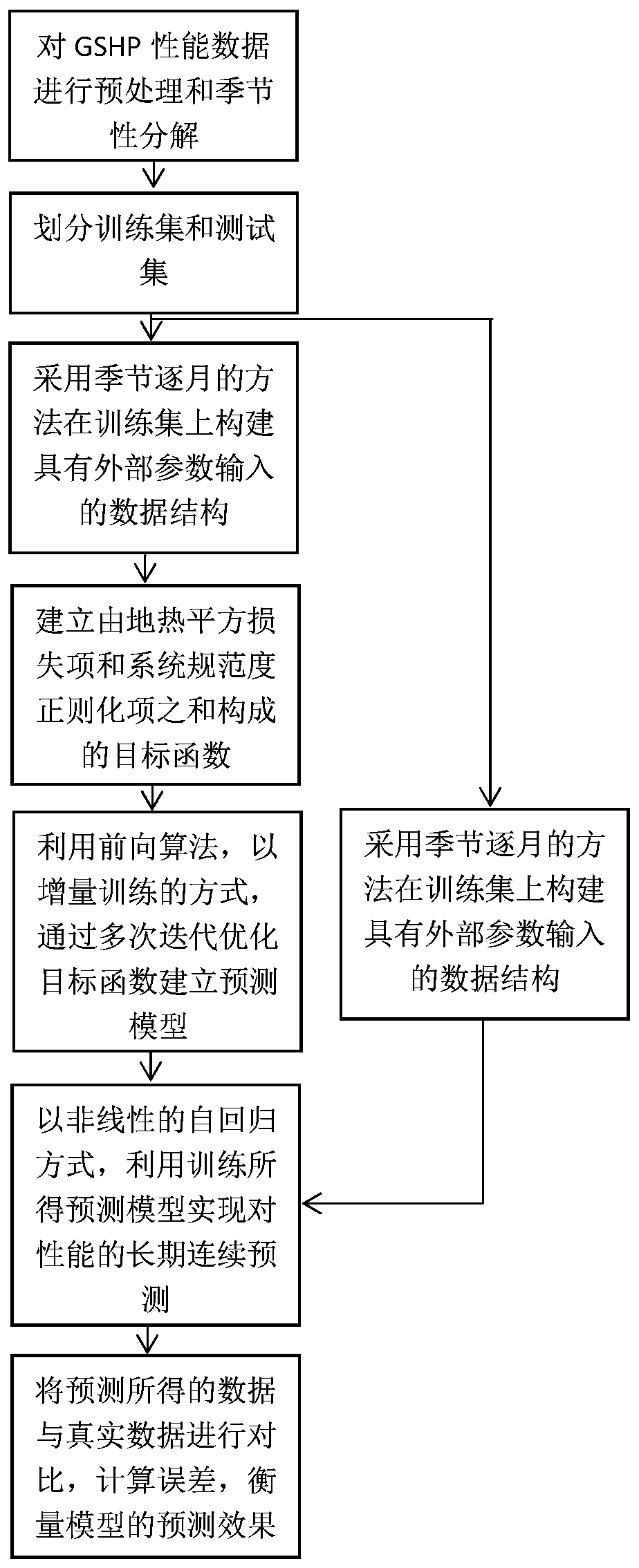
[0077] A performance prediction method for a ground source heat pump system, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
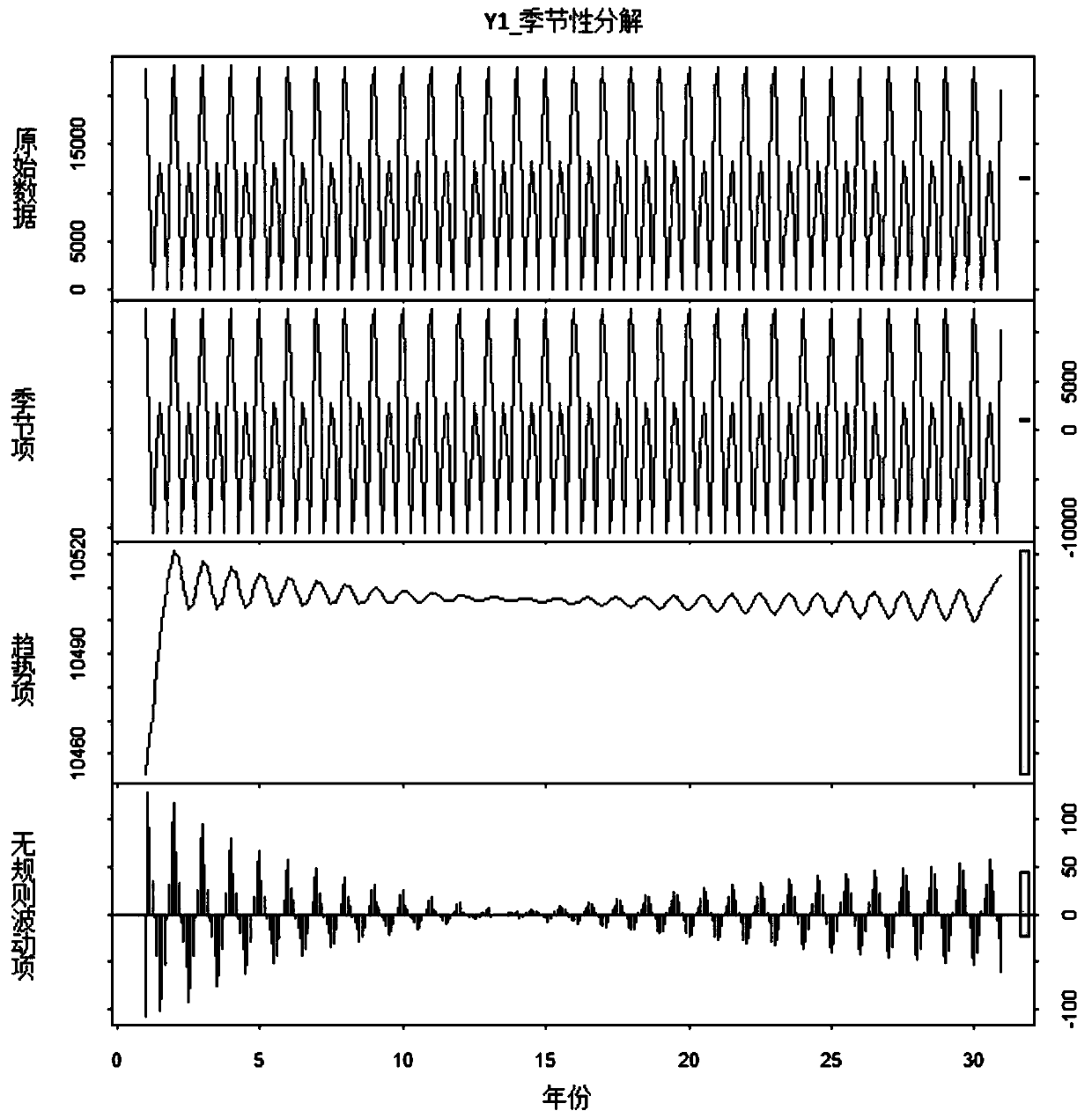
[0078] (1) Preprocess and analyze the heat transfer performance data of the GSHP system, complete data cleaning, and conduct seasonal decomposition of the heat transfer performance data to analyze its stationarity;
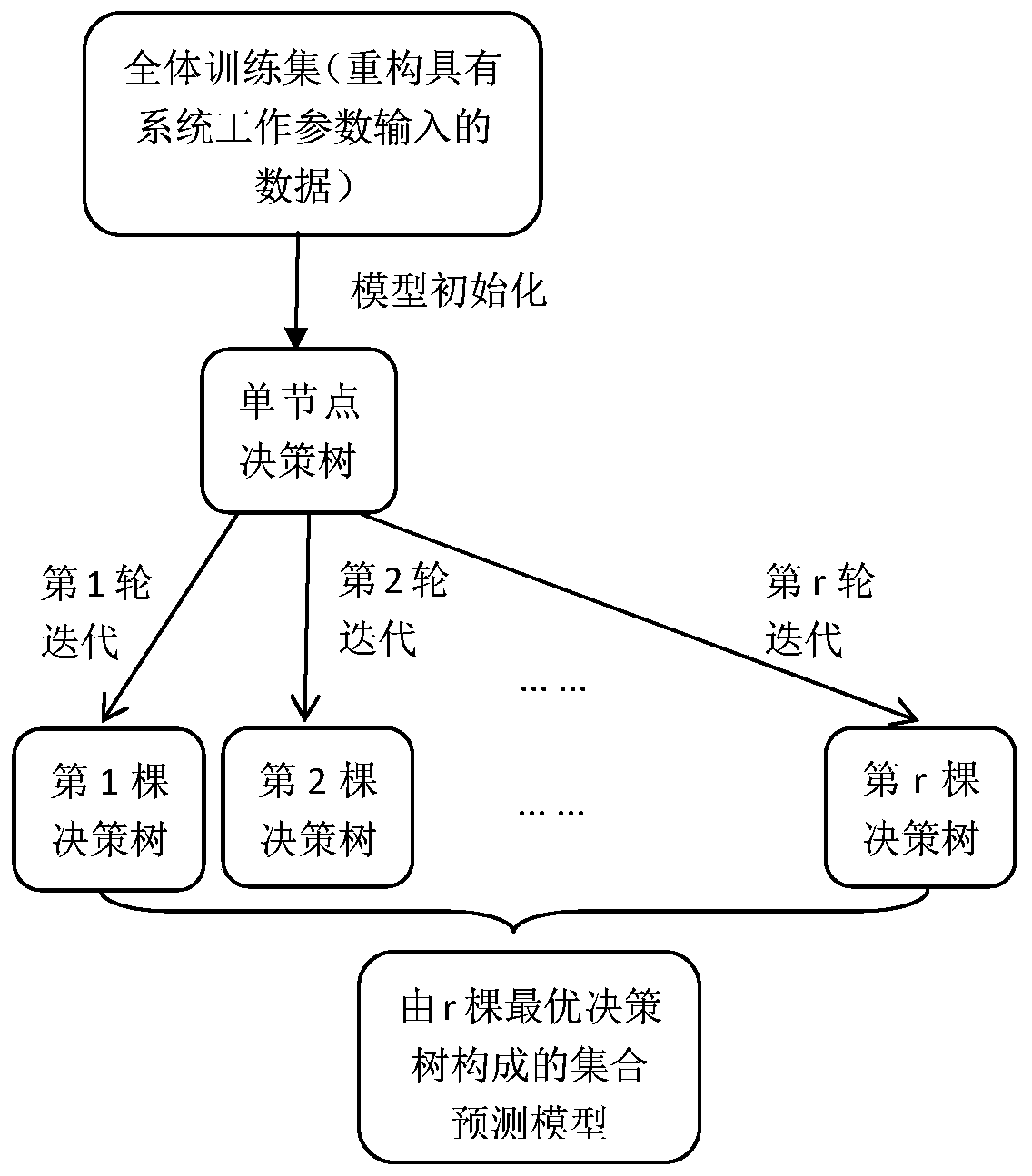
[0079] (2) Divide the heat transfer performance data of the GSHP system processed in step (1) into a training set and a test set, construct a data structure with the input of the GSHP system operating parameters, and introduce 12 operating parameters of the GSHP system, including the distribution of boreholes x 1 , drilling radius X 2 , buried pipe depth X 3 , the number of buried pipes X 4 , Transverse spacing of buried pipes X 5 , Longitudinal spacing of buried pipes X 6 , The thermal conductivity of the filling material in the tube X 7 、Nominal outer diameter of U-shaped pipe X 8 , U-tube spacing X 9 , remote rock and so...
Embodiment 2
[0084] According to a method for predicting the performance of a ground source heat pump system described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that:
[0085] Step (1), preprocessing and analyzing the heat transfer performance data of the GSHP system, including:
[0086] A. Simulate and obtain the heat transfer performance data of the GSHP system; the heat transfer performance data of the GSHP system includes several sets of time series data, and each set of time series data includes 12 system operating parameters X 1 ~X 12 and Y 1 ~Y 4 time series of Y 1 Refers to the power consumption of the heat pump unit, the unit is kWh; Y 2 Refers to the total power consumption of the GSHP system, in kWh; Y 3 It refers to the ratio of the heating or cooling capacity of the heat pump unit to the operating power of the heat pump unit; Y 4 It refers to the ratio of the heating or cooling capacity of the heat pump unit to the total power of the system; through the software "Geothermal Sta...
Embodiment 3
[0094] According to a method for predicting the performance of a ground source heat pump system described in Embodiment 2, the difference is that:
[0095] Described step (2), divides training set and test set, builds the data structure that has GSHP system working parameter input, comprises:
[0096] F. Divide the heat transfer performance data of the GSHP obtained in step E to obtain a training set and a test set; for example, the previous 4000 sets of heat transfer performance data are used as a training set, and the rest are used as a test set.
[0097] G. On the basis of step F, each group of time series data in the training set is expressed as: x i ={y i1 ,y i2 ,...,y it}, i refers to the i-th group of time series data, and the value range of i is 1it point to x i The observation value corresponding to time t in ;
[0098] Introduce GSHP system working parameter c it For each observation y it Expand to form a new belt observation value c it means y it Correspo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com